Abstract
Background
Stereotactic radiosurgery is the preferred option for treating brain arteriovenous malformation (AVM) when the risks associated with surgery outweigh the potential benefits. However, some patients require repeat radiosurgery due to residual AVM after the first procedure. This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to investigate the safety and efficacy of repeated procedure of radiosurgery for AVM.
Method
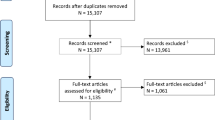
A systematic review was conducted according to the PRISMA guideline. The search was conducted on PubMed, Scopus, Embase, and Web of Science, using a pre-designed search string. Studies investigating the efficacy of repeat radiosurgery for residual AVM following initial single session radiosurgery were included. The risk of bias was assessed using the JBI tool. Meta-analysis and met-regression were performed to pool and inspect data.
Results
Our meta-analysis, with a mean follow-up of 45.57 months, reveals repeat radiosurgery as a viable option for arteriovenous malformations (AVMs), achieving a 60.82% obliteration rate with a mean time to obliteration of 33.18 months. Meta-regression identifies AVM volume and Spetzler-Martin (SM) grade as factors influencing obliteration, with smaller volume and lower SM grades associated with higher rates. Complications include 10.33% radiation-induced changes, 5.26% post-radiosurgery hemorrhage, 2.56% neurologic deficits, and 0.67% cyst formation. Heterogeneity in complications is primarily attributed to male proportion and SM grade, while factors influencing post-radiosurgery hemorrhage remain unclear. The type of radiosurgery, whether Gamma Knife Radiosurgery (GKRS) or LINAC, does not significantly impact outcomes.
Conclusion
Repeat radiosurgery is a feasible, effective, and safe treatment for AVMs following failure of initial radiosurgery. When utilized in appropriate patient subgroups, it provides an acceptable risk-to-benefit profile. Feature studies are required to clarify its clear indications.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Al-Shahi R, Warlow C (2001) A systematic review of the frequency and prognosis of arteriovenous malformations of the brain in adults. Brain 124(Pt 10):1900–1926
Batjer HH, Devous MD, Sr., Meyer YJ, Purdy PD, Samson DS (1988) Cerebrovascular hemodynamics in arteriovenous malformation complicated by normal perfusion pressure breakthrough. Neurosurgery 22(3):503–509
Hoh BL, Chapman PH, Loeffler JS, Carter BS, Ogilvy CS (2002) Results of multimodality treatment for 141 patients with brain arteriovenous malformations and seizures: factors associated with seizure incidence and seizure outcomes. Neurosurgery. 51(2):303-9; discussion 9–11
Graf CJ, Perret GE, Torner JC (1983) Bleeding from cerebral arteriovenous malformations as part of their natural history. J Neurosurg 58(3):331–337
Ondra SL, Troupp H, George ED, Schwab K (1990) The natural history of symptomatic arteriovenous malformations of the brain: a 24-year follow-up assessment. J Neurosurg 73(3):387–391
da Costa L, Wallace MC, Ter Brugge KG, O’Kelly C, Willinsky RA, Tymianski M (2009) The natural history and predictive features of hemorrhage from brain arteriovenous malformations. Stroke 40(1):100–105
Fiehler J, Stapf C (2008) ARUBA–beating natural history in unruptured brain AVMs by intervention. Neuroradiology 50(6):465–467
Rutledge WC, Abla AA, Nelson J, Halbach VV, Kim H, Lawton MT (2014) Treatment and outcomes of ARUBA-eligible patients with unruptured brain arteriovenous malformations at a single institution. Neurosurg Focus 37(3):E8
Cushing H (1928) Tumors arising from the blood vessels of the brain: angiomatous malformations and hemangiobalstomas. Springfiield IL
Ding D, Xu Z, Yen CP, Starke RM, Sheehan JP (2015) Radiosurgery for Cerebral Arteriovenous malformations in Elderly patients: Effect of Advanced Age on outcomes after intervention. World Neurosurg 84(3):795–804
Heros RC, Korosue K, Diebold PM (1990) Surgical excision of cerebral arteriovenous malformations: late results. Neurosurgery 26(4):570–577 discussion 7–8
Lawton MT, Kim H, McCulloch CE, Mikhak B, Young WL (2010) A supplementary grading scale for selecting patients with brain arteriovenous malformations for surgery. Neurosurgery 66(4):702–713 discussion 13
Spetzler RF, Martin NA (2008) A proposed grading system for arteriovenous malformations. 1986. J Neurosurg 108(1):186–193
Ohadi MAD, Iranmehr A, Chavoshi M, Fatollahi MA, Aleyasin MS, Hadjipanayis CG (2023) Stereotactic radiosurgery outcome for deep-seated cerebral arteriovenous malformations in the brainstem and thalamus/basal ganglia: systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosurg Rev 46(1):148
Ding D, Yen CP, Starke RM, Xu Z, Sun X, Sheehan JP (2014) Radiosurgery for Spetzler-Martin Grade III arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 120(4):959–969
Ding D, Yen CP, Xu Z, Starke RM, Sheehan JP (2013) Radiosurgery for primary motor and sensory cortex arteriovenous malformations: outcomes and the effect of eloquent location. Neurosurgery 73(5):816–824 discussio 24
Ding D, Yen CP, Starke RM, Xu Z, Sun X, Sheehan JP (2014) Outcomes following single-session radiosurgery for high-grade intracranial arteriovenous malformations. Br J Neurosurg 28(5):666–674
Kano H, Kondziolka D, Flickinger JC, Park KJ, Parry PV, Yang HC et al (2012) Stereotactic radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations, part 6: multistaged volumetric management of large arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 116(1):54–65
Moosa S, Chen CJ, Ding D, Lee CC, Chivukula S, Starke RM et al (2014) Volume-staged versus dose-staged radiosurgery outcomes for large intracranial arteriovenous malformations. Neurosurg Focus 37(3):E18
Kano H, Kondziolka D, Flickinger JC, Yang HC, Flannery TJ, Awan NR et al (2012) Stereotactic radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations, part 3: outcome predictors and risks after repeat radiosurgery. J Neurosurg 116(1):21–32
Yen CP, Jain S, Haq IU, Jagannathan J, Schlesinger D, Sheehan J et al (2010) Repeat γ knife surgery for incompletely obliterated cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Neurosurgery 67(1):55–64 discussion
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD et al (2021) The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 372:n71
Hozo SP, Djulbegovic B, Hozo I (2005) Estimating the mean and variance from the median, range, and the size of a sample. BMC Med Res Methodol 5(1):13
Foote KD, Friedman WA, Ellis TL, Bova FJ, Buatti JM, Meeks SL (2003) Salvage retreatment after failure of radiosurgery in patients with arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 98(2):337–341
Hak JF, Borius PY, Spatola G, Chopinet S, Testud B, Girard N et al (2022) Upfront and repeated Gamma-Knife Radiosurgery for Small (≤ 5 mL) unruptured brain arteriovenous malformation: a cohort of 249 consecutive patients. World Neurosurg 158:e889–e95
Hauswald H, Milker-Zabel S, Sterzing F, Schlegel W, Debus J, Zabel-du Bois A (2011) Repeated linac-based radiosurgery in high-grade cerebral arteriovenous-malformations (AVM) Spetzler-Martin grade III to IV previously treated with radiosurgery. Radiotherapy Oncology: J Eur Soc Therapeutic Radiol Oncol 98(2):217–222
Karlsson B, Jokura H, Yamamoto M, Söderman M, Lax I (2007) Is repeated radiosurgery an alternative to staged radiosurgery for very large brain arteriovenous malformations? J Neurosurg 107(4):740–744
Mantziaris G, Pikis S, Dumot C, Dayawansa S, Liščák R, May J et al (2023) Outcome evaluation of repeat stereotactic radiosurgery for cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Stroke 54(8):1974–1984
Mirza-Aghazadeh J, Andrade-Souza YM, Zadeh G, Scora D, Tsao MN, Schwartz ML (2006) Radiosurgical retreatment for brain arteriovenous malformation. Can J Neurol Sci Le J Canadien des Sci Neurologiques 33(2):189–194
Raza SM, Jabbour S, Thai QA, Pradilla G, Kleinberg LR, Wharam M et al (2007) Repeat stereotactic radiosurgery for high-grade and large intracranial arteriovenous malformations. Surg Neurol 68(1):24–34 discussion
Sasagasako T, Mori H, Hattori EY, Ikedo T, Hamano E, Shimonaga K et al (2023) Radiation-Induced Changes Associated with Obliteration of Brain AVMs after repeat Radiosurgery. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 44(2):143–149
Schlienger M, Nataf F, Lefkopoulos D, Mammar H, Missir O, Meder JF et al (2003) Repeat linear accelerator radiosurgery for cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 56(2):529–536
Stahl JM, Chi YY, Friedman WA (2012) Repeat radiosurgery for intracranial arteriovenous malformations. Neurosurgery 70(1):150–154 discussion 4
Karlsson B, Kihlström L, Lindquist C, Steiner L (1998) Gamma knife surgery for previously irradiated arteriovenous malformations. Neurosurgery 42(1):1–5 discussion – 6
Pollock BE, Flickinger JC, Lunsford LD, Maitz A, Kondziolka D (1998) Factors associated with successful arteriovenous malformation radiosurgery. Neurosurgery 42(6):1239–1244 discussion 44 – 7
Jokura H, Kawagishi J, Sugai K, Akabane A, Boku N, Takahashi K (2009) Gamma knife radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations: the Furukawa experience. Prog Neurol Surg 22:20–30
Nagy G, Major O, Rowe JG, Radatz MW, Hodgson TJ, Coley SC et al (2012) Stereotactic radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations located in deep critical regions. Neurosurgery. 70(6):1458-69; discussion 69–71
Buis DR, Meijer OW, van den Berg R, Lagerwaard FJ, Bot JC, Slotman BJ et al (2010) Clinical outcome after repeated radiosurgery for brain arteriovenous malformations. Radiotherapy Oncology: J Eur Soc Therapeutic Radiol Oncol 95(2):250–256
Flores GL, Sallabanda K, dos Santos MA, Gutiérrez J, Salcedo JC, Beltrán C et al (2011) Linac stereotactic radiosurgery for the treatment of small arteriovenous malformations: lower doses can be equally effective. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 89(6):338–345
Pollock BE, Gorman DA, Coffey RJ (2003) Patient outcomes after arteriovenous malformation radiosurgical management: results based on a 5- to 14-year follow-up study. Neurosurgery 52(6):1291–1296 discussion 6–7
China M, Vastani A, Hill CS, Tancu C, Grover PJ (2022) Gamma Knife radiosurgery for cerebral arteriovenous malformations: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosurg Rev 45(3):1987–2004
Starke RM, Komotar RJ, Hwang BY, Fischer LE, Otten ML, Merkow MB et al (2008) A comprehensive review of radiosurgery for cerebral arteriovenous malformations: outcomes, predictive factors, and grading scales. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 86(3):191–199
Lenck S, Schwartz M, Hengwei J, Agid R, Nicholson P, Krings T et al (2018) Management of residual brain arteriovenous malformations after stereotactic radiosurgery. World Neurosurg 116:e1105–e13
Steiner L, Leksell L, Forster DM, Greitz T, Backlund EO Stereotactic radiosurgery in intracranial arterio-venous malformations. Acta Neurochir 1974;Suppl 21:195–209
Kwon Y, Jeon SR, Kim JH, Lee JK, Ra DS, Lee DJ et al (2000) Analysis of the causes of treatment failure in gamma knife radiosurgery for intracranial arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 93(Suppl 3):104–106
Ding D, Xu Z, Shih HH, Starke RM, Yen CP, Cohen-Inbar O et al (2016) Worse outcomes after repeat vs initial stereotactic radiosurgery for cerebral arteriovenous malformations: a retrospective matched-cohort study. Neurosurgery 79(5):690–700
El Ouadih Y, Lemaire JJ, Vigier B, Gabrillargues J, Mulliez A, Dedieu V et al (2020) Patterns of failure after Linear Accelerator Radiosurgery for cerebral arteriovenous malformations. World Neurosurg 136:e141–e8
Flickinger JC, Pollock BE, Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD (1996) A dose-response analysis of arteriovenous malformation obliteration after radiosurgery. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 36(4):873–879
Flickinger JC, Kondziolka D, Maitz AH, Lunsford LD (2002) An analysis of the dose-response for arteriovenous malformation radiosurgery and other factors affecting obliteration. Radiotherapy Oncology: J Eur Soc Therapeutic Radiol Oncol 63(3):347–354
Pollock BE, Kline RW, Stafford SL, Foote RL, Schomberg PJ (2000) The rationale and technique of staged-volume arteriovenous malformation radiosurgery. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 48(3):817–824
Ilyas A, Chen CJ, Ding D, Taylor DG, Moosa S, Lee CC et al (2018) Volume-staged versus dose-staged stereotactic radiosurgery outcomes for large brain arteriovenous malformations: a systematic review. J Neurosurg 128(1):154–164
Awad AJ, Walcott BP, Stapleton CJ, Ding D, Leed CC, Loeffler JS (2015) Repeat radiosurgery for cerebral arteriovenous malformations. J Clin Neuroscience: Official J Neurosurgical Soc Australasia 22(6):945–950
Mantziaris G, Pikis S, Dumot C, Dayawansa S, Liscak R, May J et al (2023) Effect of cerebral arteriovenous malformation location on outcomes of repeat, single-fraction stereotactic radiosurgery: a matched-cohort analysis. J Neurosurg. 1–9
Maroufi SF, Fallahi MS, Khorasanizadeh M, Waqas M, Sheehan JP (2023) Radiosurgery with prior embolization Versus Radiosurgery alone for intracranial arteriovenous malformations: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Neurosurgery
Hattangadi-Gluth JA, Chapman PH, Kim D, Niemierko A, Bussière MR, Stringham A et al (2014) Single-fraction proton beam stereotactic radiosurgery for cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 89(2):338–346
Ilyas A, Chen CJ, Ding D, Buell TJ, Raper DMS, Lee CC et al (2018) Radiation-Induced Changes after Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Brain Arteriovenous malformations: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Neurosurgery 83(3):365–376
Maesawa S, Flickinger JC, Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD (2000) Repeated radiosurgery for incompletely obliterated arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 92(6):961–970
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AI, JPS, SFM: Study conception and design; MAH, SFM, MSM: Writing the primary draft; AM, NP, MM, MAH: Data gathering; SFM: Statistical analysis; JPS and AI: Review and revised the manuscript; AI: Supervision; All authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Maroufi, S.F., Habibi, M.A., Mirjani, M.S. et al. Repeat single-session stereotactic radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosurg Rev 47, 203 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-024-02438-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-024-02438-5