Abstract
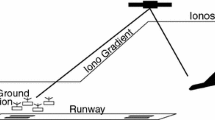
Navigation algorithms are proposed for carrier phase ambiguity integrity monitoring to support aircraft surface movement. The enhanced integrity monitoring algorithm addresses the very stringent integrity requirements for surface movement by the use of multiple test statistics and a group separation concept for single and multiple failure detection and exclusion. The algorithms are subject to a detailed performance characterization for precision approaches and airport surface movement, using simulations as well as static and dynamic field trials, taking into account operational specificities, such as multipath and potential decorrelations between the reference station and aircraft due to ionospheric anomalies. Results show that the proposed algorithms have the potential to satisfy airport surface movement requirements if the ionospheric anomalies are monitored using a special ground-based network.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai J (2008) Robust navigation algorithms for aircraft precision approach, landing and surface movement using global navigation satellite systems, PhD thesis, Imperial College London
Bai J, Schuster W, Ochieng W (2008) Advanced navigation algorithms for airport surface movement—developments & performance. ENC GNSS, Toulouse
Boeing (2005) Determining the vertical alert requirements for a level of GBAS service that is appropriate to support Cat II/III operations, Boeing report vol IV
Feng S, Ochieng W, Moore T, Hill C, Hide C (2008) Carrier phase based integrity monitoring for high accuracy positioning, GPS Solut 13(1):13–22
Klobuchar JA (1975) A first-order, worldwide, ionospheric time-delay algorithm, air force surveys in geophysics, No. 324
NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization) (1993) Standardization agreement (STANAG) Doc. 4294 EL (Edition 1), Appendix 6 to Annex A, pp. A-6–34–A-6–37. North Atlantic Treaty Organization, Brussels
Ochieng W, Feng S et al. (2007) User level integrity monitoring and quality control for seamless positioning in all conditions and environments. ION GNSS, Fort Worth
RTCA (2001) Minimum operational performance standards for GPS local area augmentation system airborne equipment, RTCA-DO253A
Schuster W, Ochieng W (2011a) Airport surface movement—critical analysis of navigation system performance requirements, J Navig 64(2):281–294
Schuster W, Ochieng W (2011b) Novel integrity concept for CAT III precision approaches and taxiing: extended GBAS (E-GBAS), J Navig 64(4)
Schuster W, Bai J, Feng S, Ochieng W (2007) Airport surface movement—performance requirements, architecture considerations & integrity algorithms. ION GNSS, Fort Worth
Schuster W et al. (2008) High accuracy navigation study report, ANASTASIA EC deliverable D3232
Schuster et al. (2009) Key technology operational performance analysis final report, ANASTASIA EC deliverable D3.4
SPIRENT (2007) SimGEN software user manual, DGP00686AAA Issue 1–22
Teunissen PJG (1990) An integrity and quality control procedure for use in multi sensor integration, ION-GPS, 513–522
Teunissen PJG (1995) The least-squares ambiguity decorrelation adjustment: a method for fast GPS integer ambiguity estimation. J Geodesy 70:65–82
Teunissen PJG (1999) An optimality property of the integer least-squares estimator. J Geodesy 73:587–593
Teunissen PJG (2001) GNSS ambiguity bootstrapping: theory and application. In: Proceedings of KIS2001, pp 246–254
TOPCON (2004) DT-200 series—digital (Laser) theodolites brochure, TOPCON Europe, Capelle a/d Ijssel, The Netherlands, October 2004
Verhagen S, Teunissen PJG (2006) New global navigation satellite system ambiguity resolution method compared to existing approaches. J Guid Control Dynamics 29(4):981–991
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the students and members of the Institute of Flight Guidance at the Technical University of Braunschweig for their support of the flight trials. Aerodata, Braunschweig, are gratefully acknowledged for providing the laser tracker. Many thanks go to Harald de Haan (NLR) for the operation of the laser tracker and to Holmer Denks (DLR) for carrying out the initial simulations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schuster, W., Bai, J., Feng, S. et al. Integrity monitoring algorithms for airport surface movement. GPS Solut 16, 65–75 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-011-0209-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-011-0209-9