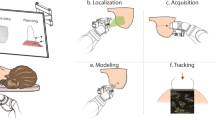
Abstract
Interventional oncology offers minimally invasive treatments for malignant tumors for curative and palliative purposes based on the percutaneous insertion of needles or catheters into the target location under image guidance. Robotic systems have been gaining increasing attention as tools that provide potential advantages for image-guided interventions. Among the robotic systems developed for intervention, those relevant to the oncology field are mainly those for guiding or driving the needles in non-vascular interventional procedures such as biopsy and tumor ablation. Needle-guiding robots support planning the needle path and align the needle robotically according to the planned trajectory, which is combined with subsequent manual needle insertion by the physician through the needle guide. Needle-driving robots can advance the needle robotically after determining its orientation. Although a wide variety of robotic systems have been developed, only a limited number of these systems have reached the clinical phase or commercialization thus far. The results of previous studies suggest that such interventional robots have the potential to increase the accuracy of needle placement, facilitate out-of-plane needle insertion, decrease the learning curve, and reduce radiation exposure. On the other hand, increased complexity and costs may be a concern when using robotic systems compared with conventional manual procedures. Further data should be collected to comprehensively assess the value of robotic systems in interventional oncology.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adam A, Kenny LM (2015) Interventional oncology in multidisciplinary cancer treatment in the 21(st) century. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 12:105–113
Putzer D, Schullian P, Braunwarth E et al (2018) Integrating interventional oncology in the treatment of liver tumors. Eur Surg 50:117–124
Hasegawa T, Chatani S, Sato Y et al (2021) Percutaneous image-guided needle biopsy of musculoskeletal tumors: technical tips. Interv Radiol 6:75–82
Iguchi T, Matsui Y, Tomita K et al (2021) Computed tomography-guided core needle biopsy for renal tumors: a review. Interv Radiol 6:69–74
Matsui Y, Hiraki T, Sakurai J et al (2022) Percutaneous needle biopsy under 1.2 Tesla open MRI guidance. Jpn J Radiol 40:430–438
Park R, Lee SM, Kim S et al (2022) Learning curve for CT-guided percutaneous transthoracic needle biopsy: retrospective evaluation among 17 thoracic imaging fellows at a tertiary referral hospital. AJR Am J Roentgenol 218:112–123
Nakatani M, Kariya S, Ono Y et al (2022) Radiation exposure and protection in computed tomography fluoroscopy. Interv Radiol 7:49–53
Seki Y, Miyazaki M, Fukushima Y et al (2020) Radiation exposure of interventional radiologists during computed tomography fluoroscopy-guided percutaneous cryoablation. Interv Radiol 5:67–73
Matsui Y, Hiraki T, Gobara H et al (2016) Radiation exposure of interventional radiologists during computed tomography fluoroscopy-guided renal cryoablation and lung radiofrequency ablation: direct measurement in a clinical setting. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 39:894–901
Unger M, Berger J, Melzer A (2021) Robot-assisted image-guided interventions. Front Robot AI 8:664622
Kwoh YS, Hou J, Jonckheere EA et al (1988) A robot with improved absolute positioning accuracy for CT guided stereotactic brain surgery. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 35:153–160
Tacher V, de Baere T (2020) Robotic assistance in interventional radiology: dream or reality? Eur Radiol 30:925–926
Christou AS, Amalou A, Lee H et al (2021) Image-guided robotics for standardized and automated biopsy and ablation. Semin Intervent Radiol 38:565–575
Cleary K, Melzer A, Watson V et al (2006) Interventional robotic systems: applications and technology state-of-the-art. Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol 15:101–113
Kettenbach J, Kronreif G (2015) Robotic systems for percutaneous needle-guided interventions. Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol 24:45–53
Arnolli MM, Hanumara NC, Franken M et al (2015) An overview of systems for CT- and MRI-guided percutaneous needle placement in the thorax and abdomen. Int J Med Robot 11:458–475
Rueda MA, Riga CT, Hamady MS (2018) Robotics in interventional radiology: past, present, and future. Arab J Interv Radiol 2:56–63
Kulkarni P, Sikander S, Biswas P et al (2019) Review of robotic needle guide systems for percutaneous intervention. Ann Biomed Eng 47:2489–2513
Fichtinger G, Troccaz J, Haidegger T (2022) Image-guided interventional robotics: lost in translation? Proc IEEE 110:932–950
Zangos S, Melzer A, Eichler K et al (2011) MR-compatible assistance system for biopsy in a high-field-strength system: initial results in patients with suspicious prostate lesions. Radiology 259:903–910
Melzer A, Gutmann B, Remmele T et al (2008) INNOMOTION for percutaneous image-guided interventions: principles and evaluation of this MR- and CT-compatible robotic system. IEEE Eng Med Biol Mag 27:66–73
Kettenbach J, Kubin K, Stadler A et al (2008) Pneumatically driven robotic system for MR-guided biopsie, drainage and tumorablation: first clinical experiences. J Vasc Interv Radiol 19:S60
Zangos S, Herzog C, Eichler K et al (2007) MR-compatible assistance system for punction in a high-field system: device and feasibility of transgluteal biopsies of the prostate gland. Eur Radiol 17:1118–1124
Schulz B, Eichler K, Siebenhandl P et al (2013) Accuracy and speed of robotic assisted needle interventions using a modern cone beam computed tomography intervention suite: a phantom study. Eur Radiol 23:198–204
Kettenbach J, Kara L, Toporek G et al (2014) A robotic needle-positioning and guidance system for CT-guided puncture: ex vivo results. Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol 23:271–278
Martinez RM, Ptacek W, Schweitzer W et al (2014) CT-guided, minimally invasive, postmortem needle biopsy using the B-Rob II needle-positioning robot. J Forensic Sci 59:517–521
Kettenbach J, Kronreif G, Figl M et al (2005) Robot-assisted biopsy using computed tomography-guidance: initial results from in vitro tests. Invest Radiol 40:219–228
Kettenbach J, Kronreif G, Figl M et al (2005) Robot-assisted biopsy using ultrasound guidance: initial results from in vitro tests. Eur Radiol 15:765–771
MICROMATETM Case Reports. https://interventional-systems.showpad.com/share/8nPSChuvOvnUwLsqh10dB. Accessed Jan 2023
Groetz S, Wilhelm K, Willinek W et al (2016) A new robotic assistance system for percutaneous CT-guided punctures: initial experience. Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol 25:79–85
Engstrand J, Toporek G, Harbut P et al (2017) Stereotactic CT-guided percutaneous microwave ablation of liver tumors with the use of high-frequency jet ventilation: an accuracy and procedural safety study. AJR Am J Roentgenol 208:193–200
Abdullah BJJ, Yeong CH, Goh KL et al (2014) Robot-assisted radiofrequency ablation of primary and secondary liver tumours: early experience. Eur Radiol 24:79–85
Koethe Y, Xu S, Velusamy G et al (2014) Accuracy and efficacy of percutaneous biopsy and ablation using robotic assistance under computed tomography guidance: a phantom study. Eur Radiol 24:723–730
Abdullah BJJ, Yeong CH, Goh KL et al (2015) Robotic-assisted thermal ablation of liver tumours. Eur Radiol 25:246–257
Mbalisike EC, Vogl TJ, Zangos S et al (2015) Image-guided microwave thermoablation of hepatic tumours using novel robotic guidance: an early experience. Eur Radiol 25:454–462
Cornelis F, Takaki H, Laskhmanan M et al (2015) Comparison of CT fluoroscopy-guided manual and CT-guided robotic positioning system for in vivo needle placements in swine liver. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 38:1252–1260
Smakic A, Rathmann N, Kostrzewa M et al (2018) Performance of a robotic assistance device in computed tomography-guided percutaneous diagnostic and therapeutic procedures. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 41:639–644
Fong AJ, Stewart CL, Lafaro K et al (2021) Robotic assistance for quick and accurate image-guided needle placement. Update Surg 73:1197–1201
Muntener M, Patriciu A, Petrisor D et al (2006) Magnetic resonance imaging compatible robotic system for fully automated brachytherapy seed placement. Urology 68:1313–1317
Stoianovici D, Song D, Petrisor D et al (2007) ‘MRI Stealth’ robot for prostate interventions. Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol 16:241–248
Patriciu A, Petrisor D, Muntener M et al (2007) Automatic brachytherapy seed placement under MRI guidance. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 54:1499–1506
Muntener M, Patriciu A, Petrisor D et al (2008) Transperineal prostate intervention: robot for fully automated MR imaging–system description and proof of principle in a canine model. Radiology 247:543–549
Stoianovici D, Kim C, Petrisor D et al (2017) MR safe robot, FDA clearance, safety and feasibility prostate biopsy clinical trial. IEEE ASME Trans Mechatron 22:115–126
Arnolli MM, Buijze M, Franken M et al (2018) System for CT-guided needle placement in the thorax and abdomen: a design for clinical acceptability, applicability and usability. Int J Med Robot 14:e1877
Arnolli MM, Buijze M, Franken M et al (2018) A precision system for computed tomography-guided needle placement in the thorax and abdomen—technical design and performance analysis. J Med Device 12:021003
Heerink WJ, Ruiter SJS, Pennings JP et al (2019) Robotic versus freehand needle positioning in CT-guided ablation of liver tumors: a randomized controlled trial. Radiology 290:826–832
de Baere T, Roux C, Noel G et al (2022) Robotic assistance for percutaneous needle insertion in the kidney: preclinical proof on a swine animal model. Eur Radiol Exp 6:13
de Baère T, Roux C, Deschamps F et al (2022) Evaluation of a new CT-guided robotic system for percutaneous needle insertion for thermal ablation of liver tumors: a prospective pilot study. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 45:1701–1709
Guiu B, De Baère T, Noel G et al (2021) Feasibility, safety and accuracy of a CT-guided robotic assistance for percutaneous needle placement in a swine liver model. Sci Rep 11:5218
Solomon SB, Patriciu A, Bohlman ME et al (2002) Robotically driven interventions: a method of using CT fluoroscopy without radiation exposure to the physician. Radiology 225:277–282
Stoianovici D, Cleary K, Patriciu A et al (2003) AcuBot: a robot for radiological interventions. IEEE Trans Robot Automat 19:927–930
Cleary K, Watson V, Lindisch D et al (2005) Precision placement of instruments for minimally invasive procedures using a “needle driver” robot. Int J Med Robot 1:40–47
Patriciu A, Awad M, Solomon SB et al (2005) Robotic assisted radio-frequency ablation of liver tumors–randomized patient study. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv 8:526–533
Pollock R, Mozer P, Guzzo TJ et al (2010) Prospects in percutaneous ablative targeting: comparison of a computer-assisted navigation system and the AcuBot robotic system. J Endourol 24:1269–1272
Stoianovici D, Whitcomb LL, Anderson JH et al (1998) A modular surgical robotic system for image guided percutaneous procedures. In: Wells WM, Colchester A, Delp S (eds) Medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention—MICCAI’98. MICCAI 1998. Lecture notes in computer science, vol 1496. Springer, Berlin, pp 404–410
Hiraki T, Kamegawa T, Matsuno T et al (2017) Robotically driven CT-guided needle insertion: preliminary results in phantom and animal experiments. Radiology 285:454–461
Hiraki T, Matsuno T, Kamegawa T et al (2018) Robotic insertion of various ablation needles under computed tomography guidance: accuracy in animal experiments. Eur J Radiol 105:162–167
Hiraki T, Kamegawa T, Matsuno T et al (2018) Zerobot®: a remote-controlled robot for needle insertion in CT-guided interventional radiology developed at Okayama university. Acta Med Okayama 72:539–546
Hiraki T, Kamegawa T, Matsuno T et al (2020) Robotic needle insertion during computed tomography fluoroscopy-guided biopsy: prospective first-in-human feasibility trial. Eur Radiol 30:927–933
Komaki T, Hiraki T, Kamegawa T et al (2020) Robotic CT-guided out-of-plane needle insertion: comparison of angle accuracy with manual insertion in phantom and measurement of distance accuracy in animals. Eur Radiol 30:1342–1349
Ben-David E, Shochat M, Roth I et al (2018) Evaluation of a CT-guided robotic system for precise percutaneous needle insertion. J Vasc Interv Radiol 29:1440–1446
Levy S, Goldberg SN, Roth I et al (2021) Clinical evaluation of a robotic system for precise CT-guided percutaneous procedures. Abdom Radiol 46:5007–5016
Yang K, Ganguli S, DeLorenzo MC et al (2018) Procedure-specific CT dose and utilization factors for CT-guided interventional procedures. Radiology 289:150–157
Kloeckner R, dos Santos DP, Schneider J et al (2013) Radiation exposure in CT-guided interventions. Eur J Radiol 82:2253–2257
Barba P, Stramiello J, Funk EK et al (2022) Remote telesurgery in humans: a systematic review. Surg Endosc 36:2771–2777
Zhou Y, Thiruvalluvan K, Krzeminski L et al (2013) CT-guided robotic needle biopsy of lung nodules with respiratory motion - experimental system and preliminary test. Int J Med Robot 9:317–330
Wei L, Jiang S, Yang Z et al (2020) A CT-guided robotic needle puncture method for lung tumours with respiratory motion. Phys Med 73:48–56
Funding
This study was not supported by any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
T.H. and Y.M. received a grant from Cannon Medical Systems for work related to this study. Other authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study did not require ethical approval because it was a review of published articles and did not directly involve human or animal subjects.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Matsui, Y., Kamegawa, T., Tomita, K. et al. Robotic systems in interventional oncology: a narrative review of the current status. Int J Clin Oncol 29, 81–88 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-023-02344-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-023-02344-8