Abstract
Object
Ultra-high field (UHF) neuroimaging is usually conducted with volume transmit (Tx) and phased array receive (Rx) coils, both tightly enclosing the object. The travelling-wave (TW) concept allows a remote excitation offering more flexible experimental setups. To investigate the feasibility of primate MRI in horizontal UHF MRI, we first compared the distribution of the electromagnetic fields in an oil phantom and then verified the concept with an in vivo experiment.
Materials and methods
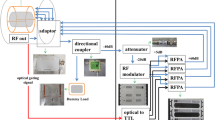
In the phantom experiments an in-house circularly polarized hybrid birdcage coil and a self-developed patch antenna were used for Tx and an eight-element phased array antenna for Rx. B +1 fields were calculated and measured for both approaches. For in vivo experiments the Rx part was replaced with an optimized three-element phased array head coil. The SAR was calculated using field simulation.
Results
In the phantom the field distribution was homogenous in a central volume of interest of about 10 cm diameter. The TW concept showed a slightly better homogeneity. Examination of a female crab-eating macaque led to homogeneous high-contrast images with a good delineation of anatomical details.
Conclusion
The TW concept opens up a new approach for MRI of medium-sized animals in horizontal UHF scanners.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brunner DO, de Zanche N, Fröhlich J, Paska J, Pruessmann KP (2009) Travelling-wave nuclear magnetic resonance. Nature 457(7232):994–998
Adriany G, van de Moortele P, Wiesinger F, Moeller S, Strupp JP, Andersen P, Snyder C, Zhang X, Chen W, Pruessmann KP, Boesiger P, Vaughan T, Uğurbil K (2005) Transmit and receive transmission line arrays for 7 Tesla parallel imaging. Magn Reson Med 53(2):434–445
Vaughan J, Adriany G, Snyder C, Tian J, Thiel T, Bolinger L, Liu H, DelaBarre L, Ugurbil K (2004) Efficient high-frequency body coil for high-field MRI. Magn Reson Med 52(4):851–859
Mispelter J, Lupu M, Briguet A (2006) NMR probeheads for biophysical and biomedical experiments. Imperial College Press, London
Staelin DH, Morgenthaler AW, Kong JA (1994) Electromagnetic waves. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ
Liu W, Collins CM, Delp PJ, Smith MB (2004) Effects of end-ring/shield configuration on homogeneity and signal-to-noise ratio in a birdcage-type coil loaded with a human head. Magn Reson Med 51(1):217–221
Herrmann T, Mallow J, Kim K, Stadler J, Bernarding J (2011) Travelling-wave for improved excitation of whole body 7T MRI with an extended RF-shield of 1.58 m length and diameter of 0.64 m. In: Proceedings of the ISMRM joint scientific meeting. Montréal, Canada, p 4154
CST AG (2011) Microwave Studio 2011. Darmstadt
Ibrahim TS, Lee R, Baertlein BA, Abduljalil AM, Zhu H, Robitaille PM (2001) Effect of RF coil excitation on field inhomogeneity at ultra high fields: a field optimized TEM resonator. Magn Reson Imaging 19(10):1339–1347
Roemer PB, Edelstein WA, Hayes CE, Souza SP, Mueller OM (1990) The NMR phased array. Magn Reson Med 16(2):192–225
Akoka S, Franconi F, Seguin F, Le Pape A (1993) Radiofrequency map of an NMR coil by imaging. Magn Reson Imaging 11(3):437–441
Setsompop K, Alagappan V, Gagoski B, Witzel T, Polimeni J, Potthast A, Hebrank F, Fontius U, Schmitt F, Wald LL, Adalsteinsson E (2008) Slice-selective RF pulses for in vivo B 1 + inhomogeneity mitigation at 7 tesla using parallel RF excitation with a 16-element coil. Magn Reson Med 60(6):1422–1432
Henning J (1988) Multiecho imaging sequences with low refocusing flip angles. J Magn Reson 78:397–407
IEC 601-2-33 Ed. 3.0 (2010) Medical electrical equipment—part 2-33 particular requirements for the safety of magnetic resonance equipment for medical diagnosis
Gabriel S, Lau RW, Gabriel C (1996) The dielectric properties of biological tissues. II. Measurements in the frequency range 10 Hz to 20 GHz. Phys Med Biol 41:2251–2269
Lei T, Udupa JK (2003) Gibbs ringing artifact and spatial correlation in MRI. In: Proceedings of SPIE
Alt S, Müller M, Umathum R, Bolz A, Bachert P, Semmler W, Bock M (2012) Coaxial waveguide MRI. Magn Reson Med 67(4):1173–1182
Brunner DO, Paska J, Froehlich J, Pruessmann KP (2011) Traveling-wave RF shimming and parallel MRI. Magn Reson Med 66:290–300
Baertlein BA, Ozbay O, Ibrahim T, Lee R, Yu Y, Kangarlu A, Robitaille PM (2000) Theoretical model for an MRI radio frequency resonator. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 47(4):535–546
Erni D, Liebig T, Rennings A, Koster NHL, Fröhlich J (2011) Highly adaptive RF excitation scheme based on conformal resonant CRLH metamaterial ring antennas for 7-Tesla traveling-wave magnetic resonance imaging. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 2011:554–558
Goense J, Logothetis NK, Merkle H (2010) Flexible, phase-matched, linear receive arrays for high-field MRI in monkeys. Magn Reson Imaging 28(8):1183–1191
Collin RE (1991) Field theory of guided waves. IEEE Press, New York
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dirk Salbert and Juergen Kanstorf for their technical advices in the construction of the designed RF transmitter and Hans-Peter Fautz from SIEMENS for providing us with his B 1 flip angle mapping sequence.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Johannes Mallow and Tim Herrmann contributed equally to this work
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mallow, J., Herrmann, T., Kim, KN. et al. Ultra-high field MRI for primate imaging using the travelling-wave concept. Magn Reson Mater Phy 26, 389–400 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-012-0358-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-012-0358-z