Abstract
Objective
The aim of the research was to study the effects of low-dose splenic irradiation and radiotherapy on immune system of patients with locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Methods
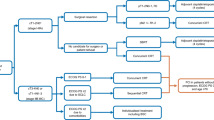
Twelve cases of stage III NSCLC in Tumor Radiotherapy Center of our hospital (the Affiliated Hospital of Medical College Qingdao University, China) were collected from July 2011 to July 2012; all patients were under 75 years old with clear pathology, measurable lesions and good personal statement. They were randomly divided into combined treatment group (D1 + D2) and control group (D1). The control group (D1) only received radiotherapy to the chest; combined treatment group (D1 + D2) received low-dose splenic irradiation plus conventional dose irradiation. Flow cytometry was used to detect the peripheral blood T lymphocyte immune indexes of patients before, during and after the treatment, classification by five blood cell analyzer was used to determine white blood cells, neutrophils, hemoglobin and platelet count. The radiation induced toxicity including esophagitis, pneumonia and gastrointestinal reaction was observed, as well as the dose when it happened.
Results
There was no significant difference in the ratio between two groups in cells CD4+, CD8+ and CD4+/CD8+ after radiotherapy (P > 0.05). There was no change in these indicators in combined treatment group after treatment (P > 0.05), but it decreased in control group (P < 0.05). There was no significant difference in the incidences of radiation esophagitis, pneumonia, gastrointestinal reactions and bone marrow suppression between two groups (P > 0.05), but the patients in combined treatment group seemed to tolerate high dose well (P < 0.05).
Conclusion
Low-dose splenic irradiation combined with radiotherapy to the chest can alleviate the injury degree of acute radiation induced the toxicity of locally advanced NSCLC patients, through affect the patient’s immune function.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pan XS, Shi YJ, Yao YM, et al. Progress of research on activation function of NK cell exposed to low dose radiation in adoptive cellular immunotherapy. J Radiat Res Radiat Process (Chinese), 2009, 27: 129–132.
Wu CM, Huang TH, Wu DS, et al. Apoptosis induction efect of pEgr-P16 genetherapy combined with low dose irradiation on esophageal cancer cells. J Shantou Univ Med Coll (Chinese), 2005, 18: 68–70.
Yang ZW, Li JA, Yang MH, et al. Comparison of blood counts in splenic, renal and mesenteric arterial and venous blood in post-pubertal rabbits. Res Vet Sci, 2005, 79: 149–154.
Choy H, Akerley W, Safran H, et al. Multiinstitutional phase II trial of paclitaxel, carboplatin, and concurrent radiation therapy for locally advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol, 1998, 16: 3316–3322.
Greenlee RT, Hill-Harmon MB, Murray T, et al. Cancer statistics, 2001. CA Cancer J Clin, 2001, 51: 15–36.
Zhao XR, Jiang EH, Li J, et al. Study on excited effect of low dose radiation and clinical application. Int J Radiat Med Nucl Med (Chinese), 2008, 32: 114–117.
Yu HS, Liu N, Ju B. Low dose radiation induced adaptive response of apoptosis in mouse spleen cells. Chinese-German J Clin Oncol, 2010, 9: 235–238.
Liu SZ. On radiation hormesis expressed in the immune system. Crit Rev Toxicol, 2003, 33: 431–441.
Yu HS, Song AQ, Lu YD, et al. Effects of low-dose radiation on tumor growth, erythrocyte immune function and SOD activity in tumor-bearing mice. Chin Med J, 2004, 117: 1036–1039.
Liu XD, Ma SM, Liu SZ. Effects of ionizing radiation on IL-12 and NF-κB activities in peritoneal macrophages of mice. Chin J Radiol Med Prot (Chinese), 2003, 23: 7–10.
Kos FJ. Engleman EG. Immune regulation: a critical link between NK cells and CTLs. Immunol Today, 1996, 17: 174–176.
Liu ZM, Yu HS. Effect of low dose radiation on tumor growth and hormesis in erythrocyte system in tumor-bearing mice. Acta Acad Med Qingdao Univ, 2007, 43: 34–37.
Wu Q, Zhao J, Wang ML. Detection and analysis of T cell subsets in peripheral blood of aged mice infected with human cytomegalovirus. Acta Univ Med Anhui (Chinese), 2010, 45: 310–314.
Safwat A. The immunobiology of low-dose total-body irradiation: more questions than answers. Radiat Res, 2000, 153: 599–604.
Wu N, Jin SZ, Pan XN, et al. Increase in efficacy of cancer radiotherapy by combination with whole-body low dose irradiation. Int J Radiat Biol, 2008, 84: 201–210.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Yu, H., Shang, Q. et al. The effects of low-dose splenic irradiation and radiotherapy on immune system of patients with locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Chin. -Ger. J. Clin. Oncol. 12, 51–55 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10330-012-1100-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10330-012-1100-z