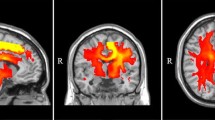
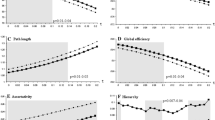
Abstract
Graph theoretical analysis of structural and functional connectivity MRI data (ie. diffusion tractography or cortical volume correlation and resting-state or task-related (effective) fMRI, respectively) has provided new measures of human brain organization in vivo. The most striking discovery is that the whole-brain network exhibits “small-world” properties shared with many other complex systems (social, technological, information, biological). This topology allows a high efficiency at different spatial and temporal scale with a very low wiring and energy cost. Its modular organization also allows for a high level of adaptation. In addition, degree distribution of brain networks demonstrates highly connected hubs that are crucial for the whole-network functioning. Many of these hubs have been identified in regions previously defined as belonging to the default-mode network (potentially explaining the high basal metabolism of this network) and the attentional networks. This could explain the crucial role of these hub regions in physiology (task-related fMRI data) as well as in pathophysiology. Indeed, such topological definition provides a reliable framework for predicting behavioral consequences of focal or multifocal lesions such as stroke, tumors or multiple sclerosis. It also brings new insights into a better understanding of pathophysiology of many neurological or psychiatric diseases affecting specific local or global brain networks such as epilepsy, Alzheimer’s disease or schizophrenia. Graph theoretical analysis of connectivity MRI data provides an outstanding framework to merge anatomical and functional data in order to better understand brain pathologies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ramnani N, Behrens TE, Penny W, Matthews PM (2004) New approaches for exploring anatomical and functional connectivity in the human brain. Biol Psychiatry 56: 613–619
Ioannidesa A (2007) Dynamic functional connectivity. Curr Opin Neurobiol 17: 161–170
Rykhlevskaia E, Gratton G, Fabiani M (2008) Combining structural and functional neuroimaging data for studying brain connectivity: a review. Psychophysiology 45: 173–187
Guye M, Bartolomei F, Ranjeva JP (2008) Imaging structural and functional connectivity: towards a unified definition of human brain organization?. Curr Opin Neurol 21: 393–403
Damoiseaux JS, Greicius MD (2009) Greater than the sum of its parts: a review of studies combining structural connectivity and resting-state functional connectivity. Brain Struct Funct
Johansen-Berg H, Rushworth MF (2009) Using diffusion imaging to study human connectional anatomy. Annu Rev Neurosci 32: 75–94
Lerch JP, Worsley K, Shaw WP, Greenstein DK, Lenroot RK, Giedd J, Evansa C (2006) Mapping anatomical correlations across cerebral cortex (MACACC) using cortical thickness from MRI. Neuroimage 31: 993–1003
Fox MD, Raichle ME (2007) Spontaneous fluctuations in brain activity observed with functional magnetic resonance imaging. Nat Rev Neurosci 8: 700–711
Auer DP (2008) Spontaneous low-frequency blood oxygenation level-dependent fluctuations and functional connectivity analysis of the ‘resting’ brain. Magn Reson Imaging 26: 1055–1064
Koch MA, Norris DG, Hund-Georgiadis M (2002) An investigation of functional and anatomical connectivity using magnetic resonance imaging. Neuroimage 16: 241–250
Hamandi K, Powell HW, Laufs H, Symms MR, Barker GJ, Parker GJ, Lemieux L, Duncan JS (2008) Combined EEG-fMRI and tractography to visualise propagation of epileptic activity. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 79: 594–597
Cohena L, Fair DA, Dosenbach NU, Miezin FM, Dierker D, Van Essen DC, Schlaggar BL, Petersen SE (2008) Defining functional areas in individual human brains using resting functional connectivity MRI. Neuroimage 41: 45–57
Lowe MJ, Beall EB, Sakaie KE, Koenig KA, Stone L, Marrie RA, Phillips MD (2008) Resting state sensorimotor functional connectivity in multiple sclerosis inversely correlates with transcallosal motor pathway transverse diffusivity. Hum Brain Mapp 29: 818–827
Van Den Heuvel M, Mandl R, Luigjes J, Hulshoff Pol H (2008) Microstructural organization of the cingulum tract and the level of default mode functional connectivity. J Neurosci 28: 10844–10851
Van Den Heuvel MP, Mandl RC, Kahn RS, Hulshoff Pol HE (2009) Functionally linked resting-state networks reflect the underlying structural connectivity architecture of the human brain. Hum Brain Mapp
Honey CJ, Sporns O, Cammoun L, Gigandet X, Thiran JP, Meuli R, Hagmann P (2009) Predicting human resting-state functional connectivity from structural connectivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106: 2035–2040
Greicius MD, Supekar K, Menon V, Dougherty RF (2009) Resting-state functional connectivity reflects structural connectivity in the default mode network. Cereb Cortex 19: 72–78
Hagmann P, Cammoun L, Gigandet X, Meuli R, Honey CJ, Wedeen VJ, Sporns O (2008) Mapping the structural core of human cerebral cortex. PLoS Biol 6: e159
Skudlarski P, Jagannathan K, Calhoun VD, Hampson M, Skudlarska BA, Pearlson G (2008) Measuring brain connectivity: diffusion tensor imaging validates resting state temporal correlations. Neuroimage 43: 554–561
Reijneveld JC, Ponten SC, Berendse HW, Stam CJ (2007) The application of graph theoretical analysis to complex networks in the brain. Clin Neurophysiol 118: 2317–2331
Bullmore E, Barnes A, Bassett DS, Fornito A, Kitzbichler M, Meunier D, Suckling J (2009) Generic aspects of complexity in brain imaging data and other biological systems. Neuroimage 47: 1125–1134
Bullmore E, Sporns O (2009) Complex brain networks: graph theoretical analysis of structural and functional systems. Nat Rev Neurosci 10: 186–198
Watts DJ, Strogatz SH (1998) Collective dynamics of ‘small-world’ networks. Nature 393: 440–442
Humphries MD, Gurney K, Prescott TJ (2006) The brainstem reticular formation is a small-world, not scale-free, network. Proc Biol Sci 273: 503–511
Humphries MD, Gurney K (2008) Network ‘small-world-ness’: a quantitative method for determining canonical network equivalence. PLoS One 3: e0002051
Latora V, Marchiori M (2001) Efficient behavior of small-world networks. Phys Rev Lett 87: 198701
Wasserman S, Faust K (1994) Social network analysis. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Adamic LA (1999) The small world web. Res Adv Tech Digit Libr Proc 1696: 443–452
Barabási A-L, Albert R (1999) Emergence of scaling in random networks. Science 286: 509–512
Sporns O, Honey CJ, Kotter R (2007) Identification and classification of hubs in brain networks. PLoS One 2: e1049
Fair DA, Cohen AL, Power JD, Dosenbach NUF, Church JA et al (2009) Functional brain networks develop from a “local to distributed” organization. PLoS Comput Biol 5(5): e1000381
Achard S, Salvador R, Whitcher B, Suckling J, Bullmore E (2006) A resilient, low-frequency, small-world human brain functional network with highly connected association cortical hubs. J Neurosci 26: 63–72
Albert R, Jeong H, Barabasia L (2000) Error and attack tolerance of complex networks. Nature 406: 378–382
Stam CJ, de Haan W, Daffertshofer A, Jones BF, Manshanden I, van Cappellen van Walsum AM, Montez T, Verbunt JPA, de Munck JC, Dijk BW, Berendse HW, Scheltens P (2008) Graph theoretical analysis of magnetoencephalographic functional connectivity in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 132: 213–224
Kaiser M, Martin R, Andras P, Young MP (2007) Simulation of robustness against lesions of cortical networks. Eur J Neurosci 25: 3185–3192
Honey CJ, Sporns O (2008) Dynamical consequences of lesions in cortical networks. Hum Brain Mapp 29: 802–809
Newman ME (2006) Modularity and community structure in networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103: 8577–8582
Ravasz E, Barabasia L (2003) Hierarchical organization in complex networks. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys 67: 026112
Sporns O, Tononi G, Edelman GM (2000) Theoretical neuroanatomy: relating anatomical and functional connectivity in graphs and cortical connection matrices. Cereb Cortex 10: 127–141
Hilgetag CC, Burns GA, O’neill MA, Scannell JW, Young MP (2000) Anatomical connectivity defines the organization of clusters of cortical areas in the macaque monkey and the cat. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 355: 91–110
Iturria-Medina Y, Canales-Rodriguez EJ, Melie-Garcia L, Valdes-Hernandez PA, Martinez-Montes E, Aleman-Gomez Y, Sanchez-Bornot JM (2007) Characterizing brain anatomical connections using diffusion weighted MRI and graph theory. Neuroimage 36: 645–660
Iturria-Medina Y, Sotero RC, Canales-Rodriguez EJ, Aleman-Gomez Y, Melie-Garcia L (2008) Studying the human brain anatomical network via diffusion-weighted MRI and graph theory. Neuroimage 40: 1064–1076
Gong G, He Y, Concha L, Lebel C, Gross DW, Evansa C, Beaulieu C (2009) Mapping anatomical connectivity patterns of human cerebral cortex using in vivo diffusion tensor imaging tractography. Cereb Cortex 19: 524–536
Hagmann P, Kurant M, Gigandet X, Thiran P, Wedeen VJ, Meuli R, Thiran JP (2007) Mapping human whole-brain structural networks with diffusion MRI. PLoS One 2: e597
He Y, Chen ZJ, Evansa C (2007) Small-world anatomical networks in the human brain revealed by cortical thickness from MRI. Cereb Cortex 17: 2407–2419
Chen ZJ, He Y, Rosa-Neto P, Germann J, Evansa C (2008) Revealing modular architecture of human brain structural networks by using cortical thickness from MRI. Cereb Cortex 18: 2374–2381
Bassett DS, Bullmore E, Verchinski BA, Mattay VS, Weinberger DR, Meyer-Lindenberg A (2008) Hierarchical organization of human cortical networks in health and schizophrenia. J Neurosci 28: 9239–9248
Schmitt JE, Lenroot RK, Wallace GL, Ordaz S, Taylor KN, Kabani N, Greenstein D, Lerch JP, Kendler KS, Neale MC et al (2008) Identification of genetically mediated cortical networks: a multivariate study of pediatric twins and siblings. Cereb Cortex 18: 1737–1747
Buckner RL, Sepulcre J, Talukdar T, Krienen FM, Liu H, Hedden T, Andrews-Hanna JR, Sperling RA, Johnson KA (2009) Cortical hubs revealed by intrinsic functional connectivity: mapping, assessment of stability, and relation to Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci 29: 1860–1873
Friston KJ, Frith CD, Liddle PF, Frackowiak RS (1993) Functional connectivity: the principal-component analysis of large (PET) data sets. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 13: 5–14
Friston K (2002) Beyond phrenology: what can neuroimaging tell us about distributed circuitry?. Annu Rev Neurosci 25: 221–250
Stam CJ, Reijneveld JC (2007) Graph theoretical analysis of complex networks in the brain. Nonlinear Biomed Phys 1: 3
Bassett DS, Bullmore E (2006) Small-world brain networks. Neuroscientist 12: 512–523
Biswal B, Yetkin FZ, Haughton VM, Hyde JS (1995) Functional connectivity in the motor cortex of resting human brain using echo-planar MRI. Magn Reson Med 34: 537–541
Fox MD, Snydera Z, Vincent JL, Corbetta M, Van Essen DC, Raichle ME (2005) The human brain is intrinsically organized into dynamic, anticorrelated functional networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102: 9673–9678
Fransson P (2005) Spontaneous low-frequency BOLD signal fluctuations: an fMRI investigation of the resting-state default mode of brain function hypothesis. Hum Brain Mapp 26: 15–29
Friston K (2009) Causal modelling and brain connectivity in functional magnetic resonance imaging. PLoS Biol 7: e33
Achard S, Bullmore E (2007) Efficiency and cost of economical brain functional networks. PLoS Comput Biol 3: e17
Salvador R, Suckling J, Coleman MR, Pickard JD, Menon D, Bullmore E (2005) Neurophysiological architecture of functional magnetic resonance images of human brain. Cereb Cortex 15: 1332–1342
Eguiluz VM, Chialvo DR, Cecchi GA, Baliki M, Apkariana V (2005) Scale-free brain functional networks. Phys Rev Lett 94: 018102
Van Den Heuvel MP, Stam CJ, Boersma M, Hulshoff Pol HE (2008) Small-world and scale-free organization of voxel-based resting-state functional connectivity in the human brain. Neuroimage 43: 528–539
Ferrarini L, Veer IM, Baerends E, Van Tol MJ, Renken RJ, Van Der Wee NJ, Veltman DJ, Aleman A, Zitman FG, Penninx BW et al (2009) Hierarchical functional modularity in the resting-state human brain. Hum Brain Mapp 30: 2220–2231
Meunier D, Achard S, Morcom A, Bullmore E (2009) Age-related changes in modular organization of human brain functional networks. Neuroimage 44: 715–723
He Y, Wang J, Wang L, Chen ZJ, Yan C, Yang H, Tang H, Zhu C, Gong Q, Zang Y et al (2009) Uncovering intrinsic modular organization of spontaneous brain activity in humans. PLoS One 4: e5226
He BJ, Shulman GL, Snydera Z, Corbetta M (2007) The role of impaired neuronal communication in neurological disorders. Curr Opin Neurol 20: 655–660
Hoffmann M, Schmitt F, Bromley E (2009) Vascular cognitive syndromes: relation to stroke etiology and topography. Acta Neurol Scand
Winter B, Bert B, Fink H, Dirnagl U, Endres M (2004) Dysexecutive syndrome after mild cerebral ischemia? Mice learn normally but have deficits in strategy switching. Stroke 35: 191–195
Lim C, Alexander MP (2009) Stroke and episodic memory disorders. Neuropsychologia
He BJ, Snydera Z, Vincent JL, Epstein A, Shulman GL, Corbetta M (2007) Breakdown of functional connectivity in frontoparietal networks underlies behavioral deficits in spatial neglect. Neuron 53: 905–918
Grefkes C, Nowak DA, Eickhoff SB, Dafotakis M, Kust J, Karbe H, Fink GR (2008) Cortical connectivity after subcortical stroke assessed with functional magnetic resonance imaging. Ann Neurol 63: 236–246
Bartolomei F, Bosma I, Klein M, Baayen JC, Reijneveld JC, Postma TJ, Heimans JJ, Van Dijk BW, De Munck JC, De Jongh A et al (2006) Disturbed functional connectivity in brain tumour patients: evaluation by graph analysis of synchronization matrices. Clin Neurophysiol 117: 2039–2049
Alstott J, Breakspear M, Hagmann P, Cammoun L, Sporns O (2009) Modeling the impact of lesions in the human brain. PLoS Comput Biol 5: e1000408
He Y, Dagher A, Chen Z, Charil A, Zijdenbos A, Worsley K, Evans A (2009) Impaired small-world efficiency in structural cortical networks in multiple sclerosis associated with white matter lesion load. Brain
Reuter F, Del Cul A, Malikova I, Naccache L, Confort-Gouny S, Cohen L, Cherifa A, Cozzone PJ, Pelletier J, Ranjeva JP et al (2009) White matter damage impairs access to consciousness in multiple sclerosis. Neuroimage 44: 590–599
Audoin B, Guye M, Reuter F, Au Duong MV, Confort-Gouny S, Malikova I, Soulier E, Viout P, Cherifa A, Cozzone PJ et al (2007) Structure of WM bundles constituting the working memory system in early multiple sclerosis: a quantitative DTI tractography study. Neuroimage 36: 1324–1330
Audoin B, Ibarrola D, Au Duong MV, Pelletier J, Confort-Gouny S, Malikova I, Ali-Cherif A, Cozzone PJ, Ranjeva JP (2005) Functional MRI study of PASAT in normal subjects. MAGMA 18: 96–102
Au Duong MV, Audoin B, Boulanouar K, Ibarrola D, Malikova I, Confort-Gouny S, Celsis P, Pelletier J, Cozzone PJ, Ranjeva JP (2005) Altered functional connectivity related to white matter changes inside the working memory network at the very early stage of MS. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 25: 1245–1253
Au Duong MV, Boulanouar K, Audoin B, Treseras S, Ibarrola D, Malikova I, Confort-Gouny S, Celsis P, Pelletier J, Cozzone PJ et al (2005) Modulation of effective connectivity inside the working memory network in patients at the earliest stage of multiple sclerosis. Neuroimage 24: 533–538
Ranjeva JP, Audoin B, Au Duong MV, Confort-Gouny S, Malikova I, Viout P, Soulier E, Pelletier J, Cozzone PJ (2006) Structural and functional surrogates of cognitive impairment at the very early stage of multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Sci 245: 161–167
Braak H, Braak E (1997) Frequency of stages of Alzheimer-related lesions in different age categories. Neurobiol Aging 18: 351–357
Seeley WW, Crawford RK, Zhou J, Miller BL, Greicius MD (2009) Neurodegenerative diseases target large-scale human brain networks. Neuron 62: 42–52
Supekar K, Menon V, Rubin D, Musen M, Greicius MD (2008) Network analysis of intrinsic functional brain connectivity in Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS Comput Biol 4: e1000100
He Y, Chen Z, Evans A (2008) Structural insights into aberrant topological patterns of large-scale cortical networks in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci 28: 4756–4766
Stam CJ, Jones BF, Nolte G, Breakspear M, Scheltens P (2007) Small-world networks and functional connectivity in Alzheimer’s disease. Cereb Cortex 17: 92–99
Karlsgodt KH, Sun D, Jimeneza M, Lutkenhoff ES, Willhite R, Van Erp TG, Cannon TD (2008) Developmental disruptions in neural connectivity in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia. Dev Psychopathol 20: 1297–1327
Begre S, Koenig T (2008) Cerebral disconnectivity: an early event in schizophrenia. Neuroscientist 14: 19–45
Jeong B, Wible CG, Hashimoto RI, Kubicki M (2009) Functional and anatomical connectivity abnormalities in left inferior frontal gyrus in schizophrenia. Hum Brain Mapp
Oh JS, Kubicki M, Rosenberger G, Bouix S, Levitt JJ, Mccarley RW, Westin CF, Shenton ME (2009) Thalamo-frontal white matter alterations in chronic schizophrenia: a quantitative diffusion tractography study. Hum Brain Mapp
Greicius M (2008) Resting-state functional connectivity in neuropsychiatric disorders. Curr Opin Neurol 21: 424–430
Liu Y, Liang M, Zhou Y, He Y, Hao Y, Song M, Yu C, Liu H, Liu Z, Jiang T (2008) Disrupted small-world networks in schizophrenia. Brain 131: 945–961
Micheloyannis S, Pachou E, Stam CJ, Breakspear M, Bitsios P, Vourkas M, Erimaki S, Zervakis M (2006) Small-world networks and disturbed functional connectivity in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 87: 60–66
Rubinov M, Knock SA, Stam CJ, Micheloyannis S, Harrisa W, Williams LM, Breakspear M (2009) Small-world properties of nonlinear brain activity in schizophrenia. Hum Brain Mapp 30: 403–416
Noonan SK, Haist F, Muller RA (2009) Aberrant functional connectivity in autism: evidence from low-frequency BOLD signal fluctuations. Brain Res 1262: 48–63
Monk CS, Peltier SJ, Wiggins JL, Weng SJ, Carrasco M, Risi S, Lord C (2009) Abnormalities of intrinsic functional connectivity in autism spectrum disorders. Neuroimage 47: 764–772
Supekar K, Musen M, Menon V (2009) Development of large-scale functional brain networks in children. PLoS Biol 7: e1000157
Wang L, Zhu C, He Y, Zang Y, Cao Q, Zhang H, Zhong Q, Wang Y (2009) Altered small-world brain functional networks in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Hum Brain Mapp 30: 638–649
Wendling F, Bartolomei F, Bellanger JJ, Bourien J, Chauvel P (2003) Epileptic fast intracerebral EEG activity: evidence for spatial decorrelation at seizure onset. Brain 126: 1449–1459
Guye M, Regis J, Tamura M, Wendling F, Mcgonigal A, Chauvel P, Bartolomei F (2006) The role of corticothalamic coupling in human temporal lobe epilepsy. Brain 129: 1917–1928
Bartolomei F, Chauvel P, Wendling F (2008) Epileptogenicity of brain structures in human temporal lobe epilepsy: a quantified study from intracerebral EEG. Brain 131: 1818–1830
Arthuis M, Valton L, Regis J, Chauvel P, Wendling F, Naccache L, Bernard C, Bartolomei F (2009) Impaired consciousness during temporal lobe seizures is related to increased long-distance cortical-subcortical synchronization. Brain 132: 2091–2101
Ahmadi ME, Hagler DJ Jr, Mcdonald CR, Tecoma ES, Iragui VJ, Dalea M, Halgren E (2009) Side matters: diffusion tensor imaging tractography in left and right temporal lobe epilepsy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol
Yogarajah M, Focke NK, Bonelli S, Cercignani M, Acheson J, Parker GJ, Alexander DC, Mcevoya W, Symms MR, Koepp MJ et al (2009) Defining Meyer’s loop-temporal lobe resections, visual field deficits and diffusion tensor tractography. Brain 132: 1656–1668
Yogarajah M, Powell HW, Parker GJ, Alexander DC, Thompson PJ, Symms MR, Boulby P, Wheeler-Kingshott CA, Barker GJ, Koepp MJ et al (2008) Tractography of the parahippocampal gyrus and material specific memory impairment in unilateral temporal lobe epilepsy. Neuroimage 40: 1755–1764
Hagler DJ Jr, Ahmadi ME, Kuperman J, Holland D, Mcdonald CR, Halgren E, Dalea M (2009) Automated white-matter tractography using a probabilistic diffusion tensor atlas: application to temporal lobe epilepsy. Hum Brain Mapp 30: 1535–1547
Concha L, Beaulieu C, Gross DW (2005) Bilateral limbic diffusion abnormalities in unilateral temporal lobe epilepsy. Ann Neurol 57: 188–196
Concha L, Beaulieu C, Collins DL, Gross DW (2009) White-matter diffusion abnormalities in temporal-lobe epilepsy with and without mesial temporal sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 80: 312–319
Mcdonald CR, Ahmadi ME, Hagler DJ, Tecoma ES, Iragui VJ, Gharapetian L, Dalea M, Halgren E (2008) Diffusion tensor imaging correlates of memory and language impairments in temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurology 71: 1869–1876
Diehl B, Busch RM, Duncan JS, Piao Z, Tkach J, Luders HO (2008) Abnormalities in diffusion tensor imaging of the uncinate fasciculus relate to reduced memory in temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia 49: 1409–1418
Powell HW, Parker GJ, Alexander DC, Symms MR, Boulby PA, Wheeler-Kingshott CA, Barker GJ, Koepp MJ, Duncan JS (2007) Abnormalities of language networks in temporal lobe epilepsy. Neuroimage 36: 209–221
Rodrigo S, Oppenheim C, Chassoux F, Golestani N, Cointepas Y, Poupon C, Semah F, Mangin JF, Le Bihan D, Meder JF (2007) Uncinate fasciculus fiber tracking in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Initial findings. Eur Radiol 17: 1663–1668
Widjaja E, Blaser S, Miller E, Kassner A, Shannon P, Chuang SH, Snead OC 3rd, Raybaud CR (2007) Evaluation of subcortical white matter and deep white matter tracts in malformations of cortical development. Epilepsia 48: 1460–1469
Bernhardt BC, Worsley KJ, Besson P, Concha L, Lerch JP, Evansa C, Bernasconi N (2008) Mapping limbic network organization in temporal lobe epilepsy using morphometric correlations: insights on the relation between mesiotemporal connectivity and cortical atrophy. Neuroimage 42: 515–524
Waitesa B, Briellmann RS, Saling MM, Abbott DF, Jackson GD (2006) Functional connectivity networks are disrupted in left temporal lobe epilepsy. Ann Neurol 59: 335–343
Addis DR, Moscovitch M, Mcandrews MP (2007) Consequences of hippocampal damage across the autobiographical memory network in left temporal lobe epilepsy. Brain 130: 2327–2342
Bettus G, Guedj E, Joyeux F, Confort-Gouny S, Soulier E, Laguitton V, Cozzone PJ, Chauvel P, Ranjeva JP, Bartolomei F et al (2009) Decreased basal fMRI functional connectivity in epileptogenic networks and contralateral compensatory mechanisms. Hum Brain Mapp 30: 1580–1591
Vaudano E, Laufs H, Kiebel SJ, Carmichael DW, Hamandi K, Guye M, Thornton R, Rodionov R, Friston KJ, Duncan JS et al (2009) Causal hierarchy within the thalamo-cortical network in spike and wave discharges. PLoS One 4: e6475
Ponten SC, Bartolomei F, Stam CJ (2007) Small-world networks and epilepsy: graph theoretical analysis of intracerebrally recorded mesial temporal lobe seizures. Clin Neurophysiol 118: 918–927
Ponten SC, Douw L, Bartolomei F, Reijneveld JC, Stam CJ (2009) Indications for network regularization during absence seizures: weighted and unweighted graph theoretical analyses. Exp Neurol 217: 197–204
Kramer MA, Kolaczyk ED, Kirsch HE (2008) Emergent network topology at seizure onset in humans. Epilepsy Res 79: 173–186
Schindler KA, Bialonski S, Horstmann MT, Elger CE, Lehnertz K (2008) Evolving functional network properties and synchronizability during human epileptic seizures. Chaos 18: 033119
Wang J, Wang L, Zang Y, Yang H, Tang H, Gong Q, Chen Z, Zhu C, He Y (2009) Parcellation-dependent small-world brain functional networks: a resting-state fMRI study. Hum Brain Mapp 30: 1511–1523
Tzourio-Mazoyer N, Landeau B, Papathanassiou D, Crivello F, Etard O, Delcroix N, Mazoyer B, Joliot M (2002) Automated anatomical labeling of activations in SPM using a macroscopic anatomical parcellation of the MNI MRI single-subject brain. Neuroimage 15: 273–289
Collins D, Holmes C, Peters T, Evans A (1995) Automatic 3D model-based neuroanatomical segmentation. Hum Brain Mapp 3: 190–208
Fischl B, Van Der Kouwe A, Destrieux C, Halgren E, Segonne F, Salat DH, Busa E, Seidman LJ, Goldstein J, Kennedy D et al (2004) Automatically parcellating the human cerebral cortex. Cereb Cortex 14: 11–22
Knock SA, Mcintosha R, Sporns O, Kotter R, Hagmann P, Jirsa VK (2009) The effects of physiologically plausible connectivity structure on local and global dynamics in large scale brain models. J Neurosci Methods 183: 86–94
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guye, M., Bettus, G., Bartolomei, F. et al. Graph theoretical analysis of structural and functional connectivity MRI in normal and pathological brain networks. Magn Reson Mater Phy 23, 409–421 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-010-0205-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-010-0205-z