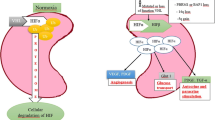
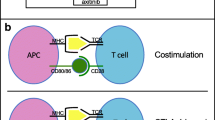
Abstract
In the last decade, the standard treatment for advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC) has evolved, mainly driven by the development and approval of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs). Currently, ICI monotherapy and ICI-based combinations with tyrosine kinase inhibitors and targeted therapies against mammalian target of rapamycin or vascular endothelial growth factor have become new standard treatments for first-line and subsequent-line therapies. ICIs play an important role as an adjuvant postoperative therapy, and this field is the subject of active research. Furthermore, ongoing randomized controlled trials are investigating the clinical value of more intense treatments by combining multiple effective treatments for RCC. Additionally, novel biomarkers for prognosis have been investigated. This study reviews the current evidence on immunotherapy as a treatment for RCC patients, randomized controlled trials, and ongoing studies including RCC patients and recent findings, and discusses future perspectives.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS et al (2023) Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin 73(1):17–48. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21763
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL et al (2021) Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21492
Lam JS, Leppert JT, Belldegrun AS et al (2005) Novel approaches in the therapy of metastatic renal cell carcinoma. World J Urol 23(3):202–212. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-004-0466-0
Capitanio U, Bensalah K, Bex A et al (2019) Epidemiology of renal cell carcinoma. Eur Urol 75(1):74–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2018.08.036
Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Tomczak P et al (2007) Sunitinib versus interferon alfa in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J 356(2):115–124. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa065044
Blas L, Roberti J, Petroni J et al (2019) Renal medullary carcinoma: a report of the current literature. Curr Urol Rep. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11934-019-0865-9
Motzer RJ, Jonasch E, Agarwal N et al (2022) Kidney Cancer, Version 3.2022, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. JNCCN J Natl Compr Cancer Netw. 20(1):71–90. https://doi.org/10.6004/jnccn.2022.0001
Griffiths RW, Elkord E, Gilham DE et al (2007) Frequency of regulatory T cells in renal cell carcinoma patients and investigation of correlation with survival. Cancer Immunol Immunother 56(11):1743–1753
Chemnitz JM, Riley JL, Frauwirth KA et al (2004) CTLA-4 and PD-1 receptors inhibit T cell activation by distinct mechanisms. Blood 104(11):2657–2657. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.v104.11.2657.2657
Motzer RJ, Tannir NM, McDermott DF et al (2018) Nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus sunitinib in advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 378(14):1277–1290. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa1712126
Heng DYC, Xie W, Regan MM et al (2009) Prognostic factors for overall survival in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with vascular endothelial growth factor-targeted agents: results from a large, multicenter study. J Clin Oncol 27(34):5794–5799. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2008.21.4809
Heng DYC, Xie W, Regan MM et al (2013) External validation and comparison with other models of the international metastatic renal-cell carcinoma database consortium prognostic model: a population-based study. Lancet Oncol 14(2):141–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(12)70559-4
Albiges L, Tannir NM, Burotto M et al (2020) Nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus sunitinib for first-line treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma: E##xtended 4-year follow-up of the phase III CheckMate 214 trial. ESMO Open 5(6):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1136/esmoopen-2020-001079
Choueiri TK, Powles T, Burotto M et al (2021) Nivolumab plus cabozantinib versus sunitinib for advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 384(9):829–841. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa2026982
Motzer RJ, Powles T, Burotto M et al (2022) Nivolumab plus cabozantinib versus sunitinib in first-line treatment for advanced renal cell carcinoma (CheckMate 9ER): long-term follow-up results from an open-label, randomized, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 23(7):888–898. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(22)00290-X
Rini BI, Plimack ER, Stus V et al (2019) Pembrolizumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib for advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 380(12):1116–1127. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa1816714
Plimack ER, Powles T, Stus V et al (2023) Pembrolizumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib as first-line treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma: 43-month follow-up of phase 3 KEYNOTE-426 study. Eur Urol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2023.06.006
Motzer R, Alekseev B, Rha SY et al (2021) Lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab or everolimus for advanced renal cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 384(14):1289–1300. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa2035716
Choueiri TK, Eto M, Motzer R et al (2023) Lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab versus sunitinib as first-line treatment of patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (CLEAR): extended follow-up from the phase 3, randomised, open-label study. Lancet Oncol 24(3):228–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(23)00049-9
Ljungberg B, Albiges L, Abu-Ghanem Y et al (2022) European Association of Urology Guidelines on renal cell carcinoma: the 2022 update. Eur Urol 82(4):399–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2022.03.006
Motzer RJ, Penkov K, Haanen J et al (2019) Avelumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib for advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 380(12):1103–1115. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa1816047
Haanen JBAG, Larkin J, Choueiri TK et al (2023) Extended follow-up from JAVELIN renal 101: subgroup analysis of avelumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib by the International Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Database Consortium risk group in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma. ESMO Open 8(3):101210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.esmoop.2023.101210
Rini BI, Powles T, Atkins MB et al (2019) Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab versus sunitinib in patients with previously untreated metastatic renal cell carcinoma (IMmotion151): a multicentre, open-label, phase 3, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 393(10189):2404–2415. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30723-8
Motzer RJ, Powles T, Atkins MB et al (2022) Final overall survival and molecular analysis in IMmotion151, a phase 3 trial comparing atezolizumab plus bevacizumab vs sunitinib in patients with previously untreated metastatic renal cell carcinoma. JAMA Oncol 8(2):275–280. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.5981
Choueiri TK, Powles T, Albiges L et al (2023) Cabozantinib plus nivolumab and ipilimumab in renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 388(19):1767–1778. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2212851
Quhal F, Mori K, Bruchbacher A et al (2021) First-line immunotherapy-based combinations for metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Eur Urol Oncol 4(5):755–765. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euo.2021.03.001
Nocera L, Karakiewicz PI, Wenzel M et al (2022) Clinical outcomes and adverse events after first-line treatment in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. J Urol 207(1):16–24. https://doi.org/10.1097/JU.0000000000002252
Blas L, Shiota M, Tsukahara S et al (2023) Adverse events of cabozantinib plus nivolumab versus ipilimumab plus nivolumab. Clin Genitourin Cancer. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clgc.2023.09.003. (Epub ahead of print)
Hammers HJ, Plimack ER, Infante JR et al (2017) Safety and efficacy of nivolumab in combination with ipilimumab in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: the checkmate 016 study. J Clin Oncol 35(34):3851–3858. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2016.72.1985
Grimm MO, Schmidinger M, Duran Martinez I et al (2019) Tailored immunotherapy approach with nivolumab in advanced renal cell carcinoma (TITAN-RCC). Ann Oncol 30(October):v892. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdz394.051
Yang Y, Mori SV, Li M et al (2022) Salvage nivolumab and ipilimumab after prior anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a meta-analysis. Cancer Med 11(7):1669–1677. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.4587
Motzer RJ, Escudier B, McDermott DF et al (2015) Nivolumab versus everolimus in advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 373(19):1803–1813. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa1510665
Motzer RJ, Escudier B, George S et al (2020) Nivolumab versus everolimus in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma: updated results with long-term follow-up of the randomized, open-label, phase 3 CheckMate 025 trial. Cancer 126(18):4156–4167. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.33033
Pal SK, Albiges L, Tomczak P et al (2023) Atezolizumab plus cabozantinib versus cabozantinib monotherapy for patients with renal cell carcinoma after progression with previous immune checkpoint inhibitor treatment (CONTACT-03): a multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 402:185–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(23)00922-4
Ornstein MC, Wood LS, Hobbs BP et al (2019) A phase II trial of intermittent nivolumab in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC) who have received prior anti-angiogenic therapy. J Immunother Cancer 7(1):1–5. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40425-019-0615-z
Lee CH, Shah AY, Rasco D et al (2021) Lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab in patients with either treatment-naive or previously treated metastatic renal cell carcinoma (Study 111/KEYNOTE-146): a phase 1b/2 study. Lancet Oncol 22(7):946–958. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00241-2
Choueiri TK, McDermott DF, Merchan J et al (2023) Belzutifan plus cabozantinib for patients with advanced clear cell renal cell carcinoma previously treated with immunotherapy: an open-label, single-arm, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol 24(5):553–562. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(23)00097-9
Eisen T, Frangou E, Oza B et al (2020) Adjuvant sorafenib for renal cell carcinoma at intermediate or high risk of relapse: results from the SORCE randomized phase III intergroup trial. J Clin Oncol 38(34):4064–4075. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.20.01800
Gross-Goupil M, Kwon TG, Eto M et al (2018) Axitinib versus placebo as an adjuvant treatment of renal cell carcinoma: results from the phase III, randomized ATLAS trial. Ann Oncol 29(12):2371–2378. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdy454
Motzer RJ, Haas NB, Donskov F et al (2017) Randomized phase III trial of adjuvant pazopanib versus placebo after nephrectomy in patients with localized or locally advanced renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 35(35):3916–3923. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2017.73.5324
Haas NB, Manola J, Dutcher JP et al (2017) Adjuvant treatment for high-risk clear cell renal cancer: updated results of a high-risk subset of the ASSURE randomized trial. JAMA Oncol 3(9):1249–1252. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.0076
Haas NB, Manola J, Uzzo RG et al (2016) Adjuvant sunitinib or sorafenib for high-risk, non-metastatic renal-cell carcinoma (ECOG-ACRIN E2805): a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet 387(10032):2008–2016. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)00559-6
Ravaud A, Motzer RJ, Pandha HS et al (2016) Adjuvant sunitinib in high-risk renal-cell carcinoma after nephrectomy. N Engl J Med 375(23):2246–2254. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa1611406
Ryan CW, Tangen CM, Heath EI et al (2023) Adjuvant everolimus after surgery for renal cell carcinoma (EVEREST): a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet (Lond, Engl) 6736(23):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(23)00913-3
Choueiri TK, Tomczak P, Park SH et al (2021) Adjuvant pembrolizumab after nephrectomy in renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 385(8):683–694. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa2106391
Allaf M, Kim SE, Harshman LC et al (2022) LBA67 phase III randomized study comparing perioperative nivolumab (nivo) versus observation in patients (Pts) with renal cell carcinoma (RCC) undergoing nephrectomy (PROSPER, ECOG-ACRIN EA8143), a National Clinical Trials Network trial. Ann Oncol 33:S1432–S1433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annonc.2022.08.072
Motzer RJ, Russo P, Grünwald V et al (2023) Adjuvant nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus placebo for localised renal cell carcinoma after nephrectomy (CheckMate 914): a double-blind, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet 401(10379):821–832. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02574-0
Pal SK, Uzzo R, Karam JA et al (2022) Adjuvant atezolizumab versus placebo for patients with renal cell carcinoma at increased risk of recurrence following resection (IMmotion010): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet 400(10358):1103–1116. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01658-0
Powles T, Tomczak P, Park SH et al (2022) Pembrolizumab versus placebo as post-nephrectomy adjuvant therapy for clear cell renal cell carcinoma (KEYNOTE-564): 30-month follow-up analysis of a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 23(9):1133–1144. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(22)00487-9
Bedke J, Albiges L, Capitanio U et al (2023) The 2022 updated European Association of Urology Guidelines on the use of adjuvant immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy for renal cell carcinoma. Eur Urol 83(1):10–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2022.10.010
Vogelzang NJ, Olsen MR, McFarlane JJ et al (2020) Safety and efficacy of nivolumab in patients with advanced non-clear cell renal cell carcinoma: results from the phase IIIb/IV CheckMate 374 study. Clin Genitourin Cancer 18(6):461-468.e3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clgc.2020.05.006
Tykodi SS, Gordan LN, Alter RS et al (2022) Safety and efficacy of nivolumab plus ipilimumab in patients with advanced non-clear cell renal cell carcinoma: results from the phase 3b/4 CheckMate 920 trial. J Immunother Cancer 10(2):e003844. https://doi.org/10.1136/jitc-2021-003844
Albiges L, Gurney H, Atduev V et al (2023) Pembrolizumab plus lenvatinib as first-line therapy for advanced non-clear-cell renal cell carcinoma (KEYNOTE-B61): a single-arm, multicentre, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol 24(8):881–891. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(23)00276-0
Lee CH, Voss MH, Carlo MI et al (2022) Phase II trial of cabozantinib plus nivolumab in patients with non-clear-cell renal cell carcinoma and genomic correlates. J Clin Oncol 40(21):2333–2341. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.21.01944
McGregor BA, McKay RR, Braun DA et al (2020) Results of a multicenter phase II study of atezolizumab and bevacizumab for patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma with variant histology and/or sarcomatoid features. J Clin Oncol 38(1):63–70. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.19.01882
Motzer RJ, Robbins PB, Powles T et al (2020) Avelumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib in advanced renal cell carcinoma: biomarker analysis of the phase 3 JAVELIN renal 101 trial. Nat Med 26(11):1733–1741. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-020-1044-8
McDermott DF, Huseni MA, Atkins MB et al (2018) Clinical activity and molecular correlates of response to atezolizumab alone or in combination with bevacizumab versus sunitinib in renal cell carcinoma. Nat Med 24(6):749–757. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-018-0053-3
Lalani AKA, Xie W, Martini DJ et al (2018) Change in neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) in response to immune checkpoint blockade for metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Immunother Cancer 6(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40425-018-0315-0
Basu A, Phone A, Bice T et al (2021) Change in neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) as a predictor of treatment failure in renal cell carcinoma patients: analysis of the IROC (Investigating RCC Outcomes) cohort. J Clin Oncol 39(6):344–354. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2021.39.6_suppl.344
Miao D, Margolis CA, Gao W et al (2018) Genomic correlates of response to immune checkpoint therapies in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Science 806(February):801–806
Ficial M, Jegede O, Sant’Angelo M, et al (2020) Evaluation of predictive biomarkers for nivolumab in patients with metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma (mccRCC) from the CheckMate-025 trial. J Clin Oncol 38(15):502
Sakuishi K, Ngiow SF, Sullivan JM et al (2013) TIM3+FOXP3+ regulatory T cells are tissue-specific promoters of T cell dysfunction in cancer. Oncoimmunology. https://doi.org/10.4161/onci.23849
Acknowledgements
We thank Mitchell Arico from Edanz (https://jp.edanz.com/ac) for editing a draft of this manuscript.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Junichi Inokuchi received honoraria from Astellas Pharma, and research funding from Ono Pharmaceutical, Astellas Pharma, AstraZeneca and Chugai Pharmaceutical. Masatoshi Eto received honoraria from Ono Pharmaceutical, Takeda Pharmaceutical, Novartis Pharma, Pfizer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Janssen Pharmaceutical, MSD, and Merck Biopharma, and research funding from Sanofi, Bayer Yakuhin, Astellas Pharma, Ono Pharmaceutical, and Takeda Pharmaceutical.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Blas, L., Monji, K., Mutaguchi, J. et al. Current status and future perspective of immunotherapy for renal cell carcinoma. Int J Clin Oncol (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-023-02446-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-023-02446-3