Abstract
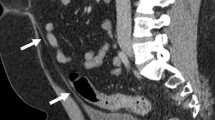
We report a case of foreign body ingestion of a blister pill pack, causing small bowel obstruction. A 76-year-old woman on multiple medications presented with 3 days of progressive abdominal distention, nausea, and vomiting. A computed tomography (CT) scan demonstrated small bowel obstruction with a distinctive metallic foreign body in the distal ileum with associated wall thickening and mesenteric inflammatory changes. At exploratory laparotomy, an impacted, intact blister pill pack was removed from the distal ileum. The ingestion of blister pill packs has been associated with a range of clinical and imaging findings. To our knowledge, this is the only reported case of CT diagnosis of small bowel obstruction caused by blister pack ingestion. Early recognition of the imaging findings of an ingested blister pill pack is important to expedite appropriate management.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hunter TB, Taljanovic MS (2003) Foreign Bodies. Radiographics 23:731–757
Tsukuda T, Kudo F (2000) Pharyngeal foreign bodies in infants persisting for two months: two case reports. Nippon Jibiinkoka Gakkai Kaiho 103:24–27 (in Japanese)
Kumagai M, Ikeda K, Oshima T, Nakatsuka S, Takasaka T (1997) A press-through-pack in the larynx. Tohoku J Exp Med 183:293–295
Yip LWL, Goh FSG, Sim RST (1998) “I’ve got a UFO stuck in my throat”—an interesting case of foreign body impaction in the esophagus. Singap Med J 39:121–123
Wecksell A, Lane E, Greenfield E (1995) Odynophagia caused by inadvertent blister pack ingestion: a case report. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 112:747–749
Goto S, Ikeda K, Adachi M, Tanno N, Takasaka T (1995) Statistical analysis of press-through-pack foreign body in the esophagus and its experimental investigation. Nippon Jibiinkoka Gakkai Kaiho 98:805–812
Tsutsui S, Masuda T, Matsuda H, Harada N, Sonoda T, Takada K (1993) Removal of a press-through package in the thoracic esophagus using two flexible endoscopes. Endoscopy 25:374–375
Dutta U, Gupta NM, Nagi B, Singh K (2001) Blister pack ingestion resulting in esophago-pleural fistula. Indian J Gastroenterol 20:79–80
Chan FKL, Sung JJY, Tam PYH, Kwong KH, Lau JWY (1997) “Blister pack”-induced gastrointestinal hemorrhage. Am J Gastroenterol 92:172–173
Kansal G, Agrawal V (2000) Intestinal perforation—a unique cause. J Indian Med Assoc 98:184–186
Sudo T, Sueyoshi S, Fujita H, Yamana H, Shirouzu K (2003) Esophageal perforation caused by a press through pack. Dis Esophagus 16:169–172
Bandyopadhyay D, Orgles CS, Dewar EP (2005) Small bowel obstruction due to inflammation secondary to ingested bone. Emerg Radiol 11:381–385
Yeen WC, Willis IH (2005) Retention of extended release nifedipine capsules in a patient with enteric stricture causing small bowel obstruction. South Med J 98:839–842
Wildhaber BE, Le Coultre C, Genin B (2005) Ingestion of magnets: innocent in solitude, harmful in groups. J Pediatr Surg 40:e33–e35
Linnau KF, Mann FA (2003) Doll’s head “bezoar”: complete craniocervical dislocation causing bowel obstruction. Am J Roentgenol 180:986
Agramunt Lerma M, Errando Mariscal JM, Delgado Cordon F, Gomez Abril S, Montalvo Oron E, Martinez Perez MJ (2002) Small bowel obstruction caused by snail’s shell: radiographic and CT findings. J Comput Assist Tomogr 26:529–531
Valente JH, Lemke T, Ridlen M, Ritter D, Clyne B, Reinert SE (2005) Aluminum foreign bodies: do they show up on X-ray? Emerg Radiol 12:30–33
Florez MV, Evans JM, Daly TR (1998) The radiodensity of medications seen on X-ray films. Mayo Clin Proc 73:516–519
Savitt DL, Hawkins HH, Roberts JR (1987) The radiopacity of ingested medications. Ann Emerg Med 16:331–339
Simmons D, Upjohn M, Gamble GD (2000) Can medication packaging improve glycemic control and blood pressure in Type 2 diabetes? Results from a randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Care 23:153–156
Chan TY (2000) Improvements in the packaging of drugs and chemicals may reduce the likelihood of severe intentional poisonings in adults. Human Exp Toxicol 19:387–391
Beckman A, Bernsten C, Parker MG, Thorslund M, Fastborn J (2005) The difficulty of opening medicine containers in old age: a population-based study. Pharm World Sci 27:393–398
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tai, A.W., Sodickson, A. Foreign body ingestion of blister pill pack causing small bowel obstruction. Emerg Radiol 14, 105–108 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10140-007-0582-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10140-007-0582-4