Abstract
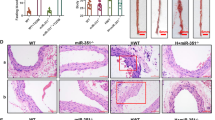
Atherosclerosis (AS) is the main cause of cardiovascular diseases. However, the role of AQP9 in AS is not well understood. In the present study, we predicted that miR-330-3p might regulate AQP9 in AS through bioinformatics analysis, and we established AS model using ApoE−/− mouse (C57BL/6) with high-fat diet (HFD). Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and Oil red O staining were used to determine atherosclerotic lesions. CCK8 and Ethyny1-2-deoxyuridine (EdU) assays were used to investigate human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) proliferation after treatment with 100 μg/mL ox-LDL. Wound scratch healing and transwell assays were used to measure the cell invasion and migration ability. Flow cytometry assay was used to determine apoptosis and cell cycle. A dual-luciferase reporter assay was performed to investigate the binding of miR-330-3p and AQP9. We identified that the expression of miR-330-3p in AS mice model decreased while the expression level of AQP9 increased. miR-330-3p overexpression or down-regulation of AQP9 could reduce cell apoptosis, promote cell proliferation, and migration after ox-LDL treatment. Dual-luciferase reporter assay result presented that AQP9 was directly inhibited by miR-330-3p. These results suggest that miR-330-3p inhibits AS by regulating AQP9. miR-330-3p/AQP9 axis may be a new therapeutic target for AS.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The dataset used and/or analyzed in this study is available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Cai C, Wang C, Ji W et al (2013) Knockdown of hepatic aquaglyceroporin-9 alleviates high fat diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in rats. Int Immunopharmacol 15:550–556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2013.01.020
Chen T, Yang Z, Liu C et al (2019) Circ_0078767 suppresses non-small-cell lung cancer by protecting RASSF1A expression via sponging miR-330–3p. Cell proliferation 52:e12548. https://doi.org/10.1111/cpr.12548
Cheng Y, Zhu H, Gao W (2020) MicroRNA-330–3p represses the proliferation and invasion of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma through downregulation of Tra2β-mediated Akt signaling. Mol Cell Probes 52:101574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcp.2020.101574
Fabian MR, Sonenberg N, Filipowicz W (2010) Regulation of mRNA translation and stability by microRNAs. Annu Rev Biochem 79:351–379. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-biochem-060308-103103
Frostegård J (2013) Immunity, atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease. BMC Med 11:117. https://doi.org/10.1186/1741-7015-11-117
Hill M, Tran N (2021) miRNA interplay: mechanisms and consequences in cancer. Disease models & mechanisms 14. https://doi.org/10.1242/dmm.047662
Inouye M, Ripatti S, Kettunen J et al (2012) Novel Loci for metabolic networks and multi-tissue expression studies reveal genes for atherosclerosis. PLoS Genet 8:e1002907. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1002907
Jiang H, Zhang J, Du Y et al (2015) microRNA-185 modulates low density lipoprotein receptor expression as a key posttranscriptional regulator. Atheroscler 243:523–532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2015.10.026
Jing J, Sun J, Wu Y et al (2021) AQP9 Is a prognostic factor for kidney cancer and a promising indicator for M2 TAM polarization and CD8+ T-cell recruitment. Front Oncol 11:770565. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.770565
Lebeck J, Cheema MU, Skowronski MT et al (2015) Hepatic AQP9 expression in male rats is reduced in response to PPARalpha agonist treatment. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 308:G198-205. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpgi.00407.2013
Libby P (2021) The changing landscape of atherosclerosis. Nat 592:524–533. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03392-8
Ren L, Li P, Li Z et al (2022) AQP9 and ZAP70 as immune-related prognostic biomarkers suppress proliferation, migration and invasion of laryngeal cancer cells. BMC Cancer 22:465. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-022-09458-8
Rojek AM, Skowronski MT, Fuchtbauer EM et al (2007) Defective glycerol metabolism in aquaporin 9 (AQP9) knockout mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:3609–3614. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0610894104
Verkerk AO, Lodder EM, Wilders R (2019) Aquaporin channels in the heart-physiology and pathophysiology. International journal of molecular sciences 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20082039
Verkman AS, Matthay MA, Song Y (2000) Aquaporin water channels and lung physiology. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 278:L867-879. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajplung.2000.278.5.L867
Wu J, Wang C, Ding H (2020) LncRNA MALAT1 promotes neuropathic pain progression through the miR1545p/AQP9 axis in CCI rat models. Mol Med Rep 21:291–303. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2019.10829
Xu S, Schlüter PM, Grossniklaus U et al (2012) The genetic basis of pollinator adaptation in a sexually deceptive orchid. PLoS genetics 8:e1002889. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1002889
Yu J, Fan Q, Li L (2021) The MCM3AP-AS1/miR-126/VEGF axis regulates cancer cell invasion and migration in endometrioid carcinoma. World J Surg Oncol 19:213. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12957-021-02316-0
Zhang S, Li L, Chen W et al (2021) Natural products: the role and mechanism in low-density lipoprotein oxidation and atherosclerosis. Phytother Res : PTR 35:2945–2967. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.7002
Zhang B, Lv D, Chen Y et al (2022) Aquaporin-9 facilitates liver regeneration following hepatectomy. Redox biology 50:102246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2022.102246
Zhang Z, Liang K, Zou G, et al. (2018) Inhibition of miR-155 attenuates abdominal aortic aneurysm in mice by regulating macrophage-mediated inflammation. Bioscience reports 38. 10.1042/bsr20171432
Zhou M, Ren P, Zhang Y et al (2019) Shen-Yuan-Dan capsule attenuates atherosclerosis and foam cell formation by enhancing autophagy and inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/mTORC1 signaling pathway. Front Pharmacol 10:603. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2019.00603
Funding
This study was supported by the Scientific Research Project of collages and universities in Anhui Province (2022AH051514).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YG contributed to the conception and design. ES carried out the experiment and wrote the paper. YY, WT, WW, and XW analyzed the data and discusses the result. ES, SZ, and YG revised the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent participate
Approval to obtain experimental tissues from patients with atherosclerosis and normal controls was obtained under informed consent. This study was reviewed and approved by the Ethic Committee of the first clinical college of Jinan University (2020173).
Animal ethics
The study was performed in accordance with the ethical standards as laid down in the Regulations on the Management of Laboratory Animals of China and approved by the ethics committee of the first clinical college of Jinan University.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shan, E., Yu, Y., Tang, W. et al. miR-330-3p alleviates the progression of atherosclerosis by downregulating AQP9. Funct Integr Genomics 23, 77 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-01001-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-01001-7