Abstract
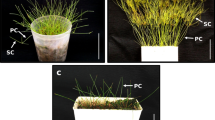
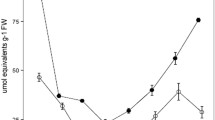
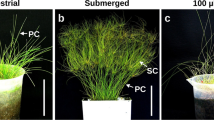
The amphibious leafless sedge Eleocharis retroflexa ssp. chaetaria expresses C4-like biochemical characteristics in both the terrestrial and submerged forms. Culms of the terrestrial form have Kranz anatomy, whereas those of the submerged form have Kranz-like anatomy combined with anatomical features of aquatic plant leaves. We examined the immunolocalization of C3 and C4 enzymes in culms of the two forms. In both forms, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase; pyruvate, Pi dikinase; and NAD-malic enzyme were compartmentalized between the mesophyll (M) and Kranz cells, but their levels were somewhat reduced in the submerged form. In the terrestrial form, ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (rubisco) occurred mainly in the Kranz cells, and weakly in the M chloroplasts. In the submerged form, the rubisco occurred at higher levels in the M cells than in the terrestrial form. In both forms, the C4 pattern of enzyme expression was clearer in the M cells adjacent to Kranz cells than in distant M cells. During the transition from terrestrial to submerged conditions, the enzyme expression pattern changed in submerged mature culms that had been formed in air before submergence, and matched that in culms newly developed underwater. It seems that effects of both environmental and developmental factors overlap in the C4 pattern expression in this plant.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarie S, Kai M, Takatsuji H, Ueno O (2002) Environmental and hormonal regulation of gene expression of C4 photosynthetic enzymes in the amphibious sedge Eleocharis vivipara. Plant Sci 163:571–580
Aramaki M, Tsuchiya T, Iwaki H (1989) Photosynthesis of submerged leaves of Nuphar japonicum DC. in Takahamairi Bay of Lake Kasumigaura, Japan. Jpn J Ecol 39:189–193
Bowes G, Salvucci ME (1989) Plasticity in the photosynthetic carbon metabolism of submerged aquatic macrophytes. Aquat Bot 34:233–266
Cheng S-H, Moore Bd, Wu J, Edwards GE, Ku MSB (1989) Photosynthetic plasticity in Flaveria brownii. Growth irradiance and the expression of C4 photosynthesis. Plant Physiol 89:1129–1135
Dengler NG, Nelson T (1999) Leaf structure and development in C4 plants. In: Sage RF, Monson RK (eds) C4 plant biology. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 133–172
Ehleringer JR, Monson RK (1993) Evolutionary and ecological aspects of photosynthetic pathway variation. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 24:411–439
Hahnen S, Joeris T, Kreuzaler F, Peterhansel C (2003) Quantification of photosynthetic gene expression in maize C3 and C4 tissues by real-time PCR. Photosynth Res 75:183–192
Kanai R, Edwards GE (1999) The biochemistry of C4 photosynthesis. In: Sage RF, Monson RK (eds) C4 plant biology. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 49–87
Keeley JE (1998) C4 photosynthetic modifications in the evolutionary transition from land to water in aquatic grasses. Oecologia 116:85–97
Keeley JE (1999) Photosynthetic pathway diversity in a seasonal pool community. Funct Ecol 13:106–118
Langdale JA, Nelson T (1991) Spatial regulation of photosynthetic development in C4 plants. Trends Genet 7:191–196
Langdale JA, Zelitch I, Miller E, Nelson T (1988) Cell position and light influence C4 versus C3 patterns of photosynthetic gene expression in maize. EMBO J 7:3643–3651
Lara MV, Casati P, Andreo CS (2002) CO2-concentrating mechanisms in Egeria densa, a submerged aquatic plant. Physiol Plant 115:487–495
Maberly SC, Spence DHN (1989) Photosynthesis and photorespiration in freshwater organisms: amphibious plants. Aquat Bot 34:267–286
Magnin NC, Cooley BA, Reiskind JB, Bowes G (1997) Regulation and localization of key enzymes during the induction of Kranz-less, C4-type photosynthesis in Hydrilla verticillata. Plant Physiol 115:1981–1989
Nishioka D, Miyake H, Taniguchi T (1996) Suppresion of granal development and accumulation of rubisco in different bundle sheath chloroplasts of the C4 succulent plant Portulaca grandiflora. Ann Bot 77:629–637
Ohsugi R, Ueno O, Komatsu T, Sasaki H, Murata T (1997) Leaf anatomy and carbon discrimination in NAD-malic enzyme Panicum species and their hybrids differing in bundle sheath cell ultrastructure. Ann Bot 79:179–184
Sage RF (2004) The evolution of C4 photosynthesis. New Phytol 161:341–370
Sculthorpe CD (1967) The biology of aquatic vascular plants. Arnold, London
Sheen J (1999) C4 gene expression. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 50:187–217
Uchino A, Samejima M, Ishii R, Ueno O (1995) Photosynthetic carbon metabolism in an amphibious sedge, Eleocharis baldwinii (Torr.) Chapman: modified expression of C4 characteristics under submerged aquatic conditions. Plant Cell Physiol 36:229–238
Ueno O (1996) Structural characterization of photosynthetic cells in an amphibious sedge, Eleocharis vivipara, in relation to C3 and C4 metabolism. Planta 199:382–393
Ueno O (1998) Induction of Kranz anatomy and C4-like biochemical characteristics in a submerged amphibious plant by abscisic acid. Plant Cell 10:571–583
Ueno O (2001) Environmental regulation of C3 and C4 differentiation in the amphibious sedge Eleocharis vivipara. Plant Physiol 127:1524–1532
Ueno O (2004) Environmental regulation of photosynthetic metabolism in the amphibious sedge Eleocharis baldwinii and comparison with related species. Plant Cell Environ 26:627–639
Ueno O, Ishimaru K (2002) Effects of an inhibitor of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase on photosynthesis of the terrestrial forms of amphibious Eleocharis species. Photosynth Res 71:265–272
Ueno O, Samejima M, Koyama T (1989) Distribution and evolution of C4 syndrome in Eleocharis, a sedge group inhabiting wet and aquatic environments, based on culm anatomy and carbon isotope ratios. Ann Bot 64:425–438
Ueno O, Samejima M, Muto S, Miyachi S (1988) Photosynthetic characteristics of an amphibious plant, Eleocharis vivipara: expression of C4 and C3 modes in contrasting environments. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:6733–6737
Ueno O, Takeda T, Samejima M, Kondo A (1998) Photosynthetic characteristics of an amphibious C4 plant, Eleocharis retroflexa ssp. chaetaria. Plant Prod Sci 1:165–173
Wakayama M, Ueno O, Ohnishi J (2003) Photosynthetic enzyme accumulation during leaf development of Arundinella hirta, a C4 grass having Kranz cells not associated with veins. Plant Cell Physiol 44:1330–1340
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a grant-in-aid from the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry, and Fisheries of Japan (Bio-Design Project) to O.U. The following antisera were provided by the late Dr. S. Muto, Nagoya University, Nagoya, Japan; Dr. T. Mutara, Iwate University, Morioka, Japan; and Dr. M. Matsuoka, Nagoya University, Nagoya, Japan, respectively: anti-pea leaf rubisco large subunit (LS) antiserum, anti-Amaranthus tricolor leaf NAD-ME antiserum, and anti-maize leaf PEPC and pyruvate, Pi dikinase (PPDK) antisera.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ueno, O., Wakayama, M. Cellular expression of C3 and C4 photosynthetic enzymes in the amphibious sedge Eleocharis retroflexa ssp. chaetaria. J Plant Res 117, 433–441 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-004-0175-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-004-0175-1