Abstract
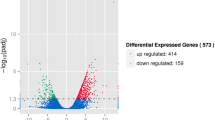
Moina micrura represents a promising model species for ecological and ecotoxicological investigations in tropical freshwater ecosystems. Illumina NovaSeq™ 6000 sequencing was employed in this study to analyze M. micrura across three distinct developmental stages: juvenile, adult, and male. Current study successfully annotated 51,547 unigenes (73.11%) derived from seven (7) different databases. A total of 554 genes were found to be significantly upregulated, while 452 genes showed significant downregulation between juvenile and male. Moreover, 1001 genes were upregulated, whereas 830 genes exhibited downregulation between the adult and male. Analysis of differentially expressed genes revealed upregulation of chitin, cuticle, myosin (MYO), mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK), fibrillin (FBN), cytochrome (CYP), glutathione s-transferase (GST), vitellogenin (VTG), acetylcholinesterase (AChE), and transforming growth factor beta (TGFB) under unfavorable environmental conditions (male), as compared to favorable environmental conditions (juveniles and adults). These alterations in gene expression significantly impact the phenological and life-history traits of M. micrura. Furthermore, the upregulation of hemoglobin (HMB), doublesex (DSX), juvenile hormone analogs (JHA), heat shock protein (HSP), and methyltransferase (METT) genes in males initiates the sex-switching effects observed in M. micrura. These findings hold substantial value for researchers interested in determining M. micrura sequences for future investigations of gene expression and comparative reproductive genome analysis within the Moina genus and cladoceran families.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The authors declare that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article and its supplementary information files.
References
Akaike A, Shimohama S, Misu Y (2018) A new aspect of cholinergic transmission in the central nervous system, in: Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor signaling in neuroprotection. In: Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Signaling in Neuroprotection. 45–58
Aksakal FI, Arslan H (2020) Detoxification and reproductive system-related gene expression following exposure to Cu(OH)2 nanopesticide in water flea (Daphnia magna Straus 1820). Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:6103–6111
American Society for Testing and Materials (2020) Standard test method for measuring the toxicity of sediment-associated contaminants with freshwater invertebrates. Pennsylvania, United States
Anders S, Huber W (2010) Differential expression analysis for sequence count data. Genome Biol 11:R106. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2010-11-10-r106
Artyom Kopp (2012) Dmrt genes in the development and evolution of sexual dimorphism. trends Genet 28:175–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tig.2012.02.002
Azuraidi OM, Yusoff FM, Shamsudin MN et al (2013) Effect of food density on male appearance and ephippia production in a tropical cladoceran, Moina micrura Kurz, 1874. Aquaculture 412–413:131–135
Berger CA, Steinberg DK, Copley NJ, Tarrant AM (2021) De novo transcriptome assembly of the Southern Ocean copepod Rhincalanus gigas sheds light on developmental changes in gene expression. Mar Genomics 58:100835. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.margen.2021.100835
Boonthai C, Somparn A, Noller B (2011) Using zooplankton, Moina micrura Kurz to evaluate the ecotoxicology of pesticides used in paddy fields of Thailand. In: Stoytcheva M (ed) Pesticides in the Modern World - Risks and Benefits. InTech
Cajaraville MP, Orive E, Villate F et al (2016) Health status of the Bilbao estuary: a review of data from a multidisciplinary approach. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 179:124–134
da S. Ferrão‐Filho A, de Abreu S Silva D, de Oliveira TA et al (2017) Single and combined effects of microcystin- and saxitoxin-producing cyanobacteria on the fitness and antioxidant defenses of cladocerans. Environ Toxicol Chem 36:2689–2697
Dahms H, Won E, Kim H et al (2016) Potential of the small cyclopoid copepod Paracyclopina nana as an invertebrate model for ecotoxicity testing. Aquat Toxicol 180:282–294
Demertzioglou M, Antonopoulou E, Voutsa D et al (2021) MAPks and HSPs’ activation of a natural Daphnia magna population in a man-perturbed lake: implications of ecological significance. Water (Switzerland) 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13030283
Dey S, Ray K (2018) Cholinergic activity is essential for maintaining the anterograde transport of Choline Acetyltransferase in Drosophila. Sci Rep 8:1–11
Elías-Gutiérrez M, Juračka PJ, Montoliu-Elena L et al (2019) Who is Moina micrura? Redescription of one of the most confusing cladocerans from terra typica, based on integrative taxonomy. Limnetica 38:227–252
Ghose SL, Donnelly MA, Kerby J, Whitfield SM (2014) Acute toxicity tests and meta-analysis identify gaps in tropical ecotoxicology for amphibians. Environ Toxicol Chem 33:2114–2119
Guo CY, Cao X, Lin CY et al (2019) Transcriptomic analysis of genes involved in reproduction at different ages in Daphnia pulex (Branchiopoda, Cladocera). Crustaceana 92:1311–1335
Holm MW, Kiørboe T, Brun P et al (2018) Resting eggs in free living marine and estuarine copepods. J Plankton Res 40:2–15
Houde M, Carter B, Douville M (2013) Sublethal effects of the flame retardant intermediate hexachlorocyclopentadiene (HCCPD) on the gene transcription and protein activity of Daphnia magna. Aquat Toxicol 140–141:213–219
Hu XL, Tang YY, Kwok ML et al (2020) Impact of juvenile hormone analogue insecticides on the water flea Moina macrocopa: growth, reproduction and transgenerational effect. Aquat Toxicol 220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2020.105402
Huylmans AK, Ezquerra AL, Parsch J, Cordellier M (2016) De novo transcriptome assembly and sex-biased gene expression in the cyclical parthenogenetic daphnia galeata. Genome Biol Evol 8:3120–3139
ISO (2012) ISO 6341:2012 − Water quality – Determination of the inhibition of the mobility of Daphnia magna Straus (Cladocera, Crustacea) − Acute toxicity test. Switzerland., 4th edn. Geneva, Switzerland
Jia J, Liu X, Li L et al (2018) Transcriptional and translational relationship in environmental stress: RNAseq and ITRAQ proteomic analysis between sexually reproducing and parthenogenetic females in Moina micrura. Front Physiol 9:1–16
Jung H, Lyons RE, Hurwood DA, Mather PB (2013) Genes and growth performance in crustacean species: A review of relevant genomic studies in crustaceans and other taxa. Rev Aquac 5:77–110
Kar S, Das P, Das U et al (2017) Culture of the zooplankton as fish food: observations on three freshwater species from Assam, India. AACL Bioflux 10:1210–1220
Kato Y, Kobayashi K, Watanabe H, Iguchi T (2011) Environmental sex determination in the branchiopod crustacean Daphnia magna : Deep conservation of a doublesex gene in the sex-determining pathway. PLOS Genet 7:e1001345. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1001345
Kim BM, Ahn SH, Choi NR et al (2017) Transcriptome profiles of Daphnia magna across to the different water chemistry of surface water of the Korean Demilitarized Zone. Toxicol Environ Health Sci 9:188–198
Kim BM, Kang S, Kim RO et al (2018) De novo transcriptome assembly of brackish water flea Diaphanosoma celebensis based on short-term cadmium and benzo[a]pyrene exposure experiments. Hereditas 155:36. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41065-018-0075-3
Kong F, Cao M, Li N et al (2020) Genome-wide identification, phylogeny, and expressional profiles of the mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase (MAPKKK) gene family in Pyropia yezoensis. Front Mar Sci 7. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2020.00193
Lee YH, Kim DH, Kang HM et al (2017) Adverse effects of methylmercury (MeHg) on life parameters, antioxidant systems, and MAPK signaling pathways in the rotifer Brachionus koreanus and the copepod Paracyclopina nana. Aquat Toxicol 190:181–189
Li B, Dewey C (2011) RSEM: accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinformatics 12:323. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-12-323
Li M, Kong Y, Wu X et al (2021) Dietary α-lipoic acid can alleviate the bioaccumulation, oxidative stress, cell apoptosis, and inflammation induced by lead (Pb) in Channa argus. Fish Shellfish Immunol 119:249–261
Li Y, Han Z, She Q et al (2019) Comparative transcriptome analysis provides insights into the molecular basis of circadian cycle regulation in Eriocheir sinensis. Gene 694:42–49
Liu Y, Zhang J, Zhao H et al (2022) Effects of polyvinyl chloride microplastics on reproduction, oxidative stress and reproduction and detoxification-related genes in Daphnia magna. Comp Biochem Physiol Part - C Toxicol Pharmacol 254:109269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2022.109269
Liu Z, Huang Y, Jiao Y et al (2020) Polystyrene nanoplastic induces ROS production and affects the MAPK-HIF-1/NFkB-mediated antioxidant system in Daphnia pulex. Aquat Toxicol 220:105420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2020.105420
Miyakawa H, Sato T, Song Y et al (2018) Ecdysteroid and juvenile hormone biosynthesis, receptors and their signaling in the freshwater microcrustacean Daphnia. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 184:62–68
Nong QD, Mohamad Ishak NS, Matsuura T et al (2017) Mapping the expression of the sex determining factor Doublesex1 in Daphnia magna using a knock-in reporter. Sci Rep 7:1–13
Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (2004) OECD guideline for testing of chemicals – Daphnia sp., Acute Immobilization Test
Parolini M, De Felice B, Ferrario C et al (2018) Benzoylecgonine exposure induced oxidative stress and altered swimming behavior and reproduction in Daphnia magna. Environ Pollut 232:236–244
Pesch YY, Riedel D, Patil KR et al (2016) Chitinases and Imaginal disc growth factors organize the extracellular matrix formation at barrier tissues in insects. Sci Rep 6:1–14
Pham TL, Bui HM (2018) Comparison of diazinon toxicity to temperate and tropical freshwater Daphnia species. J Chem 2018. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/9217815
Pirow R, Bäumer C, Paul RJ (2001) Benefits of haemoglobin in the cladoceran crustacean Daphnia magna. J Exp Biol 204:3425–3441
Powell D, Elizur A, Knibb W (2018) Sex-specific transcript expression in the hepatopancreas of the banana shrimp (Fenneropenaeus merguiensis). Hydrobiologia 825:81–90
Razak MR, Aris AZ, Yusoff FM et al (2022a) Risk assessment of bisphenol analogues towards mortality, heart rate and stress-mediated gene expression in cladocerans Moina micrura. Environ Geochem Health. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-022-01442-2
Razak MR, Aris AZ, Yusoff FM et al (2022b) Assessment of RNA extraction protocols from Cladocerans. PLoS ONE 17:1–20
Razak MR, Aris AZ, Zainuddin AH et al (2023) Acute toxicity and risk assessment of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS) in tropical cladocerans Moina micrura. Chemosphere 313:137377https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.137377
Rhee JS, Kim BM, Jeong CB et al (2013) Effect of pharmaceuticals exposure on acetylcholinesterase (AchE) activity and on the expression of AchE gene in the monogonont rotifer, Brachionus koreanus. Comp Biochem Physiol Part C Toxicol Pharmacol 158:216–224
Rietzler AC, Maia-Barbosa PM, Ribeiro MM, Menendez RM (2014) On the first record of the exotic Moina macrocopa (Straus, 1820) in Minas Gerais State, Brazil. Brazilian J Biol 74:518–520
Scherer C, Brennholt N, Reifferscheid G, Wagner M (2017) Feeding type and development drive the ingestion of microplastics by freshwater invertebrates. Sci Rep 7:1–9
Semenova AS, Tchougounov VK (2018) The distribution of Moina micrura Kurz, 1875 (Crustacea: Moinidae) in the Russian part of the Vistula Lagoon (Baltic Sea). Russ J Biol Invasions 9:175–183
Sinev AY, Gu Y, Han BP (2015) Cladocera of Hainan Island, China. Zootaxa 4006:569–585
Sugier K, Vacherie B, Cornils A et al (2018) Chitin distribution in the Oithona digestive and reproductive systems revealed by fluorescence microscopy. PeerJ 2018:1–15
Talu M, Seyoum A, Yitayew B et al (2022) Transcriptional responses of Daphnia magna exposed to Akaki river water. Environ Monit Assess 194. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-09973-y
Tarrant AM, Baumgartner MF, Hansen BH et al (2014) Transcriptional profiling of reproductive development, lipid storage and molting throughout the last juvenile stage of the marine copepod Calanus finmarchicus. Front Zool 11:1–15
Toyota K, Kato Y, Sato M et al (2013) Molecular cloning of doublesex genes of four cladocera (water flea) species. BMC Genomics 14. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-14-239
Toyota K, Miyakawa H, Hiruta C et al (2021) Sex determination and differentiation in decapod and cladoceran crustaceans: an overview of endocrine regulation. Genes (basel) 12:1–16
Verhulst EC, Van de zande L (2015) Double nexus—doublesex is the connecting element in sex determination. Brief Funct Genomics 14:396–406
Vijverberg J (2018) Zooplankton, zooplanktivorous fish and their interactions in Southeast Asian waterbodies with special reference to Sri Lanka: a review. Sri Lanka J Aquat Sci 23:3https://doi.org/10.4038/sljas.v23i1.7542
Wang J, Li Y, Lu L et al (2019) Polystyrene microplastics cause tissue damages, sex-specific reproductive disruption and transgenerational effects in marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma). Environ Pollut 254:113024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113024
Wang L, Peng Y, Nie X et al (2016) Gene response of CYP360A, CYP314, and GST and whole-organism changes in Daphnia magna exposed to ibuprofen. Comp Biochem Physiol Part - C Toxicol Pharmacol 179:49–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2015.08.010
Xu X, Song S, Wang Q et al (2009) Analysis and comparison of a set of expressed sequence tags of the parthenogenetic water flea Daphnia carinata. Mol Genet Genomics 282:197–203
Young MD, Wakefield MJ, Smyth GK, Oshlack A (2010) Gene ontology analysis for RNA-seq: accounting for selection bias. Genome Biol 11. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2010-11-2-r14
Zhang YN, Zhu XY, Wang WP et al (2016) Reproductive switching analysis of Daphnia similoides between sexual female and parthenogenetic female by transcriptome comparison. Sci Rep 6:1–9
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge Aquatic Animal Health and Therapeutics Laboratory (AquaHealth), Universiti Putra Malaysia, for permitting the usage of laboratories and equipment. The first author also would like to thank Skim Latihan Akademik Bumiputra (SLAB), awarded by the Ministry of Higher Education (MOHE), Malaysia, for financial support.
Funding
This work was supported by GIST Research Institute (GRI) grant funded by the Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST) in 2021. Ahmad Zaharin Aris has received research support from GIST.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Muhammad Raznisyafiq Razak and Ahmad Zaharin Aris contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Muhammad Raznisyafiq Razak. Ahmad Zaharin Aris contributed to supervision and funding acquisition. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Muhammad Raznisyafiq Razak and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Razak, M.R., Aris, A.Z., Yusoff, F.M. et al. De Novo Transcriptomic and Life-History Responses of Moina Micrura Under Stress Environment Conditions. Mar Biotechnol 25, 473–487 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-023-10220-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-023-10220-9