Abstract
Background
This study was conducted to determine the timing and characteristics of radiation pneumonitis (RP) associated with stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) for stage I lung cancer.
Methods
Two hundred thirty-one patients treated with SBRT using 52 Gy in 4 fractions were identified. Control rate, RP incidence rate, and predictive factors and timing of RP were evaluated retrospectively.
Results
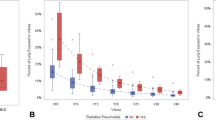
The 3-year overall survival and local control rates were 80.7 and 92.0 %, respectively. The grade ≥2 RP rate was 13.0 %; no grade 4–5 RP occurred. The most statistically significant predictive factor of grade ≥2 RP was V10. The median intervals to first graphical appearance were 4.2 and 2.5 months for grade 1 and grade 2–3 RP, respectively. Median intervals to maximum radiological density change were 6.0 and 4.6 months for grade 1 and grade 2–3 RP, respectively. A significantly different interval to first graphical appearance between grade 1 and grade 2–3 RP was observed; no significantly different interval to maximum radiological density change was noted.
Conclusions
The first graphical appearance of grade ≥2 RP was earlier than that of grade 1 RP, although the timing of maximum radiological density change was not significantly different.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Onishi H, Araki T (2013) Stereotactic body radiation therapy for stage I non-small-cell lung cancer: a historical overview of clinical studies. Jpn J Clin Oncol 43:345–350
Chi A, Liao Z, Nguyen NP et al (2010) Systemic review of the patterns of failure following stereotactic body radiation therapy in early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer: clinical implications. Radiother Oncol 94:1–11
Simone CB 2nd, Wildt B, Haas AR et al (2013) Stereotactic body radiation therapy for lung cancer. Chest 143:1784–1790
Linda A, Trovo M, Bradley JD (2011) Radiation injury of the lung after stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) for lung cancer: a timeline and pattern of CT changes. Eur J Radiol 79:147–154
Baker R, Han G, Sarangkasiri S et al (2013) Clinical and dosimetric predictors of radiation pneumonitis in a large series of patients treated with stereotactic body radiation therapy to the lung. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 85:190–195
Barriger RB, Forquer JA, Brabham JG et al (2012) A dose-volume analysis of radiation pneumonitis in non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with stereotactic body radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 82:457–462
Liu H, Zhang X, Vinogradskiy YY et al (2012) Predicting radiation pneumonitis after stereotactic ablative radiation therapy in patients previously treated with conventional thoracic radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 84:1017–1023
Takeda A, Ohashi T, Kunieda E et al (2010) Early graphical appearance of radiation pneumonitis correlates with the severity of radiation pneumonitis after stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) in patients with lung tumors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 77:685–690
Trovo M, Linda A, El Naqa I et al (2010) Early and late lung radiographic injury following stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT). Lung Cancer 69:77–85
Guckenberger M, Baier K, Polat B et al (2010) Dose-response relationship for radiation-induced pneumonitis after pulmonary stereotactic body radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol 97:65–70
Matsuo Y, Shibuya K, Nakamura M et al (2012) Dose–volume metrics associated with radiation pneumonitis after stereotactic body radiation therapy for lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 83:e545–e549
Bongers EM, Botticella A, Palma DA et al (2013) Predictive parameters of symptomatic radiation pneumonitis following stereotactic or hypofractionated radiotherapy delivered using volumetric modulated arcs. Radiother Oncol 109:95–99
Yamashita H, Kobayashi-Shibata S, Terahara A et al (2010) Prescreening based on the presence of CT-scan abnormalities and biomarkers (KL-6 and SP-D) may reduce severe radiation pneumonitis after stereotactic radiotherapy. Radiat Oncol 5:32
Chang JY, Liu H, Balter P et al (2012) Clinical outcome and predictors of survival and pneumonitis after stereotactic ablative radiotherapy for stage I non-small cell lung cancer. Radiat Oncol 7:152
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Kanemoto, A., Matsumoto, Y. & Sugita, T. Timing and characteristics of radiation pneumonitis after stereotactic body radiotherapy for peripherally located stage I lung cancer. Int J Clin Oncol 20, 680–685 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-014-0766-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-014-0766-3