Abstract
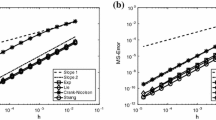
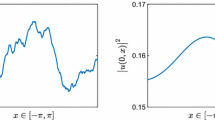
In this article, we derive and study symmetric exponential integrators. Numerical experiments are performed for the cubic Schrödinger equation and comparisons with classical exponential integrators and other geometric methods are also given. Some of the proposed methods preserve the L 2-norm and/or the energy of the system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. J. Ablowitz and J. F. Ladik, A nonlinear difference scheme and inverse scattering, Stud. in Appl. Math. 55(3) (1976), 213–229.
H. Berland, A. L. Islas, and C. M. Schober, Conservation of phase space properties using exponential integrators on the cubic Schrödinger equation, Technical report 1/06, Norwegian Institute of Science and Technology (2006), submitted to J. Comput. Phys.
H. Berland, B. Skaflestad, and W. M. Wright, EXPINT—A MATLAB package for exponential integrators, ACM Trans. Math. Softw. 33(1) (2007).
C. Besse, A relaxation scheme for the nonlinear Schrödinger equation, SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 42(3) (2004), 934–952 (electronic).
T. J. Bridges and S. Reich, Multi-symplectic integrators: numerical schemes for Hamiltonian PDEs that conserve symplecticity, Phys. Lett. A 284(4/5) (2001), 184–193.
B. Cano, Conserved quantities of some Hamiltonian wave equations after full discretization, Numer. Math. 103(2) (2006), 197–223.
J. Certaine, The solution of ordinary differential equations with large time constants, in Mathematical Methods for Digital Computers, pp. 128–132, Wiley, New York, 1960.
A. Durán and J. M. Sanz-Serna, The numerical integration of relative equilibrium solutions. The nonlinear Schrödinger equation, IMA J. Numer. Anal. 20(2) (2000), 235–261.
Z. Fei, V. M. Pérez-García, and L. Vázquez, Numerical simulation of nonlinear Schrödinger systems: a new conservative scheme, Appl. Math. Comput. 71(2/3) (1995), 165–177.
E. Hairer, Symmetric projection methods for differential equations on manifolds, BIT 40(4) (2000), 726–734.
E. Hairer, C. Lubich, and G. Wanner, Geometric Numerical Integration: Structure-Preserving Algorithms for Ordinary Differential Equations, 2nd edn., Springer Series in Computational Mathematics, Vol. 31, Springer, Berlin, 2006.
A. L. Islas, D. A. Karpeev, and C. M. Schober, Geometric integrators for the nonlinear Schrödinger equation, J. Comput. Phys. 173(1) (2001), 116–148.
A. L. Islas and C. M. Schober, On the preservation of phase space structure under multisymplectic discretization, J. Comput. Phys. 197(2) (2004), 585–609.
J. D. Lawson, Generalized Runge–Kutta processes for stable systems with large Lipschitz constants, SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 4 (1967), 372–380.
J. E. Marsden and T. S. Ratiu, Introduction to Mechanics and Symmetry: A Basic Exposition of Classical Mechanical Systems, 2nd edn., Texts in Applied Mathematics, Vol. 17, Springer, New York, 1999.
R. I. McLachlan, Symplectic integration of Hamiltonian wave equations, Numer. Math. 66(4) (1994), 465–492.
B. Minchev and W. M. Wright, A review of exponential integrators for semilinear problems, Technical report 2/05, Department of Mathematical Sciences, NTNU, Norway (2005), http://www.math.ntnu.no/preprint/.
S. Reich, Multi-symplectic Runge–Kutta collocation methods for Hamiltonian wave equations, J. Comput. Phys. 157(2) (2000), 473–499.
T. R. Taha and J. Ablowitz, Analytical and numerical aspects of certain nonlinear evolution equations. II. Numerical, nonlinear Schrödinger equation, J. Comput. Phys. 55(2) (1984), 203–230.
A. Zanna, K. Engø, and H. Munthe-Kaas, Adjoint and selfadjoint Lie-group methods, BIT 41(2) (2001), 395–421.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Dedicated to Professor Arieh Iserles on the Occasion of his Sixtieth Birthday.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Celledoni, E., Cohen, D. & Owren, B. Symmetric Exponential Integrators with an Application to the Cubic Schrödinger Equation. Found Comput Math 8, 303–317 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10208-007-9016-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10208-007-9016-7