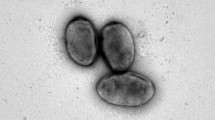
Abstract
A Gram-negative, aerobic bacterial strain RR6T was isolated from the sea sand to produce lipase and proposed as a novel species of Halopseudomonas. The optimum growth occurred at 28–37 °C, and the pH was 6.0–8.0. The optimum growth occurred at 3.0 -6.5% (w/v) NaCl. The major cellular fatty acids were C10:0 3OH, C12:0, C16:1 ω7c/16:1 ω6c, 18:1 ω7c and/or 18:1 ω6c, and C16:0. The predominant polar lipids were phosphatidylglycerol, diphosphatidylglycerol, phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylcholine, unidentified phospholipid, and unidentified lipids. The genome is 3.93 Mb, and the G + C content is 61.3%. The 16S rRNA gene sequences shared 99.73–99.87% sequence similarity with the closely related type strains of Halopseudomonas. The average nucleotide identity and average amino acid identity of strain RR6T with reference type strains were below 95–96%, and the corresponding in-silico DNA–DNA hybridization values were below 70%. Strain RR6T clustered with Halopseudomonas gallaeciensis V113T and Halopseudomonas pachastrellae CCUG 46540 T in the phylogenetic tree. Further, lipase produced by this bacterium belongs to α/β hydrolase lipase family and exhibits structural similarity to the lactonizing lipase. Based on the polyphasic analysis, the new isolates RR6T represent a novel species of Halopseudomonas for which Halopseudomonas maritima sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain is RR6T (= NBRC 115418 T = TBRC 15628 T).





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ accession numbers for the whole genome and 16S rRNA sequences of Halopseudomonas maritima strain RR6T are MZ855216 and CP079801, respectively.
Abbreviations
- ANI:
-
Average nucleotide identity
- AAI:
-
Average amino acid identity
- DDH:
-
DNA–DNA hybridization
References
Albayati SH, Masomian M, Ishak SNH, Mohamad Ali MSb, Thean AL, Mohd Shariff Fb, Muhd Noor NDb, Raja Abd Rahman RNZ (2020) Main structural targets for engineering lipase substrate specificity. Catalysts 10:747. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10070747
Arpigny JL, Jaeger KE (1999) Bacterial lipolytic enzymes: classification and properties. Biochem J 343:177–183
Bandyopadhyay S, Schumann P, Das SK (2013) Pannonibacter indica sp. nov., a highly arsenate-tolerant bacterium isolated from a hot spring in India. Arch Microbiol 195:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-012-0840-z
Bernardet JF, Nakagawa Y, Holmes B, Subcommittee on the taxonomy of Flavobacterium and Cytophaga-like bacteria of the International Committee on Systematics of Prokaryotes (2002) Proposed minimal standards for describing new taxa of the family Flavobacteriaceae and emended description of the family. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52:1049–1070. https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-52-3-1049
Bligh EG, Dyer WJ (1959) A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol 37:911–917. https://doi.org/10.1139/o59-099
Bruns A, Rohde M, Berthe-Corti L (2001) Muricauda ruestringensis gen. nov., sp. nov., a facultatively anaerobic, appendaged bacterium from German North Sea intertidal sediment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:1997–2006. https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-51-6-1997
Cheng TH, Ismail N, Kamaruding N, Saidin J, Danish-Daniel M (2020) Industrial enzymes-producing marine bacteria from marine resources. Biotechnol Rep (Amst) 27:e00482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2020.e00482
Das L, Deb S, Das SK (2020) Glutamicibacter mishrai sp. nov., isolated from the coral Favia veroni from Andaman Sea. Arch Microbiol 202:733–745. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-019-01783-0
De Santi C, Altermark B, de Pascale D, Willassen NP (2016) Bioprospecting around Arctic islands: Marine bacteria as rich source of biocatalysts. J Basic Microbiol 56:238–253. https://doi.org/10.1002/jobm.201500505
Debnath T, Kujur RRA, Mitra R, Das SK (2019) Diversity of Microbes in Hot springs and their sustainable Use. Vol: 1. Microbial Diversity in Normal & Extreme Environments. Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd., Singapore, pp 159–186. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-8315-1_6
Elleuche S, Schäfers C, Blank S, Schröder C, Antranikian G (2015) Exploration of extremophiles for high temperature biotechnological processes. Curr Opin Microbiol 25:113–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mib.2015.05.011
Glogauer A, Martini VP, Faoro H, Couto GH, Müller-Santos M, Monteiro RA, Mitchell DA, de Souza EM, Pedrosa FO, Krieger N (2011) Identification and characterization of a new true lipase isolated through metagenomic approach. Microb Cell Fact 10:54. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2859-10-54
Ihara F, Kageyama Y, Hirata M, Nihira T, Yamada Y (1991) Purification, characterization, and molecular cloning of lactonizing lipase from Pseudomonas species. J Biol Chem 266:18135–18140
Jung YT, Oh TK, Yoon JH (2012) Marinomonas hwangdonensis sp. nov., isolated from seawater. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:2062–2067. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.036582-0
Jyoti V, Narayan KD, Das SK (2010) Gulbenkiania indica sp. nov., isolated from a sulfur spring. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:1052–1055. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.014035-0
Kelley LA, Mezulis S, Yates CM, Wass MN, Sternberg MJ (2015) The Phyre2 web portal for protein modeling, prediction and analysis. Nat Protoc 10:845–858. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2015.053
Kim OS, Cho YJ, Lee K et al (2012) Introducing EzTaxon-e: a prokaryotic 16S rRNA gene sequence database with phylotypes that represent uncultured species. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:716–721. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.038075-0
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol 16:111–120. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01731581
Konstantinidis KT, Tiedje JM (2005a) Genomic insights that advance the species definition for prokaryotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:2567–2572. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0409727102
Konstantinidis KT, Tiedje JM (2005b) Towards a genome-based taxonomy for prokaryotes. J Bacteriol 87:6258–6264. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.187.18.6258-6264.2005
Kovacic F, Babic N, Krauss U, Jaeger KE (2019) Classification of Lipolytic Enzymes from Bacteria. In: Rojo F (ed) Aerobic utilization of hydrocarbons, oils and lipids. Handbook of Hydrocarbon and Lipid Microbiology. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-39782-5_39-1
Kumar A, Mukhia S, Kumar N, Acharya V, Kumar S, Kumar R (2020) A broad temperature active lipase purified from a psychrotrophic bacterium of Sikkim Himalaya with potential application in detergent formulation. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 25(8):642. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2020.00642
Kumari P, Poddar A, Das SK (2014) Marinomonas fungiae sp. nov., isolated from the coral Fungia echinata from the Andaman Sea. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:487–494. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.054809-0
Lagesen K, Hallin P, Rødland EA, Stærfeldt H-H, Rognes T, Ussery DW (2007) RNammer: consistent annotation of rRNA genes in genomic sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 35:3100–3108. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkm160
Laskowski RA, Jabłońska J, Pravda L, Vařeková RS, Thornton JM (2018) PDBsum: Structural summaries of PDB entries. Protein Sci 27:129–134. https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.3289
Lin S-Y, Hameed A, Liu Y-C, Hsu Y-H, Lai W-A, Chiu-Chung Y (2013) Pseudomonas formosensis sp. nov., a gammaproteobacteria isolated from food-waste compost in Taiwan. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:3168–3174. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.049452-0
Lowe TM, Eddy SR (1997) tRNAscan-SE: a program for improved detection of transfer RNA genes in genomic sequence. Nucleic Acids Res 25:955–964. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/25.5.0955
Masomian M, Rahman RN, Salleh AB, Basri M (2016) Analysis of comparative sequence and genomic data to verify phylogenetic relationship and explore a new subfamily of bacterial lipases. PLoS One 11:e0149851. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0149851
Meier-Kolthoff JP, Auch AF, Klenk HP, Göker M (2013) Genome sequence-based species delimitation with confidence intervals and improved distance functions. BMC Bioinform 14:60 (http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2105/14/60)
Mulet M, Sánchez D, Rodríguez AC, Nogales B, Bosch R, Busquets A, Gomila M, Lalucat J, García-Valdés E (2018) Pseudomonas gallaeciensis sp. nov., isolated from crude-oil-contaminated intertidal sand samples after the Prestige oil spill. Syst Appl Microbiol 41:340–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.syapm.2018.03.008
Na S-I, Kim YO, Yoon S-H, Ha S-M, Baek I, Chun J (2018) UBCG: up-to-date bacterial core gene set and pipeline for phylogenomic tree reconstruction. J Microbiol 56:280–285. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-018-8014-6
Nardini M, Lang DA, Liebeton K, Jaeger KE, Dijkstra BW (2000) Crystal structure of Pseudomonas aeruginosa lipase in the open conformation. The prototype for family I.1 of bacterial lipases. J Biol Chem 275:31219–31225. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M003903200
Overbeek R, Olson R, Pusch GD, Olsen GJ, Davis JJ, Disz T, Edwards RA, Gerdes S, Parrello B, Shukla M, Vonstein V, Wattam AR, Xia F, Stevens R (2014) The SEED and the Rapid Annotation of microbial genomes using Subsystems Technology (RAST). Nucleic Acids Res 42:D206–D214. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt1226
Panday D, Schumann P, Das SK (2011) Rhizobium pusense sp. nov., isolated from the rhizosphere of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:2632–2639. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.028407-0
Pham VHT, Kim J, Chang S, Chung W (2021) Investigation of lipolytic-secreting bacteria from an artificially polluted soil using a modified culture method and optimization of their lipase production. Microorganisms 9:2590. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9122590
Ramnath L, Sithole B, Govinden R (2017) Classification of lipolytic enzymes and their biotechnological applications in the pulping industry. Can J Microbiol 63:179–192. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjm-2016-0447
Robert X, Gouet P (2014) Deciphering key features in protein structures with the new ENDscript server. Nucleic Acids Res 42:W320–W324. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku316
Rodriguez-R LM, Konstantinidis KT (2016) The enveomics collection: a toolbox for specialized analyses of microbial genomes and metagenomes. PeerJ Preprints 4:e1900v1. https://doi.org/10.7287/peerj.preprints.1900v1
Romanenko LA, Uchino M, Falsen E, Frolova GM, Zhukova NV, Mikhailov VV (2005) Pseudomonas pachastrellae sp. nov., isolated from a marine sponge. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:919–924. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.63176-0
Rudra B, Gupta RS (2021) Phylogenomic and comparative genomic analyses of species of the family Pseudomonadaceae: Proposals for the genera Halopseudomonas gen. nov. and Atopomonas gen. nov., merger of the genus Oblitimonas with the genus Thiopseudomonas, and transfer of some misclassified species of the genus Pseudomonas into other genera. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 71:005011. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.005011
Salameh MA, Wiegel J (2007) Purification and characterization of two highly thermophilic alkaline lipases from Thermosyntropha lipolytica. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:7725–7731. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01509-07
Salzberg SL, Delcher AL, Kasif S, White O (1998) Microbial gene identification using interpolated Markov models. Nucleic Acids Res 26:544–548. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/26.2.544
Sánchez D, Mulet M, Rodríguez AC, David Z, Lalucat J, García-Valdés E (2014) Pseudomonas aestusnigri sp. nov., isolated from crude oil-contaminated intertidal sand samples after the Prestige oil spill. Syst Appl Microbiol 37:89–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.syapm.2013.09.004
Sharma A, Meena KR, Kanwar SS (2018) Molecular characterization and bioinformatics studies of a lipase from Bacillus thermoamylovorans BHK67. Int J Biol Macromol 107:2131–2140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.10.092
Smibert RM, Krieg NR (1994) Phenotypic characterization. In: Gerhardt P, Murray RGE, Wood WA, Krieg NR (eds) Methods for General and Molecular Bacteriology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC, pp 607–655
Stamatakis A (2014) RAxML version 8: a tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 30:1312–1313. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu033
Tamura K, Stecher G, Kumar S (2021) MEGA11: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Mol Biol Evol 38:3022–3027. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msab120
Ward AC, Bora N (2006) Diversity and biogeography of marine actinobacteria. Curr Opin Microbiol 9:279–286. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.13926
Wei Y, Mao H, Xu Y, Zou W, Fang J, Blom J (2018) Pseudomonas abyssi sp. nov., isolated from the abyssopelagic water of the Mariana Trench. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 68:2462–2467. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.002785
Xu D, Zhang Y (2011) Improving the physical realism and structural accuracy of protein models by a two-step atomic-level energy minimization. Biophys J 101:2525–2534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2011.10.024
Yoon SH, Ha SM, Lim JM, Kwon S, Chun J (2017) A large-scale evaluation of algorithms to calculate average nucleotide identity. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 110:1281–1286. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-017-0844-4
Zhang D-C, Liu H-C, Zhou Y-G, Schinner F, Margesin R (2011) Pseudomonas bauzanensis sp. nov., isolated from soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:2333–2337. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.026104-0
Acknowledgements
The author R.R.A.K. acknowledge the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), New Delhi, Government of India for providing the research fellowship. We acknowledge the Distributed Information Sub-Center (DISC) at the Institute of Life Sciences, Bhubaneswar, for the computational facility and Transmission Electron Microscopic Facility. We are thankful to Professor B. Schink (Universitaet Konstanz, Germany) for etymological advice.
Funding
This work was supported by the funding received from the Department of Biotechnology, Government of India (D.O.No. BT/BI/04/058/2002 VOL-II) to SKD.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SKD: developed the concept and designed the experiment. RRAK, MG, SB conducted the experiment. RRAK, MG, SB and SKD analysed the data and wrote the manuscript. All of us read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Ethical approval was not required to carry out this research work.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kujur, R.R.A., Ghosh, M., Basak, S. et al. Phylogeny and structural insights of lipase from Halopseudomonas maritima sp. nov., isolated from sea sand. Int Microbiol 26, 1021–1031 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10123-023-00362-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10123-023-00362-0