Abstract
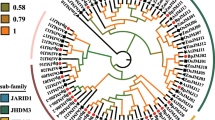
Histone demethylases containing the JmjC domain play an extremely important role in maintaining the homeostasis of histone methylation and are closely related to plant growth and development. Currently, the JmjC domain–containing proteins have been reported in many species; however, they have not been systematically studied in grapes. In this paper, 21 VviJMJ gene family members were identified from the whole grape genome, and the VviJMJ genes were classified into five subfamilies: KDM3, KDM4, KDM5, JMJD6, and JMJ-only based on the phylogenetic relationship and structural features of Arabidopsis and grape. After that, the conserved sites of VviJMJ genes were revealed by protein sequence analysis. In addition, chromosomal localization and gene structure analysis revealed the heterogeneous distribution of VviJMJ genes on grape chromosomes and the structural features of VviJMJ genes, respectively. Analysis of promoter cis-acting elements demonstrated numerous hormone, light, and stress response elements in the promoter region of the VviJMJ genes. Subsequently, the grape fruit was treated with MTA (an H3K4 methylation inhibitor), which significantly resulted in the early ripening of grape fruits. The qRT-PCR analysis showed that VviJMJ genes (except VviJMJ13c) had different expression patterns during grape fruit development. The expression of VviJMJ genes in the treatment group was significantly higher than that in the control group. The results indicate that VviJMJ genes are closely related to grape fruit ripening.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of supporting data
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary material.
References
Allis CD, Jenuwein T (2016) The molecular hallmarks of epigenetic control. Nat Rev Genet 17:487–500. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg.2016.59
Amasino R, Doyle M (2009) A single amino acid change in the enhancer of zeste ortholog CURLY LEAF results in vernalization-independent, rapid flowering in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 151:1688–1697. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.109.145581
Cairns BR (2009) The logic of chromatin architecture and remodelling at promoters. Nature 461:193–198. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08450
Chao X, Min J (2011) Structure and function of WD40 domain proteins. Protein Cell 2:202–214. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13238-011-1018-1
Chen Z, Zang J, Whetstine J, Xia H, Zhang G (2006) Structural insights into histone demethylation by JMJD2 family members. Cell 125:691–702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2006.04.024
Chen C, Chen H, Zhang Y, Thomas HR, Xia R (2020) TBtools: an integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol Plant 13:1194–1202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2020.06.009
Chen B, Ali S, Zhang X, Zhang Y, Wang M, Zhang Q, Xie L (2021) Genome-wide identification, classification, and expression analysis of the JmjC domain-containing histone demethylase gene family in birch. BMC Genomics 22:772. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-021-08063-6
Cheng K, Xu Y, Yang C, Ouellette L, Luo M (2019) Histone tales: lysine methylation, a protagonist in Arabidopsis development. J Exp Bot 71:793–807. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erz435
Ding X, Liu X, Jiang G, Li Z, Song Y, Zhang D, Jiang Y, Duan X (2022) SlJMJ7 orchestrates tomato fruit ripening via crosstalk between H3K4me3 and DML2-mediated DNA demethylation. New Phytol 233:1202–1219. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.17838
Dong Y, Lu J, Liu J, Jalal A, Wang C (2020) Genome-wide identification and functional analysis of JmjC domain-containing genes in flower development of Rosa chinensis. Plant Mol Biol 102:417–430. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-019-00955-2
Grimplet J, Adam-Blondon AF, Bert PF, Bitz O, Cantu D, Davies C, Delrot S, Pezzotti M, Rombauts S, Cramer G (2014) The grapevine gene nomenclature system. BMC Genomics 15:1077. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-15-1077
Gu T, Han Y, Huang R, Mcavoy RJ, Li Y (2016) Identification and characterization of histone lysine methylation modifiers in Fragaria vesca. Sci Rep-Uk 6:23581. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep23581
Guo DL, Xi FF, Yu YH, Zhang XY, Zhang GH, Zhong GY (2016) Comparative RNA-Seq profiling of berry development between table grape ‘Kyoho’ and its early-ripening mutant ‘Fengzao.’ BMC Genomics 17:795. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-016-3051-1
Guo JE, Hu Z, Li F, Zhang L, Yu X, Tang B, Chen G (2017) Silencing of histone deacetylase SlHDT3 delays fruit ripening and suppresses carotenoid accumulation in tomato. Plant Sci 265:29–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2017.09.013
Guo JE, Hu Z, Yu X, Li A, Li F, Wang Y, Tian S, Chen G (2017) A histone deacetylase gene, SlHDA3, acts as a negative regulator of fruit ripening and carotenoid accumulation. Plant Cell Rep 37:125–135. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-017-2211-3
Han Y, Kuang J, Chen J, Liu X, Xiao Y, Fu C, Wang J, Wu K, Lu W (2016a) Banana transcription factor MaERF11 recruits histone deacetylase MaHDA1 and represses the expression of MaACO1 and expansins during fruit ripening. Plant Physiol 171:1070–1084. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.16.00301
Han Y, Li X, Lin C, Liu Y, Wang H, Ke D, Yuan H, Zhang L, Wang L (2016b) Genome-wide analysis of soybean JmjC domain-containing proteins suggests evolutionary conservation following whole-genome duplication. Front Plant Sci 7:1800. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01800
He X, Wang Q, Pan J, Liu B, Huang Y (2021) Systematic analysis of JmjC gene family and stress-response expression of KDM5 subfamily genes in Brassica napus. PeerJ 9:e11137. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.11137
Hu B, Jin J, Guo AY, Zhang H, Luo J, Gao G (2015) GSDS 2.0: an upgraded gene feature visualization server. Bioinformatics 31:1296–1297. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu817
Huang Y, Chen D, Liu C, Shen W, Ying R (2016) Evolution and conservation of JmjC domain proteins in the green lineage. Mol Genet Genomics 291:33–49. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-015-1089-4
Jia HF, Chai YM, Li CL, Lu D, Shen YY (2011) Abscisic acid plays an important role in the regulation of strawberry fruit ripening. Plant Physiol 157:188–199. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.111.177311
Jia H, Jiu S, Zhang C, Wang C, Tariq P, Liu Z, Wang B, Cui L, Fang J (2016) Abscisic acid and sucrose regulate tomato and strawberry fruit ripening through the abscisic acid-stress-ripening transcription factor. Plant Biotechnol J 14:2046–2065. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12563
Klose RJ, Zhang Y (2007) Regulation of histone methylation by demethylimination and demethylation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Bio 8:307–318. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm2143
Lee K, Park O, Seo P (2018) JMJ30-mediated demethylation of H3K9me3 drives tissue identity changes to promote callus formation in Arabidopsis. Plant J 95:961–975. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.14002
Leng P, Bing Y, Guo Y (2014) The role of abscisic acid in fruit ripening and responses to abiotic stress. J Exp Bot 65:4577–4588. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eru204
Li W, Liu H, Cheng ZJ, Su YH, Han HN, Zhang Y, Zhang XS (2011) DNA methylation and histone modifications regulate de novo shoot regeneration in Arabidopsis by modulating WUSCHEL expression and Auxin signaling. Plos Genet 7:e1002243. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1002243
Li Q, Chen P, Dai S, Sun Y, Yuan B, Kai W, Pei Y, He S, Liang B, Zhang Y (2015) PacCYP707A2 negatively regulates cherry fruit ripening while PacCYP707A1 mediates drought tolerance. J Exp Bot 66:3765–3774. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erv169
Li Z, Jiang G, Liu X, Ding X, Duan X (2020) Histone demethylase SlJMJ6 promotes fruit ripening by removing H3K27 methylation of ripening-related genes in tomato. New Phytol 227:1138–1156. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.16590
Lin Z, Hong Y, Yin M, Li C, Ke Z, Grierson D (2010) A tomato HD-Zip homeobox protein, LeHB-1, plays an important role in floral organogenesis and ripening. Plant J 55:301–310. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03505.x
Liu C, Lu F, Cui X, Cao X (2010) Histone methylation in higher plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 61:395. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.043008.091939
Liu C, Cheng J, Zhuang Y, Ye L, Li Z, Wang Y, Qi M, Zhang Y (2018) Polycomb repressive complex 2 attenuates ABA-induced senescence in Arabidopsis. Plant J 97:368–377. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.14125
Lohani S, Trivedi PK, Nath P (2004) Changes in activities of cell wall hydrolases during ethylene-induced ripening in banana: effect of 1-MCP, ABA and IAA. Postharvest Biol Tec 31:119–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2003.08.001
Lu F, Li G, Cui X, Liu C, Wang XJ, Cao X (2008) Comparative analysis of JmjC domain-containing proteins reveals the potential histone demethylases in Arabidopsis and Rice. J Integr Plant Biol 50:886–896. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7909.2008.00692.x
Lu F, Cui X, Zhang S, Liu C, Cao X (2010) JMJ14 is an H3K4 demethylase regulating flowering time in Arabidopsis. Cell Res 20:387–390. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2010.27
Mcatee P, Karim S, Schaffer R, David K (2013) A dynamic interplay between phytohormones is required for fruit development, maturation, and ripening. Front Plant Sci 4:79. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2013.00079
Mellor J (2006) It takes a PHD to read the histone code. Cell 126:22–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2006.06.028
Niu Y, Bai J, Zheng S (2018) The regulation and function of histone methylation. J Plant Biol 61:347–357. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12374-018-0176-6
Noh B, Lee SH, Kim HJ, Yi G, Shin EA, Lee M, Jung KJ, Doyle MR, Amasino RM, Noh YS (2019) Divergent roles of a pair of homologous jumonji/zinc-finger-class transcription factor proteins in the regulation of Arabidopsis flowering time. Plant Cell 16:2601–2613. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.104.025353
Osorio S, Scossa F, Fernie A (2013) Molecular regulation of fruit ripening. Front Plant Sci 4:198. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2013.00198
Qian Y, Chen C, Jiang L, Zhang J, Ren Q (2019) Genome-wide identification, classification and expression analysis of the JmjC domain-containing histone demethylase gene family in maize. BMC Genomics 20:259. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-019-5633-1
Rotili D, Mai A (2011) Targeting histone demethylases: a new avenue for the fight against cancer. Genes Cancer 2:663–679. https://doi.org/10.1177/1947601911417976
Schneider R, Bannister AJ, Myers FA, Thorne AW, Crane-Robinson C, Kouzarides T (2004) Histone H3 lysine 4 methylation patterns in higher eukaryotic genes. Nat Cell Biol 6:73–77. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1076
Shi Y, Fei L, Matson C, Mulligan P, Whetstine JR, Cole PA, Casero RA, Shi Y (2004) Histone demethylation mediated by the nuclear amine oxidase homolog LSD1. Cell 119:941–953. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2004.12.012
Sun Z, Wang X, Qiao K, Fan S, Ma Q (2020) Genome-wide analysis of JMJ-C histone demethylase family involved in salt-tolerance in Gossypium hirsutum L. Plant Physiol Bioch 158:420–433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2020.11.029
Tsukada YI, Fang J, Erdjument-Bromage H, Warren ME, Borchers CH, Tempst P, Zhang Y (2006) Histone demethylation by a family of JmjC domain-containing proteins. Nature 439:811–816. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04433
Wang Y, Xue X, Zhu JK, Dong J (2016) Demethylation of ERECTA receptor genes by IBM1 histone demethylase affects stomatal development. Development 143:4452–4461. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.129932
Wang L, Sun X, Jakob W, Wolfram W (2017a) System-level and granger network analysis of integrated proteomic and metabolomic dynamics identifies key points of grape berry development at the interface of primary and secondary metabolism. Front Plant Sci 8:1066. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.01066
Wang Y, Guo S, Tian S, Zhang J, Ren Y, Sun H, Gong G, Zhang H, Xu Y (2017b) Abscisic acid pathway involved in the regulation of watermelon fruit ripening and quality trait evolution. PLoS ONE 12:e179944. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0179944
Wood A, Shilatifard A (2004) Posttranslational modifications of histones by methylation. Adv Protein Chem 67:201–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-3233(04)67008-2
Yan Y, Shen L, Chen Y, Bao S, Thong Z, Yu H (2014) A MYB-domain protein EFM mediates flowering responses to environmental cues in Arabidopsis. Dev Cell 30:437–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2014.07.004
Yang H, Han Z, Cao Y, Fan D, Li H, Mo H, Feng Y, Liu L, Wang Z, Yue Y (2012a) A companion cell–dominant and developmentally regulated H3K4 demethylase controls flowering time in Arabidopsis via the repression of FLC expression. Plos Genet 8:e1002664. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1002664
Yang H, Mo H, Fan D, Cao Y, Cui S, Ma L (2012b) Overexpression of a histone H3K4 demethylase, JMJ15, accelerates flowering time in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Rep 31:1297–1308. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-012-1249-5
Yuan L, Liu H, Liu X, Zhang X, Zhang H (2019) Epigenetic modification of H3K4 and oxidative stress are involved in MC-LR-induced apoptosis in testicular cells of SD rats. Environ Toxicol 35:277–297. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.22865
Zong W, Zhong X, You J, Xiong L (2012) Genome-wide profiling of histone H3K4-tri-methylation and gene expression in rice under drought stress. Plant Mol Biol 81:175–188. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-012-9990-2
Acknowledgements
We thank all the colleagues who have provided materials and experiments for this review.
Funding
This work was financially supported by Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC: U1904113), National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFD1000105) and Program for Innovative Research Team (in Science and Technology) in University of Henan Province (21IRTSTHN021).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y.Z.C. and D.L.G. conceived and designed this study; Y.Z.C. performed the experiments and wrote this paper; D.L.G. revised the manuscript; S.D.Y., G.Q.H., S.H.M., H.Y.J., J.P.M., F.H.Z.S., and X.F.L. gave advices for this study; S.D.Y. and G.Q.H. assisted the analysis tools. All the the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Human and animal ethics
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All the authors must approve the manuscript and give their consent for submission and publication.
Conflict of interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, YZ., He, GQ., Yang, SD. et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of JmjC domain–containing genes in grape under MTA treatment. Funct Integr Genomics 22, 783–795 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-022-00885-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-022-00885-1