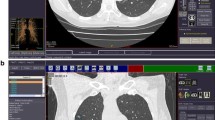
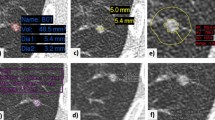
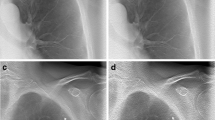
Abstract
The goal of this study was to assess whether radiologists’ search paths for lung nodule detection in chest computed tomography (CT) between different rendering and display schemes have reliable properties that can be exploited as an indicator of ergonomic efficiency for the purpose of comparing different display paradigms. Eight radiologists retrospectively viewed 30 lung cancer screening CT exams, containing a total of 91 nodules, in each of three display modes [i.e., slice-by-slice, orthogonal maximum intensity projection (MIP) and stereoscopic] for the purpose of detecting and classifying lung nodules. Radiologists’ search patterns in the axial direction were recorded and analyzed along with the location, size, and shape for each detected feature, and the likelihood that the feature is an actual nodule. Nodule detection performance was analyzed by employing free-response receiver operating characteristic methods. Search paths were clearly different between slice-by-slice displays and volumetric displays but, aside from training and novelty effects, not between MIP and stereographic displays. Novelty and training effects were associated with the stereographic display mode, as evidenced by differences between the beginning and end of the study. The stereo display provided higher detection and classification performance with less interpretation time compared to other display modes tested in the study; however, the differences were not statistically significant. Our preliminary results indicate a potential role for the use of radiologists’ search paths in evaluating the relative ergonomic efficiencies of different display paradigms, but systematic training and practice is necessary to eliminate training curve and novelty effects before search strategies can be meaningfully compared.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barish MA, Rocha TC: Multislice CT colonography: current status and limitations. Radiol Clin North Am 43:1049–1062, 2005
Rowe VL, Tucker SW Jr: Advances in vascular imaging. Surg Clin North Am 84:1189–1202, 2004
Israel GM, Bosniak MA: Renal imaging for diagnosis and staging of renal cell carcinoma. Urol Clin North Am 30:499–514, 2003
Aufort S, Charra L, Lesnik A, et al: Multidetector CT of bowel obstruction: value of post-processing. Eur Radiol 15:2323–2329, 2005
Remy J, Remy-Jardin M, Artaud D, et al: Multiplanar and three-dimensional reconstruction techniques in CT: impact on chest diseases. Eur Radiol 8:335–351, 1998
Bomans M, Hohne KH, Tiede U, et al: 3-D segmentation of MR images of the head for 3-D display. IEEE Trans Med Imag 2:177–183, 1990
Hoehne TU, Bomans KH, Pommert M, et al: Investigation of medical 3D-rendering algorithms. IEEE Comput Graph Appl 2:41–53, 1990
Calhoun PS, Kuszyk BS, Heath DG, et al: Three-dimensional volume rendering of spiral CT data: theory and method. Radiographics 19:745–764, 1999
Kuszyk BS, Heath DG, Ney DR, et al: CT Angiography with volume rendering: imaging findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol 165:445–448, 1995
Fishman EK, Ney DR, Heath DG, et al: Volume rendering versus maximum intensity projection in CT angiography: what works best, when, and why. RadioGraphics 26:905–922, 2006
Wang XH, Maitz GS, Leader JK, et al: Real-time stereographic display of volumetric datasets in radiology. SPIE Electronic Imaging 6055:1A-1–1A-6, 2006
Wang XH, Walter FG, Fuhrman CR, et al: Stereo CT image compositing methods for lung nodule detection and characterization. Acad Radiol 12:1512–1520, 2005
Demiralp C, Jackson CD, Karelitz DB, Zhang S, Laidlaw DH: CAVE and fishtank virtual-reality displays: a qualitative and quantitative comparison. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 12(3):323–330, 2006 (May–June)
Levin D, Aladl U, Germano G, et al: Techniques for efficient, real-time, 3D visualization of multi-modality cardiac data using consumer graphics hardware. Comput Med Imaging Graph 29:463–475, 2005
Yee DK, Lee W, Kim D, et al: RadGSP: a medical image display and user interface for UWGSP3. Proc SPIE 1444:292–305, 1991
Fuchs H, Levoy M, Pizer SM: Interactive visualization of 3D medical data. Computer 22:46–51, 1989
Krupinski EA: Visual search of mammographic images: influence of lesion subtlety. Acad Radiol 12:965–969, 2005
Krupinski EA, Berger WG, Dallas WJ, et al: Searching for nodules: what features attract attention and influence detection? Acad Radiol 10:861–868, 2003
Nodine CF, Mello-Thoms C, Kundel HL, et al: Time course of perception and decision making during mammographic interpretation. AJR Am J Roentgenol 179:917–923, 2002
Kundel HL, Nodine CF, Toto L: Searching for lung nodules. The guidance of visual scanning. Invest Radiol 26:777–781, 1991
Kundel HL: Visual cues in the interpretation of medical images. J Clin Neurophysiol 7:472–483, 1990
Kundel HL, Nodine CF, Krupinski EA: Searching for lung nodules. Visual dwell indicates locations of false-positive and false-negative decisions. Invest Radiol 24:472–478, 1989
Kundel HL, Nodine CF, Thickman D, et al: Searching for lung nodules. A comparison of human performance with random and systematic scanning models. Invest Radiol 22:417–422, 1987
Krupinski EA, Roehrig H: The influence of a perceptually linearized display on observer performance and visual search. Acad Radiol 7:8–13, 2000
Nodine CF, Kundel HL, Lauver SC, et al: Nature of expertise in searching mammograms for breast masses. Acad Radiol 3:1000–1006, 1996
Salvolini L, Bichi Secchi E, Costarelli L, et al: Clinical applications of 2D and 3D CT imaging of the airways-a review. Eur J Radiol 34:9–25, 2000
Ou P, Celermajer DS, Calcagni G, et al: Three-dimensional CT scanning: a novel diagnostic modality in congenital heart disease. Heart 93:908–913, 2006
Durkee NJ, Jacobson J, Jamadar D, et al: Classification of common acetabular fractures: radiographic and CT appearances. AJR Am J Roentgenol 187:915–925, 2006
Acknowledgment
This work is sponsored in part by the Department of Defense, US Army Medical Research Acquisition Center, 820 Chandler Street, Fort Detrick, MD 21702-5014 under Contract PR043488, and also by grant CA80836 from the National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health. The content of the contained information does not necessarily reflect the position or the policy of the government, and no official endorsement should be inferred.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X.H., Durick, J.E., Lu, A. et al. Characterization of Radiologists’ Search Strategies for Lung Nodule Detection: Slice-Based Versus Volumetric Displays. J Digit Imaging 21 (Suppl 1), 39–49 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-007-9076-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-007-9076-x