Abstract
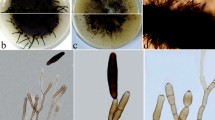
Since 1991, the sudden death of cultivated banana plants has been widely observed in the southern region of Sumatra Island, Indonesia. Wilting from loss of petiole and midrib turgidity, yellowing, and necrosis of leaves was followed by death of the whole plant. Reddish brown bacterial ooze exuded from the cut surface of infected pseudostems and fruits. The colony appearance of the isolated bacterium was similar to that of Ralstonia solanacearum. The bacterium was pathogenic to banana plants but not to tomato. Its bacteriological properties agreed with those of blood disease bacterium (BDB) of banana described previously. The 16S rDNA sequence of strain Banana E had conserved bases characteristic of BDB. Based on these results, the causal agent was identified as BDB, which is a close relative of Ralstonia. The isolates have resistance against antibiotics, such as chloramphenicol and tetracycline.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The nucleotide sequence data reported are available in the DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank databases under the accession number AB095535
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kusumoto, S., Aeny, T., Mujimu, S. et al. Occurrence of blood disease of banana in Sumatra, Indonesia. J Gen Plant Pathol 70, 45–49 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10327-003-0087-2
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10327-003-0087-2