Abstract
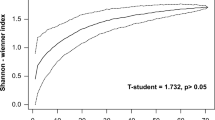
This study describes diet and feeding habits of two common bycatch elasmobranchs in East Australia: The Eastern Fiddler Ray Trygonorrhina fasciata (Muller & Henle, 1841) and the Sydney Skate Dentiraja australis (Macleay, 1884). Using stomach content analysis, we describe diet composition, food preferences and trophic levels of these batoids. Crustaceans were major components in the diet of both species which included teleosts and cephalopods. There was no indication of sex-related distinction in the diet of either species. The estimated trophic level (TL) of the T. fasciata was TL = 3.36 and the D. australis was TL = 3.43.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajemian MJ, Powers SP, Murdoch TJT (2012) Estimating the Potential Impacts of Large Mesopredators on Benthic Resources: Integrative Assessment of Spotted Eagle Ray Foraging Ecology in Bermuda. PLOS ONE
Anderson MJ (2005) Permutational multivariate analysis of variance. In: Department of Statistics, University of Auckland, Auckland, vol 26. pp 32-46
Anderson MJ (2006) Distance‐based tests for homogeneity of multivariate dispersions. Biometrics 62:245-253
Anderson MJ, Ellingsen KE, McArdle BH (2006) Multivariate dispersion as a measure of beta diversity. Ecol Lett 9:683-693
Bruce N, Adlard R, Cannon L (1994) Synoptic checklist of ascaridoid parasites (Nematoda) from fish hosts. Invert Syst 8:583-674 doi:https://doi.org/10.1071/IT9940583
Bundy A, Link J, Smith B, Cook A (2011) You are what you eat, whenever or wherever you eat it: an integrative analysis of fish food habits in Canadian and USA waters. J Fish Biol. 78:514-539
Cortés E (1997) A critical review of methods of studying fish feeding based on analysis of stomach contents: application to elasmobranch fishes. Can J Fish Aquat Sci. 54:726-738 https://doi.org/10.1139/f96-316
Cortés E (1999) Standardized diet compositions and trophic levels of sharks. ICES J Mar Sci. 56:707-717 https://doi.org/10.1006/jmsc.1999.0489
Costa T, Thayer J, Mendes L (2015) Population characteristics, habitat and diet of a recently discovered stingray Dasyatis marianae: implications for conservation. J Fish Biol. 86:527-543
Ebert DA, Bizzarro JJ (2007) Standardized diet compositions and trophic levels of skates (Chondrichthyes: Rajiformes: Rajoidei). Environ. Biol. Fishes 80:221-237 https://doi.org/10.1007/s10641-007-9227-4
Ebert DA, Cowley PD, Compagno LJV (1991) A PRELIMINARY INVESTIGATION OF THE FEEDING ECOLOGY OF SKATES (BATOIDEA, RAJIDAE) OFF THE WEST-COAST OF SOUTHERN AFRICA. South Afr J Mar Sci-Suid-Afr Tydsk. Seewetens. 10:71-81
Essington TE (2003) Development and sensitivity analysis of bioenergetics models for skipjack tuna and albacore: a comparison of alternative life histories. Trans Am Fish Soc. 132:759-770
Froese R, Pauly DE (2015) FishBase. World Wide Web electronic publication. Available at: http://www.fishbase.org. Accessed 26-02-2016
Garcia SM, Cochrane KL (2005) Ecosystem approach to fisheries: a review of implementation guidelines. ICES J Mar Sci. 62:311-318
Gordon JDM, Duncan JAR (2009) A Note on The Distribution and Diet of Deep-Water Rays (Rajidae) in An Area of The Rockall Trough. J Mar Biol Ass of the U. K. 69:655-658 https://doi.org/10.1017/s0025315400031040
Graham K, L. Andrew N, E. Hodgson K (2001) Changes in relative abundance of sharks and rays on Australian South East Fishery trawl grounds after twenty years of fishing. Mar Freshwat Res. 52:549-561 https://doi.org/10.1071/mf99174
Gray JS (1997) Marine biodiversity: patterns, threats and conservation needs. Biodivers Conserv. 6:153-175 https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1018335901847
Griffiths SP, Kuhnert PM, Fry GF, Manson FJ (2009) Temporal and size-related variation in the diet, consumption rate, and daily ration of mackerel tuna (Euthynnus affinis) in neritic waters of eastern Australia. ICES J Mar Sci 66:720-733
Hewitt G, Hine P (1972) Checklist of parasites of New Zealand fishes and of their hosts. N Z J Mar Freshwat Res. 6:69-114
Huveneers C (2015) Trygonorrhina fasciata. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2015: e.T41866A43270478. http://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T41866A43270478.en
Jacobsen IP, Bennett MB (2013) A Comparative Analysis of Feeding and Trophic Level Ecology in Stingrays (Rajiformes; Myliobatoidei) and Electric Rays (Rajiformes: Torpedinoidei). PLOS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0071348
Kaschner K, J. Rius-Barile, K. Kesner-Reyes, C. Garilao, S.O. Kullander, T. Rees, Froese. R (2013) AquaMaps: Predicted range maps for aquatic species. World wide web electronic publication, www.AquaMaps.org, Version 08/2013
Knoff M, São Clemente SCd, Pinto RM, Gomes DC (2001) Nematodes of elasmobranch fishes from the southern coast of Brazil. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 96:81-87
Last PRPR et al. (2009) Sharks and rays of Australia., 2nd ed edn. CSIRO Pub
Lipej L, Mavrič B, Paliska D, Capapé C (2012) Feeding habits of the pelagic stingray Pteroplatytrygon violacea (Chondrichthyes: Dasyatidae) in the Adriatic Sea. J. Mar. Biol. Ass. of the U. K. 93:285-290 https://doi.org/10.1017/s0025315412000197
Marasco RJ, Goodman D, Grimes CB, Lawson PW, Punt AE, Quinn II TJ (2007) Ecosystem-based fisheries management: some practical suggestions. Can J Fish Aquat Sci. 64:928-939
Michael SW (1993) Reef sharks and rays of the world: a guide to their identification, behavior, and ecology. Sea Challengers, Monterey, California
Morato T, Solà E, Grós MP, Menezes G (2003) Diets of thornback ray (Raja clavata) and tope shark (Galeorhinus galeus) in the bottom longline fishery of the Azores, northeastern Atlantic. Fish Bull. 101:590-602
Myers RA, Baum JK, Shepherd TD, Powers SP, Peterson CH (2007) Cascading Effects of the Loss of Apex Predatory Sharks from a Coastal Ocean. Science 315:1846-1850 https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1138657
Orlov A (2003) Diets, feeding habits, and trophic relations of six deep-benthic skates (Rajidae) in the western Bering Sea. J Ichthyol Aquat Biol 7:45-59
Pikitch E et al. (2004) Ecosystem-Based Fishery Management. Science 305:346-347
Ponte D, Barcelos L, Santos C, Medeiros J, Barreiros J (2016) Diet of Dasyatis pastinaca and Myliobatis aquila (Myliobatiformes) from the Azores, NE Atlantic. Cybium 40:209-214
Ritchie EG, Johnson CN (2009) Predator interactions, mesopredator release and biodiversity conservation. Ecol. Lett. 12:982-998 https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2009.01347.x
Romera SA (1993) Proleptus acutus (Nematoda: Physalopteridae), a Parasite from an Argentinian Skate, Sympterygia bonapartei (Pisces: Rajidae). J Parasitol. 79:620-623 https://doi.org/10.2307/3283393
Saglam H, Ak O, Kutlu S, Aydin İ (2009) Diet and feeding strategy of the common stingray (Dasyatis pastinaca (Linnaeus, 1758)) at the Turkish coast of south-eastern Black Sea. Cah Biol Mar. vol 51
Scandol JP, Holloway MG, Gibbs PJ, Astles KL (2005) Ecosystem-based fisheries management: an Australian perspective. Aquat Living Resour. 18:261-273
Soares LSH, Vazzoler AEAdM, Correa AR (1999) Diel feeding chronology of the skate raja Agassizii (Müller & Henle) (Pisces, Elasmobranchii) on the continental shelf off Ubatuba, Southeastern Brazil. Rev Bras Zool. 16:201-212
Stevens JD, Valenti SV (2009) Dipturus australis. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2009. http://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2009-2.RLTS.T161637A5470186.en
Walker T, Stuart Gason A (2007) Shark and other chondrichthyan byproduct and bycatch estimation in the Southern and Eastern Scalefish and Shark Fishery. Final report to Fisheries Research and Development Corporation Project No. 2001/007. (July 2007.) 182 + vi pp. (Primary Industries Research Victoria: Queenscliff, Victoria, Australia). https://doi.org/10.13140/2.1.3353.8564
Yıgın C, Ismen A (2010) Age, growth, reproduction and feed of longnosed skate, Dipturus oxyrinchus (Linnaeus, 1758) in Saros Bay, the north Aegean Sea. J Appl Ichthyol. 26:913-919 https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0426.2010.01510.x
Zander CD (1982) Feeding ecology of littoral gobiid and blennioid fish of the Banyuls area (Mediterranean Sea). 1. Main food and trophic dimension of niche and ecotope. In: Vie Millieu, vol 32. pp 1-10
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Daniel Johnson, Matt Harrison and Dr. Vic Peddemors and the Department of Primary Industries – Fisheries Observers Program for the samples provided for this study, the Sydney Institute of Marine Sciences for the use of facilities, Mr. Mark Macinante for the assistance with dissections and to the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES) for scholarship funding (Process BEX 13590-13-8). This research was conducted under animal ethics approval (ACEC ref: 16/02) to the NSW Department of Primary Industries. This is contribution number #253 to the Sydney Institute of Marine Science – SIMS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Reis, M., Figueira, W.F. Diet and feeding habits of two endemic demersal bycatch elasmobranchs: Trygonorrhina fasciata & Dentiraja australis. Ichthyol Res 67, 320–329 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10228-019-00724-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10228-019-00724-7