Abstract
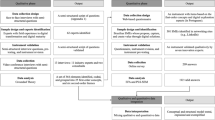
Inter-organizational systems form the basis for successful business collaboration in the Internet and B2B e-commerce era. To properly design and manage such systems one needs to understand the structure and dynamics of the relationships between organizations. The evaluation of such inter-organizational relationships (IORs) is normally conducted using “success factors”. These are often referred to as constructs, such as trust and information sharing. In strategic management and performance analysis, different methods are employed for evaluating business performance and strategies, such as the Balanced Scorecard (BSC) method. The BSC utilizes success factors for measuring and monitoring IORs against business strategies. For these reasons, a thorough understanding of success factors, the relationships between them, as well as their relationship to business strategies is required. In other words, understanding success factors allows strategists deriving measurements for success factors as well as aligning these success factors with business strategies. This underpins nowadays close relationship between business strategy, IORs and their realization by means of inter-organizational systems. In this paper, we present (1) a systematic literature review studying success factors and their impact on IORs as well as (2) an analysis of the results found. The review is based on 177 publications, published between 2000 and 2012, dealing with factors influencing IORs. The work presented provides an overview on success factors, influencing relationships between success factors, as well as their influence on the success of IORs. The work is somehow “meta-empirical” as it only looks at published studies and not on own cases. Consequently, it is based on the assumption that studies in scientific literature represent the real-world. The constructs and relationships found in the review are grouped based on their scope and summarized in a cause and effect model. The grouping of constructs results in five groups including Relationship Orientation, Relational Norm, Relational Capital, Atmosphere, and Others. Since the cause and effect model represents a directed graph, different network analysis methods may be applied for analyzing the model. In particular, an in- and out-degree analysis is applied on the cause and effect model for detecting the most influencing as well as the most influenced success factors.













Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
A list of reviewed studies is provided in our supplement which can be found at the following link: http://edimine.ec.tuwien.ac.at/supplement.
A list of extracted influencing relationships is provided in the following supplement: http://edimine.ec.tuwien.ac.at/supplement.
A list of refined influencing relationships can also be found in our provided supplement: http://edimine.ec.tuwien.ac.at/supplement.
References
Ambrose E, Marshall D, Lynch D (2010) Buyer supplier perspectives on supply chain relationships. Int J Oper product Manag 30(12):1269–1290
Aramyan LH, Lansink AGO, van der Vorst JG, van Kooten O (2007) Performance measurement in agri-food supply chains: a case study. Supply Chain Manag Int J 12(4):304–315
Ashnai B, Smirnova M, Kouchtch S, Yu Q, Barnes BR, Naudé P (2009) Assessing relationship quality in four business-to-business markets. Mark Intell Plan 27(1):86–102
Bastian M, Heymann S, Jacomy M (2009) Gephi: an open source software for exploring and manipulating networks. In: Proceedings of the third international AAAI conference on weblogs and social media (ICWSM 2009), pp 361–362
Brereton P, Kitchenham BA, Budgen D, Turner M, Khalil M (2007) Lessons from applying the systematic literature review process within the software engineering domain. J Syst Softw 80(4):571–583
Cambra-Fierro JJ, Polo-Redondo Y (2008) Creating satisfaction in the demand-supply chain: the buyers’ perspective. Supply Chain Manag Int J 13(3):211–224
Carr AS, Pearson JN (2002) The impact of purchasing and supplier involvement on strategic purchasing and its impact on firm’s performance. Int J Oper prod Manag 22(9):1032–1053
Chan FT (2003) Performance measurement in a supply chain. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 21(7):534–548
Chen IJ, Paulraj A (2004) Towards a theory of supply chain management: the constructs and measurements. J Oper Manag 22(2):119–150
Chen IJ, Paulraj A, Lado AA (2004) Strategic purchasing, supply management, and firm performance. J Oper Manag 22(5):505–523
Cheng JH (2011) Inter-organizational relationships and information sharing in supply chains. Int J Inf Manag 31(4):374–384
Cheng JH, Sheu JB (2012) Inter-organizational relationships and strategy quality in green supply chains–moderated by opportunistic behavior and dysfunctional conflict. Ind Mark Manag 41(4):563–572
Cheung MS, Myers MB, Mentzer JT (2010) Does relationship learning lead to relationship value? A cross-national supply chain investigation. J Oper Manag 28(6):472–487
Cooper MC, Ellram LM (1993) Characteristics of supply chain management and the implications for purchasing and logistics strategy. Int J Logist Manag 4(2):13–24
Corsten D, Felde J (2005) Exploring the performance effects of key-supplier collaboration: an empirical investigation into swiss buyer–supplier relationships. Int J Phys Distrib Logist Manag 35(6):445–461
Corsten D, Gruen T, Peyinghaus M (2011) The effects of supplier-to-buyer identification on operational performance–an empirical investigation of inter-organizational identification in automotive relationships. J Oper Manag 29(6):549–560
Cousins PD, Lawson B, Squire B (2008) Performance measurement in strategic buyer–supplier relationships: the mediating role of socialization mechanisms. Int J Oper Prod Manag 28(3):238–258
Daugherty PJ, Richey RG, Roath AS, Min S, Chen H, Arndt AD, Genchev SE (2006) Is collaboration paying off for firms? Bus Horiz 49(1):61–70
de Toni A, Nassimbeni G (1999) Buyer–supplier operational practices, sourcing policies and plant performances: results of an empirical research. Int J Prod Res 37(3):597–619
Doucette WR (1996) The influence of relational norms and trust on customer satisfaction in interfirm exchange relationships. J Consum Satisf Dissatisf Complain Behav 9:95–103
Duffy R, Fearne A, Hornibrook S, Hutchinson K, Reid A (2012) Engaging suppliers in CRM: the role of justice in buyer–supplier relationships. Int J Inf Manag 33(1):20–27
Eckerson WW (2006) Performance dashboards. Wiley, Hoboken
Fantazy KA, Kumar V, Kumar U (2010) Supply management practices and performance in the Canadian hospitality industry. Int J Hosp Manag 29(4):685–693
Flynn BB, Huo B, Zhao X (2010) The impact of supply chain integration on performance: a contingency and configuration approach. J Oper Manag 28(1):58–71
Gautier P (2010) Inter-organizational relationships and supply chain performance: case study of the subsidiary company of a car parts manufacturer. In: Proceedings of the international conference on industrial engineering (ICINDE 2010)
Gil-Saura I, Frasquet-Deltoro M, Cervera-Taulet A (2009) The value of B2B relationships. Ind Manag Data Syst 109(5):593–609
Green KW Jr, Whitten D, Inman RA (2008) The impact of logistics performance on organizational performance in a supply chain context. Supply Chain Manag Int J 13(4):317–327
Hald KS, Cordón C, Vollmann TE (2009) Towards an understanding of attraction in buyer–supplier relationships. Ind Mark Manag 38(8):960–970
Heide JB, John G (1992) Do norms matter in marketing relationships? J Mark 56(2):32–44
Hernández-Espallardo M, Rodríguez-Orejuela A, Sánchez-Pérez M (2010) Inter-organizational governance, learning and performance in supply chains. Supply Chain Manag Int J 15(2):101–114
Hsu CC, Kannan VR, Tan KC, Leong GK (2008) Information sharing, buyer–supplier relationships, and firm performance: a multi-region analysis. Int J Phys Distrib Logist Manag 38(4):296–310
Hu S, Ye Q, Chi W, Flynn BB (2010) Supply chain structure, inventory turnover, and financial performance: evidence from manufacturing companies in China. In: Proceedings of the 21th annual conference of the production and operations management society (POMS 2010)
Huan SH, Sheoran SK, Wang G (2004) A review and analysis of supply chain operations reference (SCOR) model. Supply Chain Manag Int J 9(1):23–29
Johnston DA, McCutcheon DM, Stuart F, Kerwood H (2004) Effects of supplier trust on performance of cooperative supplier relationships. J Oper Manag 22(1):23–38
Jonsson P, Zineldin M (2003) Achieving high satisfaction in supplier–dealer working relationships. Supply Chain Manag Int J 8(3):224–240
Kaplan RS, Norton DP (1992) The balanced scorecard–measures that drive performance. Harv Bus Rev 70(1):71–79
Kaplan RS, Norton DP (2004) Focusing your organization on strategy-with the balanced scorecard. Harvard Business School Publishing, Cambridge
Ke W, Wei KK (2005) Critical factors affecting the firm to share knowledge with trading partners: a comparative exploratory case study. In: Proceedings of the 7th international conference on electronic commerce (ICEC 2005), ACM, pp 177–183
Kim KK, Park SH, Ryoo SY, Park SK (2010) Inter-organizational cooperation in buyer–supplier relationships: both perspectives. J Bus Res 63(8):863–869
Kohtamäki M, Vesalainen J, Henneberg S, Naudé P, Ventresca MJ (2012) Enabling relationship structures and relationship performance improvement: the moderating role of relational capital. Ind Mark Manag 41(8):1298–1309
Kotabe M, Martin X, Domoto H (2002) Gaining from vertical partnerships: knowledge transfer, relationship duration, and supplier performance improvement in the US and Japanese automotive industries. Strateg Manag J 24(4):293–316
Krause DR, Handfield RB, Tyler BB (2007) The relationships between supplier development, commitment, social capital accumulation and performance improvement. J Oper Manag 25(2):528–545
Landauer TK, Foltz PW, Laham D (1998) An introduction to latent semantic analysis. Discourse Process 25(2–3):259–284
Lee CW, Kwon IWG, Severance D (2007) Relationship between supply chain performance and degree of linkage among supplier, internal integration, and customer. Supply Chain Manag Int J 12(6):444–452
Leone N, Pfeifer G, Faber W, Eiter T, Gottlob G, Perri S, Scarcello F (2006) The DLV system for knowledge representation and reasoning. ACM Trans Comput Log 7(3):499–562
Li S, Lin B (2006) Accessing information sharing and information quality in supply chain management. Decis Support Syst 42(3):1641–1656
Li S, Ragu-Nathan B, Ragu-Nathan T, Rao SS (2006) The impact of supply chain management practices on competitive advantage and organizational performance. Omega 34(2):107–124
Lin D (1998) Automatic retrieval and clustering of similar words. In: Proceedings of the 17th international conference on computational linguistics-volume 2 (COLING 1998), association for computational linguistics, pp 768–774
Liu Y, Luo Y, Liu T (2009) Governing buyer–supplier relationships through transactional and relational mechanisms: evidence from china. J Oper Manag 27(4):294–309
Liu Y, Huang Y, Luo Y, Zhao Y (2012) How does justice matter in achieving buyer–supplier relationship performance? J Oper Manag 30(5):355–367
Maloni M, Benton W Jr (2000) Power influences in the supply chain. J Bus Logist 21(1):49–74
Meaklim T (2013) Considering game theory to improve leadership in partnership working within the UK public services. Int J Lead Public Serv 9(1/2):22–31
Mohr JJ, Fisher RJ, Nevin JR (1996) Collaborative communication in interfirm relationships: moderating effects of integration and control. J Mark 60(3):103–115
Möller K (2010) Partner selection, partner behavior, and business network performance: an empirical study on german business networks. J Acc organ Change 6(1):27–51
Moon CW (2011) The influence of credibility on satisfaction with supplier performance in the inter-organizational relationship. Int Bus Econ Res J 10(9):47–58
Morgan RM, Hunt SD (1994) The commitment-trust theory of relationship marketing. J Mark 58(3):20–38
Mysen T, Svensson G, Payan JM (2011) Causes and outcomes of satisfaction in business relationships. Mark Intell Plan 29(2):123–140
Newman M (2010) Networks: an introduction. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Otto A, Kotzab H (2003) Does supply chain management really pay? Six perspectives to measure the performance of managing a supply chain. Eur J Oper Res 144(2):306–320
Paulraj A, Lado AA, Chen IJ (2008) Inter-organizational communication as a relational competency: antecedents and performance outcomes in collaborative buyer–supplier relationships. J Oper Manag 26(1):45–64
Powell WW, Koput KW, Smith-Doerr L (1996) Interorganizational collaboration and the locus of innovation: networks of learning in biotechnology. Adm Sci Q 41(1):116–145
Prajogo D, Chowdhury M (2010) The relationship between supplier management and firm’s performance: a multidimensional perspective. In: Proceedings of the 8th international conference on supply chain management and information systems (SCMIS 2010), IEEE, pp 1–7
Premkumar G, Ramamurthy K (1995) The role of interorganizational and organizational factors on the decision mode for adoption of interorganizational systems. Decis Sci 26(3):303–336
Premkumar G, Ramamurthy K, Saunders CS (2005) Information processing view of organizations: an exploratory examination of fit in the context of interorganizational relationships. J Manag Inf Syst 22(1):257–294
Provan KG, Sydow J (2008) Evaluating inter-organizational relationships. In: Cropper S, Huxham C, Ebers M, Ring PS (eds) The Oxford handbook of inter-organizational relations. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 691–718
Ratnasingam P (2000) The influence of power on trading partner trust in electronic commerce. Internet Res 10(1):56–63
Ryssel R, Ritter T, Gemünden HG (2000) Trust, commitment and value-creation in inter-organizational customer–supplier relationships. In: Proceedings of the 16th IMP conference (IMP 2000)
Ryu I, So S, Koo C (2009) The role of partnership in supply chain performance. Ind Manag Data Syst 109(4):496–514
Saunders C, Wu YA, Li Y, Weisfeld S (2004) Interorganizational Trust in B2B Relationships. In: Proceedings of the 6th international conference on electronic commerce (ICEC 2004), ACM, pp 272–279
Seppänen R (2008) Trust in Inter-organizational Relationships, PhD thesis. School of Business, Lappeenranta University of Technology, Lappeenranta, Finland
Seppänen R, Blomqvist K, Sundqvist S (2007) Measuring inter-organizational trust—a critical review of the empirical research in 1990–2003. Ind Mark Manag 36(2):249–265
Shin H, Collier DA, Wilson DD (2000) Supply management orientation and supplier/buyer performance. J Oper Manag 18(3):317–333
Singh D, Oberoi JS, Ahuja IS, Sahib F (2011) A survey of literature of conceptual frameworks assessing supply chain flexibility. Int J Appl Eng Res 2(1):172–182
Soni G, Kodali R (2010) Internal benchmarking for assessment of supply chain performance. Benchmarking Int J 17(1):44–76
Subramani M (2004) How do suppliers benefit from information technology use in supply chain relationships? MIS Q 28(1):45–73. http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=2017212.2017216
Talib F, Rahman Z, Qureshi M (2011) A study of total quality management and supply chain management practices. Int J Prod Perform Manag 60(3):268–288
Vereecke A, Muylle S (2006) Performance improvement through supply chain collaboration in Europe. Int J Oper Prod Manag 26(11):1176–1198
Vijayasarathy LR (2010) Supply integration: an investigation of its multi-dimension-ality and relational antecedents. Int J Prod Econ 124(2):489–505
von Neumann J, Morgenstern O (2007) Theory of games and economic behavior (60th Anniversary, Commemorative edition) Princeton University Press, Princeton
Whipple JM, Lynch DF, Nyaga GN (2010) A buyer’s perspective on collaborative versus transactional relationships. Ind Mark Manag 39(3):507–518
Wiengarten F, Humphreys P, Cao G, Fynes B, McKittrick A (2010) Collaborative supply chain practices and performance: exploring the key role of information quality. Supply Chain Manag Int J 15(6):463–473
Woo K, Ennew CT (2004) Business-to-business relationship quality: an IMP interaction-based conceptualization and measurement. Eur J Mark 38(9/10):1252–1271
Yeung AC (2008) Strategic supply management, quality initiatives, and organizational performance. J Oper Manag 26(4):490–502
Zaheer A, Harris J (2006) Interorganizational Trust. In: Shenkar O, Reuer JJ (eds) Handbook of strategic alliances, Sage Publications, London, Chap 10. pp 169–197
Zhang W, Yu C, Reagan B, Nakajima H (1995) Context-dependent interpretations of linguistic terms in fuzzy relational databases. In: Proceedings of the 11th international conference on data engineering (ICDE 1995), IEEE, pp 139–146
Zhao F (2002) Performance measures for inter-organisational partnerships. In: Proceedings of the 7th international conference on ISO 9000 and TQM (7-ICIT 2002)
Zhou H, Benton W Jr (2007) Supply chain practice and information sharing. J Oper Manag 25(6):1348–1365
Ziggers GW, Henseler J (2009) Inter-firm network capability: how it affects buyer–supplier performance. Br Food J 111(8):794–810
Acknowledgments
This research has been conducted in the context of the EDImine project and has been funded by the Vienna Science and Technology Fund (WWTF) through Project ICT10-010. Two of the authors of this paper were also supported by the Vienna Ph.D. School of Informatics (Krathu and Xiao) and the EU Project Optique FP7-318338 (Xiao).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krathu, W., Pichler, C., Xiao, G. et al. Inter-organizational success factors: a cause and effect model. Inf Syst E-Bus Manage 13, 553–593 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10257-014-0258-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10257-014-0258-z