Abstract
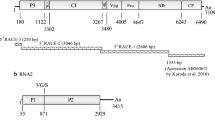
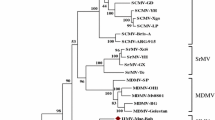
In 2005, soybean plants with severe mosaic and leaf rugose symptoms were found in Japan. The plants contained flexuous and filamentous virus-like particles with a modal length of 500 nm. Double-stranded RNA analysis revealed a single major band of ~7000 bp. Reverse transcription-PCR for Potyviridae diagnosis generated a 1.5-kbp cDNA fragment, which contained a partial NIb gene, a coat protein (CP) gene, a 3′-noncoding region, and a poly(A) tract. The CP gene consisted of 248 amino acids and had less than 40% amino acid sequence identity with CPs of other member in Potyviridae. The C-terminal region of the NIb gene had ~60% amino acid sequence identity with Barley mild mosaic virus and other Bymovirus isolates. The NIb amino acid sequence contained the GDD motif, while the CP had no motifs associated with aphid transmission. Phylogenetic analyses of the amino acid sequence of the CP core region showed that this virus was independent from other potyvirus genera. In a host range test, the virus infected 10 plant species in four families. The virus was not transmitted via seeds or aphids, but soybeans became diseased when grown in virus-infested soil. The characteristics of this virus suggest that it is not related to any of the previously described soybean viruses; thus, we tentatively propose the name soybean leaf rugose mosaic virus (SLRMV).




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atreya CD, Raccah B, Pirone TP (1990) A point mutation in the coat protein abolishes aphid transmissibility of a potyvirus. Virology 178:161–165
Atreya PL, Lopez-Moya JJ, Chu M, Atreya CD, Pirone TP (1995) Mutational analysis of the coat protein N-terminal amino acids involved in potyvirus transmission by aphids. J Gen Virol 76:265–270
Berger PH, Adams MJ, Barnett OW, Brunt AA, Hammond J, Hill JH, Jordan RL, Kashiwazaki S, Rybicki E, Spence N, Stenger DC, Ohki ST, Uyeda I, van Zaayen A, Valkonen J, Vetten HJ (2005) Family Potyviridae. In: Fauquet CM, Mayo MA, Maniloff J, Desselberger U, Ball LA (eds) Virus taxonomy: eighth report of the international committee on taxonomy of viruses. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 819–841
Chen J, Chen J, Adams MJ (2001) A universal PCR primer to detect members of the Potyviridae and its use to examine the taxonomic status of several members of the family. Arch Virol 146:757–766
Dale J, Gibbs A (1976) Soybean virus Z: its characteristics and taxonomy. Intervirology 6:325–332
Dougherty WG, Cary SM, Parks TD (1989) Molecular genetic analysis of a plant virus polyprotein cleavage site: a model. Virology 171:356–364
Hsu YC, Yeh TJ, Chang YC (2005) A new combination of RT-PCR and reverse dot blot hybridization for rapid detection and identification of potyviruses. J Virol Methods 128:54–60
Jeanmougin F, Thompson JD, Gouy M, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1998) Multiple sequence alignment with Clustal X. Trends Biochem Sci 23:403–405
Kamer G, Argos P (1984) Primary structural comparison of RNA-dependent polymerases from plant, animal and bacterial viruses. Nucleic Acids Res 12:7269–7282
Kashiwazaki S, Hayano Y, Minobe Y, Omura T, Hibino H, Tsuchizaki T (1989) Nucleotide sequence of the capsid protein gene of barley yellow mosaic virus. J Gen Virol 70:3015–3023
Nevins JR (1983) The pathway of eukaryotic mRNA formation. Annu Rev Biochem 52:441–466
Ohki ST (1997) Techniques and designs for plant virus identification (in Japanese). Japan Plant Protection Association, Tokyo, p 148
Pearson WR, Lipman DJ (1988) Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:2444–2448
Peerenboom E, Jacobi V, Antoniw JF, Schlichter U, Cartwright EJ, Steinbiss HH, Adams MJ (1996) The complete nucleotide sequence of RNA-2 of a fungally-transmitted UK isolate of barley mild mosaic bymovirus and identification of amino acid combinations possibly involved in fungus transmission. Virus Res 40:149–159
Peerenboom E, Cartwright EJ, Foulds I, Adams MJ, Stratford R, Rosner A, Steinbiss HH, Antoniw JF (1997) Complete RNA1 sequences of two UK isolates of barley mild mosaic virus: a wild-type fungus-transmissible isolate and a non-fungus-transmissible derivative. Virus Res 50:175–183
Perrière G, Gouy M (1996) WWW-query: an on-line retrieval system for biological sequence banks. Biochimie 78:364–369
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Shukla DD, Frenkel MJ, Ward CW (1991) Structure and function of the potyvirus genome with special reference to the coat protein coding region. Can J Plant Pathol 13:178–191
Takahashi K, Tanaka T, Iida W, Tsuda Y (1980) Studies on virus diseases and causal viruses of soybean in Japan (in Japanese with English summary). Bull Tohoku Natl Agric Exp Stn 62:1–130
Wang WQ, Natsuaki T, Okuda S, Teranaka M (1988) Comparison of cucumber mosaic virus isolates by double-stranded RNA analysis. Ann Phytopathol Soc Jpn 54:536–539
Ward CW, Shukla DD (1991) Taxonomy of potyviruses: current problems and some solutions. Intervirology 32:269–296
Zaret KS, Sherman F (1982) DNA sequence required for efficient transcription termination in yeast. Cell 28:563–573
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Shigeo Nakamura (Miyagi Prefectural Agriculture and Horticulture Research Center) for providing virus isolates and Dr. Toshiyuki Morikawa (Toyama Agricultural Research Center) and Dr. Ryoei Harasawa (Niigata Agricultural Research Institute) for useful suggestions and discussions. We are also grateful to Mr. Takahiro Koizumi (Niigata Prefectural Government) for useful information and technical assistance. DNA sequencing and analysis was conducted at the Life Research Support Center, Akita Prefectural University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuroda, T., Nabata, K., Hori, T. et al. Soybean leaf rugose mosaic virus, a new soilborne virus in the family Potyviridae, isolated from soybean in Japan. J Gen Plant Pathol 76, 382–388 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10327-010-0272-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10327-010-0272-z