Abstract
Purpose
To compare the causes of indeterminate CT pulmonary angiograms using standard mode and high-pitch mode, and determine at what level of the pulmonary arterial tree studies were non-diagnostic.
Methods
IRB approval was obtained. A retrospective review of patients at our institution who underwent a CT pulmonary angiogram, between November 1, 2015 and February 10, 2016 was performed. CT pulmonary angiograms using both high-pitch mode and standard mode were evaluated with positive and indeterminate rates calculated. Causes of indeterminate studies and the level of the pulmonary arterial tree at which the study became non-diagnostic were determined by a board certified radiologist by looking at the images of each indeterminate study. The indeterminate rates were compared between high-pitch and standard modes using a generalized estimating equation.
Results
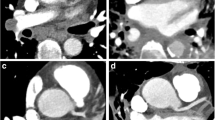
Five hundred fifty-nine CT pulmonary angiograms using high-pitch mode were evaluated, while 661 standard mode scans were evaluated. 69/559 (12.3%) scans with high-pitch mode were positive and 84/661 (12.7%) scans with standard mode were positive (not statistically significant, p > 0.05). There was a higher rate of indeterminate scans with standard mode compared to the high-pitch mode (80 [12.1%] standard vs. 25 [4.5%] high-pitch, p value < 0.0001). Findings were indeterminate at the lobar level in 4 (16%), at the segmental level in 11 (44%), and at the subsegmental level in 10 (40%) using high-pitch mode. The most common causes of an indeterminate scan using high-pitch mode were motion in 11 (44%), transient interruption of contrast in 6 (24%), and contrast timing in 5 (20%). Findings were indeterminate at the main pulmonary artery level in 1 (1.3%), at the lobar level in 13 (16.3%), at the segmental level in 28 (35.0%), and at the subsegmental level in 38 (47.5%) using the standard mode. The most common causes of an indeterminate scan using the standard mode were motion in 53 (66.3%), transient interruption of contrast in 19 (23.8%), and contrast timing in 15 (18.8%).
Conclusions
High-pitch mode results in statistically significant fewer indeterminate studies compared with standard mode. Furthermore, there were statistically significant fewer indeterminate studies due to motion artifact with high-pitch mode compared with standard mode.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Horlander KT, Mannino DM, Leeper KV (2003) Pulmonary embolism mortality in the United States, 1979-1998: an analysis using multiple-cause mortality data. Arch Intern Med 163(14):1711–1717
Agnelli G, Becattini C (2010) Acute pulmonary embolism. N Engl J Med 363(3):266–274
Zhang LJ, Lu GM, Meinel FG, McQuiston AD, Ravenel JG, Schoepf UJ (2015) Computed tomography of acute pulmonary embolism: state-of-the-art. Eur Radiol 25(9):2547–2557
Achenbach S, Marwan M, Schepis T, Pflederer T, Bruder H, Allmendinger T, Petersilka M, Anders K, Lell M, Kuettner A, Ropers D, Daniel WG, Flohr T (2009) High-pitch spiral acquisition: a new scan mode for coronary CT angiography. J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr 3(2):117–121
Lell M, Hinkmann F, Anders K, Deak P, Kalender WA, Uder M, Achenbach S (2009) High-pitch electrocardiogram-triggered computed tomography of the chest: initial results. Investig Radiol 44(11):728–733
Sahani D, Saini S, D’Souza RV, O’Neill MJ, Prasad SR, Kalra MK, Halpern EF, Mueller P (2003) Comparison between low (3:1) and high (6:1) pitch for routine abdominal/pelvic imaging with multislice computed tomography. J Comput Assist Tomogr 27(2):105–109
Hou DJ, Tso DK, Davison C, Inacio J, Louis LJ, Nicolaou S, Reimann AJ (2013) Clinical utility of ultra high pitch dual source thoracic CT imaging of acute pulmonary embolism in the emergency department: are we one step closer towards a non-gated triple rule out? Eur J Radiol 82(10):1793–1798
Jones SE, Wittram C (2005) The indeterminate CT pulmonary angiogram: imaging characteristics and patient clinical outcome. Radiology 237(1):329–337
Yeo JH, Zhou L, Lim R (2017) Indeterminate CT pulmonary angiogram: why and does it matter? J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol 61(1):18–23
Martini K, Meier A, Higashigaito K, Saltybaeva N, Alkadhi H, Frauenfelder T (2016) Prospective randomized comparison of high-pitch CT at 80 kVp under free breathing with standard-pitch CT at 100 kVp under breath-hold for detection of pulmonary embolism. Acad Radiol 23(11):1335–1341
Tsiflikas I, Thomas C, Ketelsen D, Seitz G, Warmann S, Claussen CD, Schäfer JF (2014) High pitch computed tomography of the lung in pediatric patients: and intraindividual comparison of image quality and radiation dose to conventional 64-MDCT. Rofo 186(6):585–590
Lell MM, May M, Deak P, Alibek S, Kuefner M, Kuettner A, Köhler H, Achenbach S, Uder M, Radkow T (2011) High-pitch spiral computed tomography: effect on image quality and radiation dose in pediatric chest computed tomography. Investig Radiol 46(2):116–123
Nakagawa J, Tasaki O, Watanabe Y, Azuma T, Ohnishi M, Ukai I, Tahara K, Ogura H, Kuwagata Y, Hamasaki T, Shimazu T (2013) Reduction of thoracic aorta motion artifact with high-pitch 128-slice dual-source computed tomographic angiography: a historical control study. J Comput Assist Tomogr 37(5):755–759
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Institutional board review was obtained for this Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act compliant study.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Doolittle, D.A., Froemming, A.T. & Cox, C.W. High-pitch versus standard mode CT pulmonary angiography: a comparison of indeterminate studies. Emerg Radiol 26, 155–159 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10140-018-1656-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10140-018-1656-1