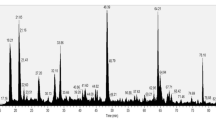
Abstract
Vibrio parahaemolyticus causes seafood-borne gastroenteritis infection in human which can even lead to death. The pathogenic strain of V. parahaemolyticus secretes different types of virulence factors that are directly injected into the host cell by a different type of secretion system which helps bacteria to establish its own ecological niche within the organism. Therefore, the aim of this study was to isolate the extracellular secreted proteins from the trh positive strain of V. parahaemolyticus and identify them using two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and MALDI-TOFMS/MS. Seventeen different cellular proteins viz, Carbamoyl-phosphate synthase, 5-methyltetrahydropteroyltriglutamate, tRNA-dihydrouridine synthase, Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, Orotidine 5′-phosphate decarboxylase, Molybdenum import ATP-binding protein, DnaJ, DNA polymerase IV, Ribosomal RNA small subunit methyltransferase G, ATP synthase subunit delta and gamma, Ribosome-recycling factor, 4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl diphosphate synthase, tRNA pseudouridine synthase B, Ditrans, polycis-undecaprenyl-diphosphate synthase, Oxygen-dependent coproporphyrinogen-III oxidase, and Peptide deformylase 2 were identified which are mainly involved in different metabolic and biosynthetic pathways. Furthermore, the molecular function of the identified proteins were associated with catalytic activity, ligase activity, transporter, metal binding, and ATP synthase when they are intercellular. However, to understand the importance of these secreted proteins in the infection and survival of bacteria inside the host cell, pathogen–host protein-protein interactions (PPIs) were carried out which identified the association of eight secreted proteins with 41 human proteins involved in different cellular pathways, including ubiquitination degradation, adhesion, inflammation, immunity, and programmed cell death. The present study provides unreported strategies on host-cell environment’s survival and adaptation mechanisms for the successful establishment of infections and intracellular propagation.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The article and supplementary information contain all the relevant data pertaining to the study.
References
Aguilera L, Ferreira E, Giménez R, Fernández FJ, Taulés M, Aguilar J, Vega MC, Badia J, Baldomà L (2012) Secretion of the housekeeping protein glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase by the LEE-encoded type III secretion system in enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 44(6):955–962
Albuquerque PC, Nakayasu ES, Rodrigues ML, Frases S, Casadevall A, Zancope-Oliveira RM, Almeida IC, Nosanchuk JD (2008) Vesicular transport in Histoplasma capsulatum: an effective mechanism for trans-cell wall transfer of proteins and lipids in ascomycetes. Cell Microbiol 10(8):1695–1710
Alvarez AH, Martinez-Cadena G, Silva ME, Saavedra E, Avila EE (2007) Entamoeba histolytica: ADP-ribosylation of secreted glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Exp Parasitol 117(4):349–356
Ammari MG, Gresham CR, McCarthy FM, Nanduri B (2016) HPIDB 2.0: a curated database for host–pathogen interactions. Database (Oxford) 3:2016
Ashida H, Mimuro H, Ogawa M, Kobayashi T, Sanada T, Kim M, Sasakawa C (2011) Cell death and infection: a double-edged sword for host and pathogen survival. J Cell Biol 195(6):931–942
Barbey C, Budin-Verneuil A, Cauchard S, Hartke A, Laugier C, Pichereau V, Petry S (2009) Proteomic analysis and immunogenicity of secreted proteins from Rhodococcus equi ATCC 33701. Vet Microbiol 135(3-4):334–345
Barbosa MS, Báo SN, Andreotti PF, de Faria FP, Felipe MSS, dos Santos FL, de Almeida M-GMJS, Soares CM (2006) Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase of Paracoccidioides brasiliensis is a cell surface protein involved in fungal adhesion to extracellular matrix proteins and interaction with cells. Infect Immun 74(1):382–389
Baron C (2009) Mechanistic and Structural Analysis of Type IV Secretion Systems. In: Wooldridge K (ed) Bacterial Secreted Proteins: Secretory Mechanisms and Role in Pathogenesis. Caister Academic Press, Hethersett, Norwich, UK, pp 117–137
Bennuru S, Semnani R, Meng Z, Ribeiro JM, Veenstra TD, Nutman TB (2009) Brugia malayi excreted/secreted proteins at the host/parasite interface: stage-and gender-specific proteomic profiling. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 3(4):e410
Beys-da-Silva WO, Santi L, Berger M, Calzolari D, Passos DO, Guimarães JA, Moresco JJ, Yates JR (2014) Secretome of the biocontrol agent Metarhizium anisopliae induced by the cuticle of the cotton pest Dysdercus peruvianus reveals new insights into infection. J Proteome Res 13(5):2282–2296
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72(1-2):248–254
Burdette DL, Yarbrough ML, Orvedahl A, Gilpin CJ, Orth K (2008) Vibrio parahaemolyticus orchestrates a multifaceted host cell infection by induction of autophagy, cell rounding, and then cell lysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(34):12497–12500
Chitlaru T, Gat O, Grosfeld H, Inbar I, Gozlan Y, Shafferman A (2007) Identification of in vivo-expressed immunogenic proteins by serological proteome analysis of the Bacillus anthracis secretome. Infect Immun 75(6):2841–2852
Christie-Oleza JA, Armengaud J, Guerin P, Scanlan DJ (2015) Functional distinctness in the exoproteomes of marine S. ynechococcus. Environ Microbiol 17(10):3781–3794
Cline MS, Smoot M, Cerami E, Kuchinsky A, Landys N, Workman C, Christmas R, Avila-Campilo I, Creech M, Gross B, Hanspers K (2007) Integration of biological networks and gene expression data using Cytoscape. Nat Protoc 2(10):2366–2382
Coburn B, Sekirov I, Finlay BB (2007) Type III secretion systems and disease. Clin Microbiol Rev 20(4):535–549
Cornejo-Granados F, Zatarain-Barrón ZL, Cantu-Robles VA, Mendoza-Vargas A, Molina-Romero C, Sánchez F, Del Pozo-Yauner L, Hernandez-Pando R, Ochoa-Leyva A (2017) Secretome prediction of two M. tuberculosis clinical isolates reveals their high antigenic density and potential drug targets. Front Microbiol 8:128
Cornells GR (2000) Type III secretion: a bacterial device for close combat with cells of their eukaryotic host. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 355(1397):681–693
Cui T, Li W, Liu L, Huang Q, He ZG (2016) Uncovering new pathogen–host protein–protein interactions by pairwise structure similarity. PLoS One 11(1):e0147612
Delannoy A, Wilhelm E, Eilebrecht S, Alvarado-Cuevas EM, Benecke AG, Bell B (2018) BIM and NOXA are mitochondrial effectors of TAF6δ-driven apoptosis. Cell Death Dis 9(2):1–15
Deng W, Marshall NC, Rowland JL, McCoy JM, Worrall LJ, Santos AS, Strynadka NC, Finlay BB (2017) Assembly, structure, function and regulation of type III secretion systems. Nat Rev Microbiol 15(6):323
Dufies O, Boyer L (2021) RhoGTPases and inflammasomes: guardians of effector-triggered immunity. PLoS Pathog 17(4):e1009504
Dyer MD, Neff C, Dufford M, Rivera CG, Shattuck D, Bassaganya-Riera J, Murali TM, Sobral BW (2010) The human-bacterial pathogen protein interaction networks of Bacillus anthracis, Francisella tularensis, and Yersinia pestis. PLoS One 5(8):e12089
Ebner P, Luqman A, Reichert S, Hauf K, Popella P, Forchhammer K, Otto M, Götz F (2017) Non-classical protein excretion is boosted by PSMα-induced cell leakage. Cell Rep 20(6):1278–1286
Egea L, Aguilera L, Gimenez R, Sorolla MA, Aguilar J, Badía J, Baldoma L (2007) Role of secreted glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase in the infection mechanism of enterohemorrhagic and enteropathogenic Escherichia coli: interaction of the extracellular enzyme with human plasminogen and fibrinogen. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 39(6):1190–1203
Farhan H, Rabouille C (2011) Signalling to and from the secretory pathway. J Cell Sci 124(2):171–180
Galka F, Wai SN, Kusch H, Engelmann S, Hecker M, Schmeck B, Hippenstiel S, Uhlin BE, Steinert M (2008) Proteomic characterization of the whole secretome of Legionella pneumophila and functional analysis of outer membrane vesicles. Infect Immun 76(5):1825–1836
García K, Yáñez C, Plaza N, Peña F, Sepúlveda P, Pérez-Reytor D, Espejo RT (2017) Gene expression of Vibrio parahaemolyticus growing in laboratory isolation conditions compared to those common in its natural ocean environment. BMC Microbial 17(1):1–10
Geraci J, Neubauer S, Pöllath C, Hansen U, Rizzo F, Krafft C, Westermann M, Hussain M, Peters G, Pletz MW, Löffler B (2017) The Staphylococcus aureus extracellular matrix protein (Emp) has a fibrous structure and binds to different extracellular matrices. Sci Rep 7(1):13665
Glowalla E, Tosetti B, Krönke M, Krut O (2009) Proteomics-based identification ofanchorless cell wall proteins as vaccine candidates against Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun 77(7):2719–2729
Gotoh K, Kodama T, Hiyoshi H, Izutsu K, Park KS, Dryselius R, Akeda Y, Honda T, Iida T (2010) Bile acid-induced virulence gene expression of Vibrio parahaemolyticus reveals a novel therapeutic potential for bile acid sequestrants. PLoS One 5(10):e13365
Gralnick JA, Newman DK (2007) Extracellular respiration. Mol Microbiol 65(1):1–11
Green ER, Mecsas J (2016) Bacterial secretion systems: an overview. Virulence mechanisms of bacterial pathogen. Microbiol Spectr 4(1):1–19
Gupta MK, Subramanian V, Yadav JS (2009) Immunoproteomic identification of secretory and subcellular protein antigens and functional evaluation of the secretome fraction of Mycobacterium immunogenum, a newly recognized species of the Mycobacterium chelonae-Mycobacterium abscessus group. J Proteome Res 8(5):2319–2330
Hallgren J, Tsirigos KD, Pedersen MD, Armenteros JJA, Marcatili P, Nielsen H, Krogh A, Winther O (2022) DeepTMHMM predicts alpha and beta transmembrane proteins using deep neural networks. bioRxiv 10:2022 04
He Y, Wang H, Chen L (2015) Comparative secretomics reveals novel virulence-associated factors of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Front Microbiol 6:707
Hiller K, Grote A, Scheer M, Münch R, Jahn D (2004) PrediSi: prediction of signal peptides and their cleavage positions. Nucleic Acids Res 32:W375–W379
Hubbard TP, Chao MC, Abel S, Blondel CJ, zur Wiesch PA, Zhou X, Davis BM, Waldor MK (2016) Genetic analysis of Vibrio parahaemolyticus intestinal colonization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113:6283–6288
Huo T, Liu W, Guo Y, Yang C, Lin J, Rao Z (2015) Prediction of host-pathogen protein interactions between Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Homo sapiens using sequence motifs. BMC Bioinform 16:100
Islam N, Nagy A, Garrett WM, Shelton D, Cooper B, Nou X (2016) Different cellular origins and functions of extracellular proteins from Escherichia coli O157: H7 and O104: H4 as determined by comparative proteomic analysis. Appl Environ Microbiol 82:4371–4378
Kapur SK, Katz AJ (2013) Review of the adipose derived stem cell secretome. Biochimie 95:2222–2228
Karam J, Méresse S, Kremer L, Daher W (2020) The roles of tetraspanins in bacterial infections. Cell Microbiol 22:e13260
Kenny B, Finlay BB (1995) Protein secretion by enteropathogenic Escherichia coli is essential for transducing signals to epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:7991–7995
Kumar R, Nanduri B (2010) HPIDB-a unified resource for host-pathogen interactions. BMC Bioinform 11:S16
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680
Lamkanfi M, Dixit VM (2010) Manipulation of host cell death pathways during microbial infections. Cell Host Microbe 8:44–54
Lehr S, Hartwig S, Sell H (2012) Adipokines: a treasure trove for the discovery of biomarkers for metabolic disorders. Proteomics Clin Appl 6:91–101
Lerm M, Schmidt G, Aktories K (2000) Bacterial protein toxins targeting rho GTPases. FEMS Microbiol Lett 188:1–6
Letchumanan V, Chan KG, Khan TM, Bukhari SI, Ab Mutalib NS, Goh BH, Lee LH (2017) Bile sensing: the activation of Vibrio parahaemolyticus virulence. Front Microbiol 8:728
Li P, Rivera-Cancel G, Kinch LN, Salomon D, Tomchick DR, Grishin NV, Orth K (2016) Bile salt receptor complex activates a pathogenic type III secretion system. Elife 5:e15718
Löwer M, Weydig C, Metzler D, Reuter A, Starzinski-Powitz A, Wessler S, Schneider G (2008) Prediction of extracellular proteases of the human pathogen Helicobacter pylori reveals proteolytic activity of the Hp1018/19 protein HtrA. PLoS One 3(10):e3510
Ma W, Guttman DS (2008) Evolution of prokaryotic and eukaryotic virulence effectors. Curr Opin Plant Biol 11:412–419
Maffei B, Francetic O, Subtil A (2017) Tracking proteins secreted by bacteria: what's in the toolbox? Front Cell Infect Microbiol 7:221
Mahdavi A, Szychowski J, Ngo JT, Sweredoski MJ, Graham RL, Hess S, Schneewind O, Mazmanian SK, Tirrell DA (2014) Identification of secreted bacterial proteins by noncanonical amino acid tagging. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:433–438
Marketon JIW, Sternberg EM (2010) The glucocorticoid receptor: a revisited target for toxins. Toxins 2:1357–1380
Michel GP, Voulhoux R (2009) The type II secretory system (T2SS) in Gram-negative bacteria: a molecular nanomachine for secretion of Sec and Tatdependent extracellular proteins. In: Wooldridge KG (ed) Bacterial Secreted Proteins: Secretory Mechanisms and Role in Pathogenesis. Caister Academic Press, Norfolk, pp 67–92
Mota LJ, Sorg I, Cornelis GR (2005) Type III secretion: the bacteria-eukaryotic cell express. FEMS Microbiol Lett 252(1):1–10
Muthukrishnan G, Quinn GA, Lamers RP, Diaz C, Cole AL, Chen S, Cole AM (2011) Exoproteome of Staphylococcus aureus reveals putative determinants of nasal carriage. J Proteome Res 10(4):2064–2078
Naderer T, Fulcher MC (2018) Targeting apoptosis pathways in infections. J Leukoc Biol 103(2):275–285
O’Farrell PH (1975) High- resolution two-dimentional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem 250(10):4007–4027
Pace JL, Chai TJ, Rossi HA, Jiang X (1997) Effect of bile on Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Appl Environ Microbiol 63(6):2372–2377
Paria P, Behera BK, Mohapatra PKD, Parida PK (2021) Virulence factor genes and comparative pathogenicity study of tdh, trh and tlh positive Vibrio parahaemolyticus strains isolated from Whiteleg shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone, 1931) in India. Infect Genet Evol 95:105083
Paria P, Chakraborty HJ, Behera BK (2022) Identification of novel salt tolerance-associated proteins from the secretome of Enterococcus faecalis. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 38(10):177
Paria P, Chakraborty HJ, Behera BK, Mohapatra PKD, Das BK (2019) Computational characterization and molecular dynamics simulation of the thermostable direct hemolysin-related hemolysin (TRH) amplified from Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Microb Pathog 127:172–182
Park KS, Ono T, Rokuda M, Jang MH, Okada K, Iida T, Honda T (2004) Functional characterization of two type III secretion systems of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Infect Immun 72(11):6659–6665
Pathak VM (2017) Review on the current status of polymer degradation: a microbial approach. Bioresour Bioprocess 4:1–31
Pearson WR (2013) An introduction to sequence similarity (“homology”) searching. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics 42(1):3–1
Petronella N, Ronholm J (2018) The mechanisms that regulate Vibrio parahaemolyticus virulence gene expression differ between pathotypes. Microb Genom 4(6):e000182
Renier S, Micheau P, Talon R, Hébraud M, Desvaux M (2012) Subcellular localization of extracytoplasmic proteins in monoderm bacteria: rational secretomics-based strategy for genomic and proteomic analyses. PLoS One 7(8):e42982
Salomon D, Klimko JA, Orth K (2014) H-NS regulates the Vibrio parahaemolyticus type VI secretion system 1. Microbiology 160(Pt 9):1867
Sangsri T, Saiprom N, Tubsuwan A, Monk P, Partridge LJ, Chantratita N (2020) Tetraspanins are involved in Burkholderia pseudomallei-induced cell-to-cell fusion of phagocytic and non-phagocytic cells. Sci Rep 10(1):17972
Satala D, Karkowska-Kuleta J, Zelazna A, Rapala-Kozik M, Kozik A (2020) Moonlighting proteins at the candidal cell surface. Microorganisms 8(7):1046
Schweppe DK, Harding C, Chavez JD, Wu X, Ramage E, Singh PK, Manoil C, Bruce JE (2015) Host-microbe protein interactions during bacterial infection. Chem Biol 22(11):1521–1530
Shan X, Fu J, Li X, Peng X, Chen L (2022) Comparative proteomics and secretomics revealed virulence, and coresistance-related factors in non O1/O139 Vibrio cholerae recovered from 16 species of consumable aquatic animals. J Proteome 251:104408
Shevchenko A, Tomas H, Havli J, Olsen JV, Mann M (2006) In-gel digestion for mass spectrometric characterization of proteins and proteomes. Nat Protoc 1(6):2856–2860
Singh B, Fleury C, Jalalvand F, Riesbeck K (2012) Human pathogens utilize host extracellular matrix proteins laminin and collagen for adhesion and invasion of the host. FEMS Microbiol Rev 36(6):1122–1180
Stojanovic M, Germain M, Nguyen M, Shore GC (2005) BAP31 and its caspase cleavage product regulate cell surface expression of tetraspanins and integrin-mediated cell survival. J Biol Chem 280(34):30018–30024
Szklarczyk D, Gable AL, Lyon D, Junge A, Wyder S, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Doncheva NT, Morris JH, Bork P, Jensen LJ (2019) STRING v11: protein–protein association networks with increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide experimental datasets. Nucleic Acids Res 47(D1):D607–D613
Tato CM, Hunter CA (2002) Host-pathogen interactions: subversion and utilization of the NF-κB pathway during infection. Infect Immun 70(7):3311–3317
Terán LC, Distefano M, Bellich B, Petrosino S, Bertoncin P, Cescutti P, Sblattero D (2020) Proteomic studies of the biofilm matrix including outer membrane vesicles of Burkholderia multivorans C1576, a strain of clinical importance for cystic fibrosis. Microorganisms 8(11):1826
Teufel F, Almagro Armenteros JJ, Johansen AR, Gíslason MH, Pihl SI, Tsirigos KD, Winther O, Brunak S, von Heijne G, Nielsen H (2022) SignalP 6.0 predicts all five types of signal peptides using protein language models. Nat Biotechnol 40(7):1023–1025
Trost M, Wehmhöner D, Kärst U, Dieterich G, Wehland J, Jänsch L (2005) Comparative proteome analysis of secretory proteins from pathogenic and nonpathogenic Listeria species. Proteomics 5(6):1544–1557
Tunio SA, Oldfield NJ, Ala'Aldeen DA, Wooldridge KG, Turner DP (2010) The role of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GapA-1) in Neisseria meningitidis adherence to human cells. BMC Microbiol 10:280
Ulett GC, Maclean KH, Nekkalapu S, Cleveland JL, Adderson EE (2005) Mechanisms of group B streptococcal-induced apoptosis of murine macrophages. J Immunol 175(4):2555–2562
Vaca DJ, Thibau A, Schütz M, Kraiczy P, Happonen L, Malmström J, Kempf VA (2020) Interaction with the host: the role of fibronectin and extracellular matrix proteins in the adhesion of Gram-negative bacteria. Med Microbiol Immunol 209(3):277–299
Van den Bossche S, Vandeplassche E, Ostyn L, Coenye T, Crabbé A (2020) Bacterial interference with lactate dehydrogenase assay leads to an underestimation of cytotoxicity. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 10:494
Welling GW, Weijer WJ, van der Zee R, Welling-Wester S (1985) Prediction of sequential antigenic regions in proteins. FEBS Lett 188(2):215–218
Wilhelm E, Kornete M, Targat B, Vigneault-Edwards J, Frontini M, Tora L, Benecke A, Bell B (2010) TAF6δ orchestrates an apoptotic transcriptome profile and interacts functionally with p53. BMC Mol Biol 11(1):1–15
Yu CS, Chen YC, Lu CH, Hwang JK (2006) Prediction of protein subcellular localization. Proteins 64(3):643–651
Zhang L, Orth K (2013) Virulence determinants for Vibrio parahaemolyticus infection. Curr Opin Microbiol 16(1):70–77
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Dr. Praveen Maurye, Scientist, ICAR-Central Inland Fisheries Research Institute, Barrackpore, Kolkata, for providing laboratory support and guidance for 2D Gel Electrophoresis. The authors express their gratitude to Dr. Satabdi Ganguly, ICAR-CIFRI, Barrackpore for reviewing the manuscript and providing valuable suggestions that contributed to its improvement.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Prasenjit Paria: conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, writing—original draft, methodology, investigation; Hirak Jyoti Chakraborty: formal analysis, investigation, methodology; Abhijit Pakhira: writing—original draft, formal analysis, investigation; Manoharmayum Shaya Devi: formal analysis, writing—review and editing; Pradeep Kumar Das Mohapatra: conceptualization, supervision, writing—review and editing. Bijay Kumar Behera: supervision, funding acquisition, review and editing
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or live vertebrates and/or higher invertebrates.
Consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
All authors have provided their consent for the publication of this manuscript.
Institutional review board statement
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Paria, P., Chakraborty, H.J., Pakhira, A. et al. Identification of virulence-associated factors in Vibrio parahaemolyticus with special reference to moonlighting protein: a secretomics study. Int Microbiol (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10123-023-00429-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10123-023-00429-y