Abstract
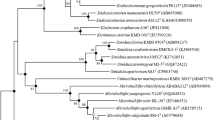
From cell cultures of Suberites domuncula was isolated a bacterial strain, SDC-1, which was identified by 16S ribosomal RNA sequence analysis as an α-Proteobacterium of the genus Ruegeria. The occurrence of the strain in sponge cell culture could be explained by its resistance to the antibiotics used in the isolation of sponge cell cultures or by the preservation of SDC-1 by host sponge cells. The fatty acid composition of SDC-1 is characterized by branched C-12 methyl fatty acids. Two new and 8 known cyclic dipeptides were isolated and characterized from the fermentation broth of SDC-1. Cyclodipeptides are one of the families of cell-cell signaling compounds and may have some role to play in sponge-bacteria interactions.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Adamczeski E. Quiñoá P. Crews (1989) ArticleTitleNovel sponge-derived amino acids, 5. Structures, stereochemistry, and synthesis of several new heterocycles. J Am Chem Soc 111 647–654 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1MXnt1Ontw%3D%3D
B.L. Bassler (2002) ArticleTitleSmall talk: cell-to-cell communication in bacteria. Cell 109 421–424 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XjvFKgtL8%3D Occurrence Handle12086599
W.D. Bauer J.B. Robinson (2002) ArticleTitleDisruption of bacterial quorum sensing by other organisms. Curr Opin Biotechnol 13 234–237 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0958-1669(02)00310-5 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XkvVemsLY%3D Occurrence Handle12180098
M. Böhm U. Hentschel A. Friedrich L. Fieseler R. Steffen V. Gamulin I.M. Müller W.E.G. Müller (2001) ArticleTitleMolecular response of the sponge Suberites domuncula to bacterial infection. Mar Biol 139 1037–1045 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s002270100656
G. Brelles-Mariño E.J. Bedmar (2001) ArticleTitleDetection, purification and characterisation of quorum-sensing signal molecules in plant-associated bacteria. J Biotechnol 91 197–209 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0168-1656(01)00330-3 Occurrence Handle11566391
J.M.J. Cronan T.M. Davidson F.L. Singleton R.R. Colwell I I, J.H. Cardellina (1998) ArticleTitlePlant growth promoters isolated from a marine bacterium associated with Palythoa sp. Nat Prod Lett 11 271–278 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXjtVOgtbY%3D
G. Degrassi C. Aguilar M. Bosco S. Zahariev S. Pongor V. Venturi (2002) ArticleTitlePlant growth-promoting Pseudomonas putida WCS358 produces and secretes four cyclic dipeptides: cross-talk with quorum sensing bacterial sensors. Curr Microbiol 45 250–254 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XmsFWlsbc%3D Occurrence Handle12192521
S. De Rosa S. De Caro C. Iodice G. Tommonaro K. Stefanov S. Popov (2003a) ArticleTitleDevelopment in primary cell culture of demosponges. J Biotechnol 100 119–125 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38Xotl2jsrw%3D
S. De Rosa C. Iodice J. Nechev K. Stefanov S. Popov (2003b) ArticleTitleComposition of the lipophylic extract from the sponge Suberites domuncula. J Serb Chem Soc 68 249–256 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXktlOqtLw%3D
S. De Rosa M. Mitova G. Tommonaro (2003c) ArticleTitleMarine bacteria associated with sponge as source of cyclic peptides. Biomol Eng 20 311–316 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXmt1Khs7k%3D
S. Engel P.R. Jensen W. Fenical (2002) ArticleTitleChemical ecology of marine microbial defense. J Chem Ecol 28 1971–1985 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1020793726898 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XnvFOitbY%3D Occurrence Handle12474894
D.J. Faulkner M.D. Unson C.A. Bewley (1994) ArticleTitleThe chemistry of some sponges and their symbionts. Pure Appl Chem 66 1983–1990 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXmsFWnu7Y%3D
W. Fenical (1993) ArticleTitleChemical studies of marine bacteria: developing a new resource. Chem Rev 93 1673–1683 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3sXkvFSrsb0%3D
A.B. Friedrich H. Merkert T. Fendert J. Hacker P. Proksch U. Hentschel (1999) ArticleTitleMicrobial diversity in the marine sponge Aplysina cavernicola (formerly Verongia cavernicola) analyzed by fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). Mar Biol 134 461–470 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s002270050562
A.B. Friedrich I. Fischer P. Proksch J. Hacker U. Hentschel (2001) ArticleTitleTemporal variation of the microbial community associated with the mediterranean sponge Aplysina aerophoba. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 38 105–113
U. Hentschel M. Steinert J. Hacker (2000) ArticleTitleCommon molecular mechanisms of symbiosis and pathogenesis. Trends Microbiol 8 226–231 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3czpt1aisQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10785639
U. Hentschel M. Schmid M. Wagner L. Fieseler C. Gernert J. Hacker (2001) ArticleTitleIsolation and phylogenetic analysis of bacteria with antimicrobial activities from the Mediterranean sponge Aplysina aerophoba and Aplysina cavernicola. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 35 305–312 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXislGrsbk%3D Occurrence Handle11311441
M.T.G. Holden S.R. Chhabra R. de Nys P. Stead N.J. Bainton P.J. Hill M. Manefield N. Kumar M. Labatte D. England S. Rice M. Givskov G.P.C. Salmond G.S.A.B. Stewart B.W. Bycroft S. Kjelleberg P. Williams (1999) ArticleTitleQuorum-sensing cross talk: isolation and chemical characterization of cyclic dipeptides from Pseudomonas aeruginosa and other gram-negative bacteria. Mol Microbiol 33 1254–1266 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2958.1999.01577.x Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXmtlajsL8%3D Occurrence Handle10510239
E. Jantzen K. Bryn (1985) Whole-cell and lipopolysaccharide fatty acids and sugars of gram-negative bacteria. M. Goodfellow D.E. Minnikin (Eds) Chemical Methods in Bacterial Systematics Academic Press Orlando, Fla. 145–171
G.S. Jayatilake M.P. Thornton A.C. Leonard J.E. Grimwade B.J. Baker (1996) ArticleTitleMetabolites from an antarctic sponge-associated bacterium, Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Nat Prod 59 293–296 Occurrence Handle10.1021/np960095b Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28Xhtleju7w%3D Occurrence Handle8882433
Z. Jiang K.G. Boyd A. Mearns-Spragg D.R. Adams P.C. Wright J.G. Burgess (2000) ArticleTitleTwo diketopiperazines and one halogenated phenol from cultures of the marine bacterium, Pseudoalteromonas luteoviolacea. Nat Prod Lett 14 435–440 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXlvFamsw%3D%3D
M.R. Parsek E.P. Greenberg (2000) ArticleTitleAcyl-homoserine lactone quorum sensing in gram-negative bacteria: a signaling mechanism involved in associations with higher organisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97 8789–8793 Occurrence Handle10.1073/pnas.97.16.8789 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXls12lt7g%3D Occurrence Handle10922036
C. Prasad (1995) ArticleTitleBioactive cyclic dipeptides. Peptides 16 151–164 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0196-9781(94)00017-Z Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXjtlWkur0%3D Occurrence Handle7716068
C.M. Preston K.Y. Wu T.F. Molinski E.F. DeLong (1996) ArticleTitleA psychrophilic crenarchaeon inhabits a marine sponge: Cenarchaeum symbiosum gen. nov., sp. nov. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93 6241–6246 Occurrence Handle10.1073/pnas.93.13.6241 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XjvFejtrk%3D Occurrence Handle8692799
P. Proksch R.A. Edrada R. Ebel (2002) ArticleTitleDrugs from the seas—current status and microbiological implications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 59 125–134 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00253-002-1006-8 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XlvV2ktbg%3D Occurrence Handle12111137
H.J. Rüger M.G. Höfle (1992) ArticleTitleMarine star-shaped-aggregate-forming bacteria: Agrobacterium atlanticum sp. nov.; Agrobacterium meteori sp.nov.; Agrobacterium ferrugineum sp.nov., nom.rev.; Agrobacterium gelatinovorum sp.nov., nom.rev.; and Agrobacterium stellulatum sp.nov., nom.rev. Int J Syst Bacteriol 42 133–143 Occurrence Handle1371058
E.W. Schmidt A.Y. Obraztsova S.K. Davidson D.J. Faulkner M.G. Haygood (2000) ArticleTitleIdentification of the antifungal peptide-containing symbiont of the marine sponge Theonella swinhoei as a novel δ-proteobacterium, “Candidatus Entotheonella palauensis. Mar Biol 136 969–977 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXms1agtrc%3D
H.C. Schröder F. Brummer E. Fattorusso A. Aiello M. Menna S. De Rosa R. Batel W.E.G. Müller (2003) Sustainable production of bioactive compounds from sponges: primmorphs as bioreactors. W.E.G. Müller (Eds) Sponges Springer-Verlag Berlin 163–197
H. Shigemori M. Tenma K. Shimazaki J. Kobayashi (1998) ArticleTitleThree new metabolites from the marine yeast Aureobasidium pullulans. J Nat Prod 61 696–698 Occurrence Handle10.1021/np980011u Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXislSjsLs%3D Occurrence Handle9599283
A.C. Stierle II Cardellina J.H. F.L. Singleton (1988) ArticleTitleA marine Micrococcus produces metabolites ascribed to the sponge Tedania ignis. Experientia 44 1021 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1MXhtFWntL8%3D Occurrence Handle3197807
N.L. Thakur U. Hentschel A. Krasko Ch.T. Pabel A.C. Anil W.E.G. Müller (2003) ArticleTitleAntibacterial activity of the sponge Suberites domuncula and its primmorphs: potential basis for epibacterial chemical defense. Aquat Microb Ecol 31 77–83
J.A. Trischman (1993) A chemical study of microbial antibiosis in eustarine extreme marine environments. Ph.D. thesis. University of California San Diego
Y. Uchino A. Hirata A. Yokota J. Sugiyama (1998) ArticleTitleReclassification of marine Agrobacterium species: proposals of Stappia stellulata gen.nov, comb.nov., Stappia aggregata sp.nov., nom.rev., Ruegeria atlantica gen.nov., comb.nov., Ruegeria gelatinovora comb.nov., Ruegeria algicola comb.nov., and Ahrensia kieliense gen.nov., sp.nov., nom.rev. J Gen Appl Microbiol 44 201–210 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXmvF2ntr8%3D Occurrence Handle12501429
N.S. Webster R.T. Hill (2001) ArticleTitleThe culturable microbial community of the Great Barrier Reef sponge Rhopaloeides odorabile is dominated by an α-Proteobacterium. Mar Biol 138 843–851 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXjvFKnsrw%3D
N.S. Webster K.J. Wilson L.L. Blackall R.T. Hill (2001) ArticleTitlePhylogenetic diversity of bacteria associated with the marine sponge Rhopaloeides odorabile. Appl Environ Microbiol 67 434–444 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXjtVWlug%3D%3D Occurrence Handle11133476
C.R. Wilkinson (1984) ArticleTitleImmunological evidence for the Precambrian origin of bacterial symbiosis in marine sponges. Proc R Soc Lond B 220 509–517
C.R. Wilkinson (1987) ArticleTitleSignificance of microbial symbionts in sponge evolution and ecology. Symbiosis 4 135–146
H. Withers S. Swift P. Williams (2001) ArticleTitleQuorum sensing as an integral component of gene regulatory networks in gram-negative bacteria. Curr Opin Microbiol 4 186–193 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S1369-5274(00)00187-9 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXjvVartL4%3D Occurrence Handle11282475
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by a Marie Curie fellowship of the European Community program “Quality of Life and Management of Living Resources” contract QLK5-CT-2001-50974 and by Project SPONGE, contract QLK3-1999-00672. “Servizio di Spettrometria di Massa del CNR-Napoli and Servizio NMR, ICB-CNR” provided the MS and NMR spectra, respectively. The assistance of Dr. S. De Caro, Mr. C. Iodice, and O. De Luca is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mitova, M., Tommonaro, G., Hentschel, U. et al. Exocellular Cyclic Dipeptides from a Ruegeria Strain Associated with Cell Cultures of Suberites domuncula . Mar. Biotechnol. 6, 95–103 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-003-0018-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-003-0018-4