Abstract
Purpose
This single-arm, multicenter, phase-II trial evaluated the efficacy and safety of hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy (HAIC) using fine-powder cisplatin and iodized-oil suspension in patients with intermediate- and advanced-stage [Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) stage-B and stage-C] hepatocellular carcinomas (HCCs).
Methods
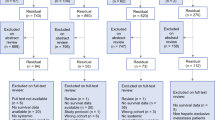
The Institutional Review Board approved this study and patients provided written informed consent. Thirty-five patients (24 men and 11 women, mean 74 ± 6 years [range 60–87 years]) with BCLC stage-B (57 %, 20/35) or stage-C (43 %, 15/35) HCCs who were not candidates for other locoregional treatments were enrolled. HAIC was performed using a suspension of fine-powder cisplatin with a maximum dose of 65 mg/m2 and iodized oil on demand. The primary endpoint was the response rate evaluated based on Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumor (RECIST) and modified RECIST (mRECIST). Secondary endpoints were overall survival, progression-free survival, and safety.
Results
The initial and best overall response rates at 4 weeks and 3 months, respectively, were 14 and 17 % based on RECIST, and 57 and 23 % based on mRECIST. The median overall and progression-free survival times were 18 and 4 months, respectively. The most frequent grade-3 or grade-4 adverse events were elevation of serum alanine (23 %) and aspartate aminotransferase (20 %), and thrombocytopenia (17 %).
Conclusion
This HAIC provides promising therapeutic effects with acceptable safety to patients with intermediate-stage and advanced-stage HCCs.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM et al (2011) Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 61:69–90
El-Serag HB (2012) Epidemiology of viral hepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 142:1264–1273
Bruix J, Boix L, Sala M et al (2004) Focus on hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell 5:215–219
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V et al (2008) SHARP Investigators Study Group. Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients in the Asia–Pacific region with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase III randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. N Engl J Med 359:378–390
Cheng AL, Kang YK, Chen Z et al (2009) Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients in the Asia–Pacific region with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase III randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 10:25–34
Kudo M, Izumi N, Kokudo N et al (2011) HCC Expert Panel of Japan Society of Hepatology. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma in Japan: Consensus-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines proposed by the Japan Society of Hepatology (JSH) 2010 updated version. Dig Dis 29:339–364
Yamashita T, Kaneko S (2013) Treatment strategies for hepatocellular carcinoma in Japan. Hepatol Res 43:44–50
Chung YH, Song IH, Song BC et al (2000) Combined therapy consisting of intraarterial cisplatin infusion and systemic interferon-alpha for hepatocellular carcinoma patients with major portal vein thrombosis or distant metastasis. Cancer 88:1986–1991
Ikeda M, Okusaka T, Ueno H et al (2007) Hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy with epirubicin in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma and portal vein tumor thrombosis. Oncology 72:188–193
Kim BK, Park JY, Choi HJ et al (2011) Long-term clinical outcomes of hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy with cisplatin with or without 5-fluorouracil in locally advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 137:659–667
Yoshikawa M, Saisho H, Ebara M et al (1994) A randomized trial of intrahepatic arterial infusion of 4′-epidoxorubicin with Lipiodol versus 4′-epidoxorubicin alone in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 33:S149–S152
Yoshikawa M, Ono N, Yodono H et al (2008) Phase II study of hepatic arterial infusion of a fine-powder formulation of cisplatin for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Res 38:474–483
Beppu T, Sugimoto K, Shiraki K et al (2012) Clinical utility of transarterial infusion chemotherapy using cisplatin–lipiodol emulsion for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Anticancer Res 32:4923–4930
Ikeda M, Maeda S, Ashihara H et al (2010) Transcatheter arterial infusion chemotherapy with cisplatin–lipiodol suspension in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol 45:60–67
Yamashita Y, Taketomi A, Itoh S et al (2010) Phase I/II study of the lipiodolization using DDP-H (CDDP powder; IA-call(®)) in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 65:301–307
Oken MM, Creech RH, Tormey DC et al (1982) Toxicity and response criteria of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. Am J Clin Oncol 5:649–655
Tublin ME, Dodd GD III, Baron RL (1997) Benign and malignant portal vein thrombosis: differentiation by CT characteristics. Am J Roentgenol 168:719–723
Takaki Y, Kaminou T, Shabana M et al (2008) Suitable blending method of lipiodol–cisplatin in transcatheter arterial embolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: evaluation of sustained release and accumulation nature. Hepatogastroenterology 55:202–206
Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA et al (2000) New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer, National Cancer Institute of the United States, National Cancer Institute of Canada. J Natl Cancer Inst 92:205–216
Lencioni R, Llovet JM (2010) Modified RECIST (mRECIST) assessment for hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Liver Dis 30:52–60
U.S. Department of Health and Human Service (2008) Common terminology criteria for adverse events (CTCAE). http://www.eortc.be/services/doc/ctc/CTCAE_4.03_2010-06-14_QuickReference_5x7.pdf#search=‘CTCAE+v4’. Accessed Nov 2013
Iwasa S, Ikeda M, Okusaka T et al (2010) Transcatheter arterial infusion chemotherapy with a fine-powder formulation of cisplatin for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma refractory to transcatheter arterial chemoembolization. Jpn J Clin Oncol 41:770–775
Kondo M, Morimoto M, Numata K et al (2011) Hepatic arterial infusion therapy with a fine powder formulation of cisplatin for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis. Jpn J Clin Oncol 41:69–75
Ikeda M, Okusaka T, Furuse J et al (2013) A multi-institutional phase II trial of hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy with cisplatin for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 72:463–470
Ikeda M, Mitsunaga S, Shimizu S et al (2014) Efficacy of sorafenib in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma refractory to transcatheter arterial chemoembolization. J Gastroenterol 49:932–940
Takayasu K, Shima Y, Muramatsu Y et al (1987) Hepatocellular carcinoma: treatment with intraarterial iodized oil with and without chemotherapeutic agents. Radiology 163:345–351
Heresbach D, Raoul JL, Bentue-Ferrer D et al (1989) Chemotherapy combined with Lipiodol. In vitro study of the kinetics of release of adriamycin. Gastroenterol Clin Biol 13:775–778
Nakamura H, Hashimoto T, Oi H et al (1989) Transcatheter oily chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma. Radiology 170:783–786
Hu HT, Kim JH, Lee LS et al (2011) Chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: multivariate analysis of predicting factors for tumor response and survival in a 362-patient cohort. J Vasc Interv Radiol 22:917–923
Tsai Y-J, Hsu C-Y, Huang Y-H et al (2011) Early identification of poor responders to transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Int 5:975–984
Peng SY, Chen WJ, Lai PL et al (2004) High alpha-fetoprotein level correlates with high stage, early recurrence and poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: significance of hepatitis virus infection, age, p53 and beta-catenin mutations. Int J Cancer 112:44–50
Gramenzi A, Golfieri R, Mosconi C et al (2014) Yttrium-90 radioembolization vs sorafenib for intermediate-locally advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a cohort study with propensity score analysis. Liver Int. doi:10.1111/liv.12574
Mazzaferro V, Sposito C, Bhoori S et al (2013) Yttrium-90 radioembolization for intermediate–advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase 2 study. Hepatology 57:1826–1837
Hilgard P, Hamami M, Fouly AE et al (2010) Radioembolization with yttrium-90 glass microspheres in hepatocellular carcinoma: European experience on safety and long-term survival. Hepatology 52:1741–1749
Edeline J, Lenoir L, Boudjema K et al (2013) Volumetric changes after (90)y radioembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: an option to portal vein embolization in a preoperative setting? Ann Surg Oncol 20:2518–2525
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number 23591816. We thank the members of Institute of Human Research Promotion and Drug Development (Dr. Masakatsu Nishikawa, Dr. Satoshi Tamaru, and Dr. Tomomi Yamada) for their support with the data management and advice related to statistical methods. We also thank the members of the study committee for safety and efficacy monitoring (Dr. Shigeaki Narimatsu and Dr. Tsuneo Ishiguchi) and the members of the committee for efficacy evaluation (Dr. Hiroshi Kondo, Dr. Yozo Sato, and Dr. Hideyuki Nishiofuku).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
On behalf of the Clinical Research Group of the Japanese Society for Transcatheter Hepatic Arterial Embolization.
About this article
Cite this article
Takaki, H., Yamakado, K., Tsurusaki, M. et al. Hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy with fine-powder cisplatin and iodized-oil suspension in patients with intermediate-stage and advanced-stage (Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage-B or stage-C) hepatocellular carcinoma: multicenter phase-II clinical study. Int J Clin Oncol 20, 745–754 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-014-0773-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-014-0773-4