Abstract
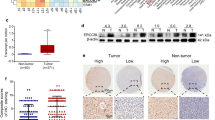
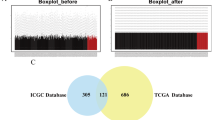
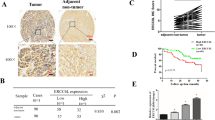
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a malignant tumor with high incidence worldwide. The underlying mechanisms remain poorly understood. The DNA metabolic process of homologous recombination repair (HRR) has been linked to a high probability of tumorigenesis and drug resistance. This study aimed to determine the role of HRR in HCC and identify critical HRR-related genes that affect tumorigenesis and prognosis. A total of 613 tumor and 252 para-carcinoma tissue samples were collected from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and the International Cancer Genome Consortium (ICGC) to obtain differentially expressed genes (DEGs). HRR-related genes were assessed using gene enrichment and pathway analyses. Survival analysis was performed using the Kaplan–Meier method in the Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis portal. The levels of RAD54L in the HRR pathway were detected by RT-qPCR and western blotting in para-carcinoma and HCC tissues and in L02 normal human liver cells and Huh7 HCC cells. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) was performed on the clinical specimens to determine the connection between gene expression and clinical features. Bioinformatics analysis revealed that the HRR pathway was enriched in HCC tissues. Upregulation of HRR pathway DEGs in HCC tissues was positively correlated with tumor pathological staging and negatively associated with patient overall survival. RAD54B, RAD54L, and EME1 genes in the HRR pathway were screened as markers for predicting HCC prognosis. RT-qPCR identified RAD54L as the most significantly expressed of the three genes. Western blotting and IHC quantitative analyses further demonstrated that RAD54L protein levels were higher in HCC tissues. IHC analysis of 39 pairs of HCC and para-carcinoma tissue samples also revealed an association between RAD54L and Edmondson-Steiner grade and the proliferation-related gene Ki67. The collective findings positively correlate RAD54L in the HRR signaling pathway with HCC staging and implicate RAD54L as a marker to predict HCC progression.







Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
13 May 2024
This article has been retracted. Please see the Retraction Notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-024-01365-4
References
Bruix J, Qin S, Merle P et al (2017) Regorafenib for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma who progressed on sorafenib treatment (RESORCE): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 389:56–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)32453-9
Choi E-H, Yoon S, Hahn Y, Kim KP (2017) Cellular dynamics of Rad51 and Rad54 in response to postreplicative stress and DNA damage in HeLa cells. Mol Cells 40:143–150. https://doi.org/10.14348/molcells.2017.2275
Curtin NJ (2012) DNA repair dysregulation from cancer driver to therapeutic target. Nat Rev Cancer 12:801–817. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc3399
De Zio D, Cianfanelli V, Cecconi F (2013) New insights into the link between DNA damage and apoptosis. Antioxid Redox Signal 19:559–571. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2012.4938
Feng S, Liu J, Hailiang L et al (2021) Amplification of RAD54B promotes progression of hepatocellular carcinoma via activating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Transl Oncol 14:101124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tranon.2021.101124
Gao B, Wang Y, Lu S (2022) Construction and validation of a novel signature based on epithelial-mesenchymal transition-related genes to predict prognosis and immunotherapy response in hepatocellular carcinoma by comprehensive analysis of the tumor microenvironment. Funct Integr Genomics 23:6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-022-00933-w
Gorbalenya AE, Koonin EV (1993) Helicases: amino acid sequence comparisons and structure-function relationships. Curr Opin Struct Biol 3:419–429. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0959-440X(05)80116-2
Heyer W-D, Li X, Rolfsmeier M, Zhang X-P (2006) Rad54: the Swiss Army knife of homologous recombination? Nucleic Acids Res 34:4115–4125. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkl481
Jepsen P, West J (2021) We need stronger evidence for (or against) hepatocellular carcinoma surveillance. J Hepatol 74:1234–1239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2020.12.029
Jiang M, Jia K, Wang L et al (2021) Alterations of DNA damage response pathway: biomarker and therapeutic strategy for cancer immunotherapy. Acta Pharm Sin B 11:2983–2994. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2021.01.003
Launonen I-M, Lyytikäinen N, Casado J et al (2022) Single-cell tumor-immune microenvironment of BRCA1/2 mutated high-grade serous ovarian cancer. Nat Commun 13:835. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-28389-3
Li P, Chen C, Li J et al (2022) Homologous recombination related signatures predict prognosis and immunotherapy response in metastatic urothelial carcinoma. Front Genet 13:875128. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2022.875128
Li P, Xu Y, Zhang Q et al (2019) Evaluating the role of RAD52 and its interactors as novel potential molecular targets for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell Int 19:279. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-019-0996-6
Long Y, Lv Z, Wang S et al (2023) Comparison of preoperative ultrasound and MRI in the diagnosis of microvascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma. Funct Integr Genomics 23:100. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-01006-2
Luo X-Y, Wu K-M, He X-X (2021) Advances in drug development for hepatocellular carcinoma: clinical trials and potential therapeutic targets. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 40:172. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-021-01968-w
Marnef A, Legube G (2021) R-loops as Janus-faced modulators of DNA repair. Nat Cell Biol 23:305–313. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-021-00663-4
Mason JM, Dusad K, Wright WD et al (2015) RAD54 family translocases counter genotoxic effects of RAD51 in human tumor cells. Nucleic Acids Res 43:3180–3196. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv175
Moon AM, Singal AG, Tapper EB (2020) Contemporary epidemiology of chronic liver disease and cirrhosis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 18:2650–2666. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2019.07.060
Nguyen L, WM Martens J, Van Hoeck A, Cuppen E (2020) Pan-cancer landscape of homologous recombination deficiency. Nat Commun 11:5584. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-19406-4
Nicoletto MO, Donach M, De Nicolo A et al (2001) BRCA-1 and BRCA-2 mutations as prognostic factors in clinical practice and genetic counselling. Cancer Treat Rev 27:295–304. https://doi.org/10.1053/ctrv.2001.0233
Richardson C, Stark JM, Ommundsen M, Jasin M (2004) Rad51 overexpression promotes alternative double-strand break repair pathways and genome instability. Oncogene 23:546–553. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207098
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D et al (2015) limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res 43:e47–e47. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv007
Roos WP, Thomas AD, Kaina B (2016) DNA damage and the balance between survival and death in cancer biology. Nat Rev Cancer 16:20–33. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc.2015.2
Royfman R, Whiteley E, Noe O et al (2021) BRCA1/2 signaling and homologous recombination deficiency in breast and ovarian cancer. Future Oncol 17:2817–2830. https://doi.org/10.2217/fon-2021-0072
Sharma M, Anand P, Padwad YS et al (2022) DNA damage response proteins synergistically affect the cancer prognosis and resistance. Free Radic Biol Med 178:174–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.11.033
Slade D (2020) PARP and PARG inhibitors in cancer treatment. Genes Dev 34:360–394. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.334516.119
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK et al (2005) Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:15545–15550. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0506580102
Tang Z, Li C, Kang B et al (2017) GEPIA: a web server for cancer and normal gene expression profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res 45:W98–W102. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx247
Toh M, Ngeow J (2021) Homologous recombination deficiency: cancer predispositions and treatment implications. Oncologist 26:e1526–e1537. https://doi.org/10.1002/onco.13829
Tutt ANJ, Garber JE, Kaufman B et al (2021) Adjuvant olaparib for patients with BRCA1 - or BRCA2 -mutated breast cancer. N Engl J Med 384:2394–2405. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2105215
Ui A, Chiba N, Yasui A (2020) Relationship among DNA double-strand break (DSB), DSB repair, and transcription prevents genome instability and cancer. Cancer Sci 111:1443–1451. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.14404
Unlu S, Kim JW (2022) Emerging role of PARP inhibitors in metastatic prostate cancer. Curr Oncol Rep. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11912-022-01305-0
Vogel A, Meyer T, Sapisochin G et al (2022) Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet 400:1345–1362. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01200-4
Wagener-Ryczek S, Merkelbach-Bruse S, Siemanowski J (2021) Biomarkers for homologous recombination deficiency in cancer. JPM 11:612. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11070612
Wang J, Lou Y, Lu J et al (2021) A deep look into the program of rapid tumor growth of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Transl Hepatol 9:22–31. https://doi.org/10.14218/JCTH.2020.00084
Waterman DP, Haber JE, Smolka MB (2020) Checkpoint responses to DNA double-strand breaks. Annu Rev Biochem 89:103–133. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-biochem-011520-104722
Xu H, Xiong C, Chen Y et al (2021) Identification of Rad51 as a prognostic biomarker correlated with immune infiltration in hepatocellular carcinoma. Bioengineered 12:2664–2675. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2021.1938470
Xue L, Liu J, Xie J, Luo J (2021) Prognostic value of SLC16A3(MCT4) in lung adenocarcinoma and its clinical significance. Int J Gen Med 14:8413–8425. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJGM.S337615
Yang X-D, Kong F-E, Qi L et al (2021) PARP inhibitor Olaparib overcomes Sorafenib resistance through reshaping the pluripotent transcriptome in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer 20:20. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-021-01315-9
Zhang Z, Fan H-Y, Goldman JA, Kingston RE (2007) Homology-driven chromatin remodeling by human RAD54. Nat Struct Mol Biol 14:397–405. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb1223
Zhou Q, Huang J, Zhang C et al (2020) The bromodomain containing protein BRD-9 orchestrates RAD51–RAD54 complex formation and regulates homologous recombination-mediated repair. Nat Commun 11:2639. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-16443-x
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the Central Laboratory of the Affiliated Hospital of Jiangsu University for providing the experimental facilities.
Funding
The study was funded by the Excellent Talents Fund of Xuzhou Medical University (No. XYFY202244) and the Doctoral Initiation Fund of Affiliated Hospital of Jiangsu University (jdfyRC2021009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Qing Zhou designed the study. Hongda Li wrote the manuscript. Hongda Li and Haiwen Zhuang completed the experiment. Tengfei Gu collected data. Guangyu Li and Yuhang Jiang analyzed the data. Qing Zhou and Sanrong Xu revised the manuscript. Sanrong Xu and Haiwen Zhuang provided funding for the study. All authors approved the final version for submission. Hongda Li and Haiwen Zhuang contributed to the work equally and should be regarded as co-first authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Affiliated Hospital of Jiangsu University and the ethical approval number is KY2022K0912. All patients provided written informed consent to participate in the study. Written informed consent was obtained from each individual(s) for the publication of potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article has been retracted. Please see the retraction notice for more detail:https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-024-01365-4
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Zhuang, H., Gu, T. et al. RETRACTED ARTICLE: RAD54L promotes progression of hepatocellular carcinoma via the homologous recombination repair pathway. Funct Integr Genomics 23, 128 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-01060-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-01060-w