Abstract
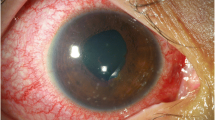
A 58-year-old man was admitted to our hospital complaining of fever and arthralgia. His clinical course and marked ciliary hyperemia led us to suspect tubulointestinal nephritis and uveitis (TINU) syndrome, which was confirmed ophthalmologically and by renal biopsy. Results of a drug-induced lymphocyte-stimulating test were positive for the Chinese herb “Goreisan.” This is the first case in which the use of “Goreisan” was causally related to TINU syndrome.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dobrin RS, Vernier RL, Fish AL. Acute eosinophilic interstitial nephritis and renal failure with bone marrow-lymph node granulomas and anterior uveitis. A new syndrome. Am J Med. 1975;59:325–33.
Yoshioka K, Takemura T, Kanasaki M, Akano N, Maki S. Acute interstitial nephritis and uveitis syndrome: activated immune cell infiltration in the kidney. Pediatr Nephrol. 1991;5:232–4.
Mandeville JT, Levinson RD, Holland GN. The tubulointerstitial nephritis and uveitis syndrome. Surv Ophthalmol. 2001;46:195–208.
Tanaka A, Nishida R, Maeda K, Sugawara A, Kuwahara T. Chinese herb nephropathy in Japan presents adult-onset Fanconi syndrome: could different components of aristolochic acids cause a different type of Cinese herb nephropathy? Clin Nephrol. 2000;53:301–6.
Saad N, Kalowski S, Mikus V. Primary tubulointerstitial nephritis and uveitis syndrome. Aust N Z J Ophthalmol. 1993;21:279.
Grefer J, Santer R, Ankermann T, Faul S, Nolle B, Eggert P. Tubulointerstitial nephritis and uveitis in association with Epstein-Barr virus infection. Pediatr Nephrol. 1999;13:336–9.
Pichler WJ, Tilch J. The lymphocyte transformation test in the diagnosis of drug hypersensitivity. Allergy. 2004;59:809–20.
Mantani N, Sakai S, Kogure T, Goto H, Shibahara N, Kita T, et al. Herbal medicine and false-positive results on lymphocyte transformation test. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2002;122:399–402.
Sessa A, Meroni M, Battini G, Vigano G, Brambilla PL, Paties CT. Acute renal failure due to idiopathic tublo-interstinal nephritis and uveitis: “TINU syndrome”. Case report and review of the literature. J Nephrol. 2000;13:377–80.
Cacoub P, Deray G, Le Hoang P, Baumelou A, Beaufils H, de Groc F, et al. Idiopathic acute interstitial nephriyis associated with anterior uveitis in adults. Clin Nephrol. 1989;31:307–10.
Salu P, Stempels N, Vanden Houte K, Verbeelen D. Acute tubulointerstitial nephritis and uveitis syndrome in the elderly. Br J Ophthalmol. 1990;74:53–5.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Suzuki, H., Yoshioka, K., Miyano, M. et al. Tubulointerstitial nephritis and uveitis (TINU) syndrome caused by the Chinese herb “Goreisan”. Clin Exp Nephrol 13, 73–76 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-008-0069-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-008-0069-y