Abstract
Introduction
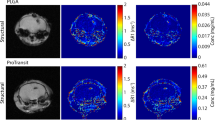
The aim of this work was to map E-selectin expression in a traumatic brain injury model using a newly-designed MR contrast agent. Iron cores, responsible for susceptibility effects and therefore used as T2* contrast agents, need to be coated in order to be stabilized and need to be targeted to be useful.
Methods
We have designed a molecule coating composed, at one end, of bisphosphonate to ensure anchorage of the coating on the iron core and, at the other end, of Fukuda’s defined heptapeptide known to target selectin binding sites.
Conclusion
The synthesized nanoparticles were able to non-invasively target the traumatic brain lesion, inducing a specific T2* decrease of about 25% up to at least 70 min post-injection of the targeted contrast agent.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- IL1-β and TNF-α :
-
Interleukin-1-β and tumor necrosis factor-α
- IELLQAR:
-
Isoleucine-glutamate-leucine-leucine-glutamine-alanine-arginine heptapeptide
- BP:
-
Bisphosphonate
- 99mTc-BP:
-
Technetium chelated to bisphosphonate
- EG3:
-
Ethylene glycol block repeated three times
- Hd:
-
Hydrodynamic diameter
- ζ :
-
Zeta potential
- e:
-
Polyelectrolyte accessible layer depth
- d q :
-
Charge density (in C/m3)
- RARE:
-
Rapid acquisition with relaxation enhancement
- ADC:
-
Apparent diffusion coefficient
- 3DmGE:
-
3D multi-gradient echos sequence
References
Thurman D, Alverson C, Dunn K, Guerrero J, JE S (1999) Traumatic brain injury in the United States: a public health perspective. J Head Trauma Rehabil 14: 602–615
Kay A, Teasdale G (2001) Head injury in the United Kingdom. World J Surg 25: 1210–1220
Mathe J, Richard I, Rome J (2005) Serious brain injury and public health, epidemiologic and financial considerations, comprehensive management and care. Ann Fr Anesth Reanim 24: 688–694
Klatzo I (1987) Pathophysiological aspects of brain edema. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 72: 236–239
Kawamata T, Katayama Y, Hovda D, Yoshino A, Becker D (1995) Lactate accumulation following concussive brain injury: the role of ionic fluxes induced by excitatory amino acids. Brain Res 674: 196–204
Reinert M, Khaldi A, Zauner A, Doppenberg E, Choi S, Bullock R (2000) High level of extracellular potassium and its correlates after severe head injury: relationship to high intracranial pressure. J Neurosurg 93: 800–807
Stanimirovic D, Satoh K (2000) Inflammatory mediators of cerebral endothelium: a role in ischemic brain inflammation. Brain Pathol 10: 113–126
Frijns C, Kappelle L (2002) Inflammatory cell adhesion molecules in ischemic cerebrovascular disease. Stroke 33: 2115–2122
Danton G, Dietrich W (2003) Inflammatory mechanisms after ischemia and stroke. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 62: 127–136
Williams A, Wei H, Dave J, Tortella F (2007) Acute and delayed neuroinflammatory response following experimental penetrating ballistic brain injury in the rat. J Neuroinflammation 4: 17
Wang Q, Tang X, Yenari M (2007) The inflammatory response in stroke. J Neuroimmunol 184: 53–68
McEver R (1997) Selectin–carbohydrate interactions during inflammation and metastasis. Glycoconj J 14: 585–591
Stoolman L (1989) Adhesion molecules controlling lymphocyte migration. Cell 56: 907–910
Phillips M, Nudelman E, Gaeta F, Perez M, Singhal A, Hakomori S, Paulson J (1990) ELAM-1 mediates cell adhesion by recognition of a carbohydrate ligand, sialyl-Lex. Science 250: 1130–1132
Ley K (2003) Sulfated sugars for rolling lymphocytes. J Exp Med 198: 1285–1288
Kneuer C, Ehrhardt C, Radomski M, Bakowsky U (2006) Selectins-potential pharmacological targets. Drug Discov Today 11: 1034–1040
Kang H, Josephson L, Petrovsky A, Weissleder R, Bogdanov AJ (2002) Magnetic resonance imaging of inducible E-selectin expression in human endothelial cell culture. Bioconjug Chem 13: 122–127
Sibson N, Blamire A, Bernades-Silva M, Laurent S, Boutry S, Muller R, Styles P, Anthony D (2004) MRI detection of early endothelial activation in brain inflammation. Magn Reson Med 51: 248–252
Barber P, Foniok T, Kirk D, Buchan A, Laurent S, Boutry S, Muller R, Hoyte L, Tomanek B, Tuor U (2004) MR molecular imaging of early endothelial activation in focal ischemia. Ann Neurol 56: 116–120
Boutry S, Burtea C, Laurent S, Toubeau G, Vander Elst L, Muller R (2005) Magnetic resonance imaging of inflammation with a specific selectin-targeted contrast agent. Magn Reson Med 53: 800–807
Funovics M, Montet X, Reynolds F, Weissleder R, Josephson L (2005) Nanoparticles for the optical imaging of tumor E-selectin. Neoplasia 7: 892–899
Reynolds P, Larkman D, Haskard D, Hajnal J, Kennea N, George A, Edwards A (2006) Detection of vascular expression of E-selectin in vivo with MR imaging. Radiology 241: 469–476
Canet-Soulas E, Letourneur D (2007) Biomarkers of atherosclerosis and the potential of MRI for the diagnosis of vulnerable plaque. Mag Reson Mater Phys 20: 129–142
Chapman P, Jamar F, Harrison A, Binns R, Peters A, Haskard D (1994) Noninvasive imaging of E-selectin expression by activated endothelium in urate crystal-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 37: 1752–1756
Zinn K, Chaudhuri T, Smyth C, Wu Q, Liu H, Fleck M, Mountz J, Mountz J (1999) Specific targeting of activated endothelium in rat adjuvant arthritis with a 99mTc-radiolabeled E-selectin-binding peptide. Arthritis Rheum 42: 641–649
Runnels J, Zamiri P, Spencer J, Veilleux I, Wei X, Bogdanov A, Lin C (2006) Imaging molecular expression on vascular endothelial cells by in vivo immunofluorescence microscopy. Mol Imaging 5: 31–40
Lindner J, Song J, Christiansen J, Klibanov A, Xu F, Ley K (2001) Sound assessment of inflammation and renal tissue injury with microbubbles targeted to P-selectin. Circulation 104: 2107–2112
Weller G, Villanueva F, Tom E, Wagner W (2003) Targeted ultrasound contrast agents: in vitro assessment of endothelial dysfunction and multi-targeting to ICAM-1 and sialyl Lewisx. Biotechnol Bioeng 92: 780–788
Ham A, Goetz D, Klibanov A, Lawrence M (2007) Microparticle adhesive dynamics and rolling mediated by selectin-specific antibodies under flow. Biotechnol Bioeng 96: 596–607
Laurent S, Vander Elst L, Fu Y, Muller R (2004) Synthesis and physicochemical characterization of Gd-DTPA-B(sLex)A, a new MRI contrast agent targeted to inflammation. Bioconjug Chem 15: 99–103
Fukuda M, Ohyama C, Lowitz K, Matsuo O, Pasqualini R, Ruoslahti E, Fukuda M (2000) A peptide mimic of E-selectin ligand inhibits sialyl Lewis X-dependent lung colonization of tumor cells. Cancer Res 60: 450–456
Renkonen R, Fukada MN, Petrov L, Paavonen T, Renkonen J, Häyry P, Fukuda M (2002) A peptide mimic of selectin ligands abolishes in vivo inflammation but has no effect on the rat heart allograft survival. Transplantation 74: 2–6
Babes L, Denizot B, Tanguy G, Le Jeune J, Jallet P (1999) Synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles used as MRI contrast agents: a parametric study. J Colloid Interface Sci 212: 474–482
Portet D, Denizot B, Rump E, Le Jeune J-J, Jallet P (2001) Nonpolymeric coatings of iron oxide colloids for biological use as magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents. J Colloid Interface Sci 238: 37–42
Mowat P, Franconi F, Chapon C, Lemaire L, Dorat J, Hindre F, Benoit JP, Richomme P, Le Jeune JJ (2007) Evaluating SPIO-labelled cell MR efficiency by three-dimensional quantitative T2* MRI. NMR Biomed 20: 21–27
Ohshima H (2000) On the general expression for the electrophoretic mobility of a soft particle. J Colloid Interface Sci 228: 190–193
Vonarbourg A, Saulnier P, Passirani C, Benoit JP (2005) Electrokinetic properties of noncharged lipid nanocapsules: influence of the dipolar distribution at the interface. Electrophoresis 26: 2066–2075
Stejskal E, Tanner J (1965) Spin diffusion measurements: spin-echoes in the presence of a time-dependent field gradient. J Chem Phys 42: 288–292
Van Putten H, Bouwhuis M, Muizelaar J, Lyeth B, Berman R (2005) Diffusion-weighted imaging of edema following traumatic brain injury in rats: effects of secondary hypoxia. J Neurotrauma 22: 857–872
Lythgoe M, Busza A, Calamante F, Sotak C, King M, Bingham A, Williams S, Gadian D (1997) Effects of diffusion anisotropy on lesion delineation in a rat model of cerebral ischemia. Magn Reson Med 38: 662–668
Franconi F, Mowat P, Lemaire L, Richomme P, Le Jeune JJ (2006) Single-scan quantitative T2* methods with susceptibility artifact reduction. NMR Biomed 19: 527–534
Springer TA (1990) Adhesion receptors of the immune system. Nature 346: 425–434
Lasky LA (1995) Selectin–carbohydrate interactions and the initiation of the inflammatory response. Annu Rev Biochem 64: 113–139
Martens CL, Cwirla SE, Lee RY, Whitehorn E, Chen EY, Bakker A, Martin EL, Wagstrom C, Gopalan P, Smith CW et al (1995) Peptides which bind to E-selectin and block neutrophil adhesion. J Biol Chem 270: 21129–21136
Ohyama C, Tsuboi S, Fukuda M (1999) Dual roles of sialyl Lewis X oligosaccharides in tumor metastasis and rejection by natural killer cells. Embo J 18: 1516–1525
Raghavendra Rao VL, Dhodda VK, Song G, Bowen KK, Dempsey RJ (2003) Traumatic brain injury-induced acute gene expression changes in rat cerebral cortex identified by GeneChip analysis. J Neurosci Res 71: 208–219
McAfee JG, Krauss DJ, Subramanian G, Thomas FD, Roskopf M, Ritter C, Lyons B, Schoonmaker JE, Finn RD (1983) Comparison of 99mTc phosphate and diphosphonate complexes in experimental renal infarcts. Invest Radiol 18: 479–484
Pasco A, Lemaire L, Franconi F, Lefur Y, Noury F, Saint-Andre JP, Benoit JP, Cozzone PJ, Le Jeune JJ (2007) Perfusional deficit and the dynamics of cerebral edemas in experimental traumatic brain injury using perfusion and diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. J Neurotrauma 24: 1321–1330
Beaumont A, Fatouros P, Gennarelli T, Corwin F, Marmarou A (2006) Bolus tracer delivery measured by MRI confirms edema without blood–brain barrier permeability in diffuse traumatic brain injury. Acta Neurochir Suppl 96: 171–174
Dardzinski BJ, Schmithorst VJ, Holland SK, Boivin GP, Imagawa T, Watanabe S, Lewis JM, Hirsch R (2001) MR imaging of murine arthritis using ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide particles. Magn Reson Imaging 19: 1209–1216
Gellissen J, Axmann C, Prescher A, Bohndorf K, Lodemann KP (1999) Extra- and intracellular accumulation of ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxides (USPIO) in experimentally induced abscesses of the peripheral soft tissues and their effects on magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Imaging 17: 557–567
Beduneau A, Hindre F, Clavreul A, Leroux JC, Saulnier P, Benoit JP (2008) Brain targeting using novel lipid nanovectors. J Control Release 126: 44–49
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chapon, C., Franconi, F., Lacoeuille, F. et al. Imaging E-selectin expression following traumatic brain injury in the rat using a targeted USPIO contrast agent. Magn Reson Mater Phy 22, 167–174 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-008-0161-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-008-0161-z