Abstract
Introduction
At present, the presence of lead (Pb2+) continues to be a problem in water bodies due to its continuous use and high toxicity. The aim of this study was to investigate the bacterial diversity of a potential consortium used as a biosorbent for the removal of lead in an aqueous solution.
Methods
The minimum inhibitory concentration and the mean lethal dose of the consortium were determined, and then the optimal variables of pH and temperature for the removal process were obtained. With the optimal conditions, the kinetic behavior was evaluated, and adjustments were made to different mathematical models. A Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy analysis was performed to determine the functional groups of the biomass participating in the removal process, and the diversity of the bacterial consortium was evaluated during Pb2+ removal by an Ion Torrent Personal Genome Machine System.
Results
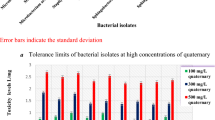
It was found that the intraparticle diffusion model was the one that described the adsorption kinetics showing a higher rate constant with a higher concentration of Pb2+, while the Langmuir model was that explained the isotherm at 35 °C, defining a maximum adsorption load for the consortium of 54 mg/g. In addition, it was found that Pb2+ modified the diversity and abundance of the bacterial consortium, detecting genera such as Pseudomonas, Enterobacter, Citrobacter, among others.
Conclusions
Thus, it can be concluded that the bacterial consortium from mining soil was a biosorbent with the ability to tolerate high concentrations of Pb2+ exposure. The population dynamics during adsorption showed enrichment of Proteobacteria phyla, with a wide range of bacterial families and genera capable of resisting and removing Pb2+ in solution.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All experimental and analyzed data are available.
References
Babel S, Kurniawan TA (2003) Low-cost adsorbents for heavy metals uptake from contaminated water: a review. J Hazard Mat 97:219–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3894(02)00263-7
Bowman N, Patel D, Sanchez A, Xu W, Alsaffar A, Tiquia-Arashiro SM (2018) Lead-resistant bacteria from Saint Clair River sediments and Pb removal in aqueous solutions. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102:2391–2398. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-8772-4
Brierley CL (1990) Metal immobilization using bacteria. In: Ehrlich HL, Brierley CL (eds) Microbial mineral recovery. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 303–324
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Gonzalez-Peña A, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI, Huttley GA, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koenig JE, Ley RE, Lozupone CA, McDonald D, Muegge BD, Pirrung M, Reeder J, Sevinsky JR, Turnbaugh PJ, Walters WA, Widmann J, Yatsunenko T, Zaneveld J, Knight R (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7:335–433. https://doi.org/10.1038/NMETH.F.303
Charkiewicz AE, Backstrand JR (2020) Lead toxicity and pollution in Poland. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17(12):4385. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17124385
Chen Z, Xing B, McGill WB (1999) A unified sorption variable for environmental applications of the Freundlich isotherm. J Environ Qual 28:1422–1428. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq1999.00472425002800050005x
Chen C, Xu XJ, Xie P, Yuan Y, Zhou X, Wang AJ, Ren NQ (2017) Pyrosequencing reveals microbial community dynamics in integrated simultaneous desulfurization and denitrification process at different influent nitrate concentrations. Chemosphere 171:294–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.11.159
Chojnacka K, Chojnacki A, Gorecka H (2005) Biosorption of Cr3+, Cd2+ and Cu2+ ions by blue–green algae Spirulina sp.: kinetics, equilibrium and the mechanism of the process. Chemosphere 59:75–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.10.005
Chojnacka K (2010) Biosorption and bioaccumulation–the prospects for practical applications. Environ Int 36:299–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2009.12.001
Congeevaram S, Dhanarani S, Park J, Dexilin M, Thamaraiselvi K (2007) Biosorption of chromium and nickel by heavy metal resistant fungal and bacterial isolates. J Hazard Mater 146:270–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.12.017
Cristani M, Naccari C, Nostro A, Pizzimenti A, Trombetta D, Pizzimenti F (2012) Possible use of Serratia marcescens in toxic metal biosorption (removal). Environment Sci Pollut Res 19:161–168. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-011-0539-8
Elovich SY, Larinov OG (1962) Theory of adsorption from solutions of non-electrolytes on solid (I) equation adsorption from solutions and the analysis of its simplest form, (II) verification of the equation of adsorption isotherm from solutions. Izv Akad Nauk SSSR, Otd Khim Nauk 2:209–216
Frank JJ, Poulakos AG, Tornero-Velez R, Xue J (2019) Systematic review and meta-analyses of lead (Pb) concentrations in environmental media (soil, dust, water, food, and air) reported in the United States from 1996 to 2016. Sci Total Environ 694:133489–133489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.07.295
Gabr RM, Hassan SHA, Shoreit AAM (2008) Biosorption of lead and nickel by living and non-living cells of Pseudomonas aeruginosa ASU 6a. Int Biodeter Biodegr 62:195–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2008.01.008
Gadd GM (2009) Heavy metal pollutants: environmental and biotechnological aspects. In: Schaechter M (ed) Encyclopedia of microbiology, 3rd edn. Elsevier, Oxford, pp 321–334
García-Mena J, Murugesan S, Pérez-Muñoz AA, García-Espitia M, Maya O, Jacinto-Montiel M, Núñez-Cardona MT (2016) Airborne bacterial diversity from the low atmosphere of Greater Mexico City. Microb Ecol 72:70–84. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-016-0747-3
Hernández-Quiroz F, Nirmalkar K, Villalobos-Flores LE, Murugesan S, Cruz-Narváez Y, Rico-Arzate E, Hoyo-Vadillo C, Chavez-Carbajal A, Pizano-Zárate ML, García-Mena J (2019) Influence of moderate beer consumption on human gut microbiota and its impact on fasting glucose and β-cell function. Alcohol 12:77–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.alcohol.2019.05.006
Ho YS, McKay G (1998) Sorption of dye from aqueous solution by peat. Chem Eng J 70:115–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0923-0467(98)00076-1
Huang H, Cao L, Wan Y, Zhang R, Wang W (2012) Biosorption behavior and mechanism of heavy metals by the fruiting body of jelly fungus (Auricularia polytricha) from aqueous solutions. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 96:829–840. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3846-6
Jafarian V, Ghaffari F (2017) A unique metallothionein-engineered in Escherichia coli for biosorption of lead, zinc, and cadmium; absorption or adsorption? Microbiol 86:73–81. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261717010064
Kamaraj SK, Rivera AE, Murugesan S, García-Mena J, Maya O, Frausto-Reyes C, Tapia-Ramírez J, Espino HS, Caballero-Briones F (2019) Electricity generation from Nopal biogas effluent using a surface modified clay cup (cantarito) microbial fuel cell. Heliyon 5(4):e01506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e01506
Kuffner M, Puschenreiter M, Wieshammer G, Gorfer M, Sessitsch A (2008) Rhizosphere bacteria affect growth and metal uptake of heavy metal accumulating willows. Plant Soil 304:35–44. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-007-9517-9
Lakzian A, Berenji AR, Karimi E, Razavi S (2008) Adsorption capability of lead, nickel and zinc by exopolysaccharide and dried cell of Ensifer meliloti. Asian J Chem 20:6075–6080
Langmuir I (1918) The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J Am Chem Soc 40:1361–1403
Largegren S (1898) About the theory of so-called adsorption of soluble substances. Kungliga Suensk Vetenskapsakademiens Handlingar 24:1–39
Li L, Guo S, Sun Y, Li X, Gao Y, Xu H, Li Y (2019) Detoxification effect of single inoculation and co-inoculation of Oudemansiella radicata and Serratia marcescens on Pb and fluoranthene co-contaminated soil. J Soil Sediment 19:3008–3017. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-019-02304-8
Liu C, Lin H, Dong Y, Li B, Liu Y (2018) Investigation on microbial community in remediation of lead-contaminated soil by Trifolium repensL. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 165:52–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.08.054.10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.08.054
Lu WB, Shi JJ, Wang CH, Chang JS (2006) Biosorption of lead, copper and cadmium by an indigenous isolate Enterobacter sp. J1 possessing high heavy-metal resistance. J Hazard Mater 134:80–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.10.036
McLean RJC, Beveridge TJ (1990) Metal binding capacity of bacterial surfaces and their ability to form mineralized aggregates. In: Ehrlicg HL, Brierley CL (eds) Microbial mineral recovery. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 185–222
Morosanu I, Teodosiu C, Paduraru C, Ibanescu D, Tofan L (2017) Biosorption of lead ions from aqueous effluents by rapeseed biomass. New Biotechnol 39:110–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbt.2016.08.002
Muñoz AJ, Espínola F, Ruiz E (2018) Removal of heavy metals by Klebsiella sp. 3S1. Kinetics, equilibrium and interaction mechanisms of Zn (II) biosorption. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 93:1370–1380. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.5503
Naik MM, Dubey SK (2013) Lead resistant bacteria: lead resistance mechanisms, their applications in lead bioremediation and biomonitoring. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 98:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2013.09.039
Naranjo VI, Hendricks M, Jones KS (2020) Lead toxicity in children: an unremitting public health problem. Pediatr Neurol 113:51–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2020.08.005
Nirmalkar K, Murugesan S, Pizano-Zárate ML, Villalobos-Flores LE, García-González C, Morales Hernández RM, Nuñez-Hernández JA, Hernández-Quiroz F, Romero-Figueroa MDS, Hernández Guerrero C, Hoyo-Vadillo C, García-Mena J (2018) Gut microbiota and endothelial dysfunction markers in obese Mexican children and adolescents. Nutrients 10:2009. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10122009
Pieper KJ, Krometis LAH, Gallagher DL, Benham BL, Edwards M (2015) Incidence of waterborne lead in private drinking water systems in Virginia. J Water Health 13:897–908. https://doi.org/10.2166/wh.2015.275
Priyadarshanee M, Das S (2021) Biosorption and removal of toxic heavy metals by metal tolerating bacteria for bioremediation of metal contamination: a comprehensive review. J Environ Chem Eng 9(1):104686. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104686
Qu Y, Meng Q, Zhao Q, Ye Z (2015) Biosorption of Pb(II) and Zn(II) from aqueous solutions by living B350 biomass. Desalination Water Treat 55:1832–1839. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2014.929978
Ramrakhiani L, Halder A, Majumder A, Mandal AK, Majumdar S, Ghosh S (2017) Industrial waste derived biosorbent for toxic metal remediation: mechanism studies and spent biosorbent management. Chem Eng J 308:1048–1064. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.09.145
Shomar B, Al-Darwish K, Vincent A (2020) Optimization of wastewater treatment processes using molecular bacteriology. J Water Process Eng 33:101030. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2019.101030
Temkin MI, Pyzhev V (1940) Kinetics of ammonia synthesis on promoted iron catalyst. Acta Physiochim URSS 12:217–222
Tiquia-Arashiro SM (2018) Lead absorption mechanisms in bacteria as strategies for lead bioremediation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102:5437–5444. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-8969-6
Topcu A, Bulat T (2010) Removal of cadmium and lead from aqueous solution by Enterococcus faecium strains. J Food Sci 75:T13–T17. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1750-3841.2009.01429.x
Tunali S, Çabuk A, Akar T (2006) Removal of lead and copper ions from aqueous solutions by bacterial strain isolated from soil. Chem Eng J 115:203–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2005.09.023
Ubalde MC, Braña V, Sueiro F, Morel MA, Martínez-Rosales C, Marquez C, Castro-Sowinski S (2012) The versatility of Delftia sp. isolates as tools for bioremediation and biofertilization technologies. Curr Microbiol 64:597–603. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-012-0108-5
Uslu G, Tanyol M (2006) Equilibrium and thermodynamic parameters of single and binary mixture biosorption of lead (II) and copper (II) ions onto Pseudomonas putida: effect of temperature. J Hazard Mater 135:87–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.11.029
Verma A, Bishnoi NR, Gupta A (2017) Optimization study for Pb (II) and COD sequestration by consortium of sulphate-reducing bacteria. Appl Water Sci 7:2309–2320. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-016-0402-7
Velázquez-Jimenez LH, Pavlick A, Rangel-Mendez JR (2013) Chemical characterization of raw and treated agave bagasse and its potential as adsorbent of metal cations from water. Ind Crop Prod 43:200–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2012.06.049
Wang J, Chen C (2006) Biosorption of heavy metals by Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a review. Biotechnol Adv 24(5):427–451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2006.03.001
Wang X, Deng W, Xie Y, Wang C (2013) Selective removal of mercury ions using a chitosan – poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogel adsorbent with three-dimensional network structure. Chem Eng J 228:232–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.04.104
Wang J, Li Q, Li MM, Chen TH, Zhou YF, Yue ZB (2014) Competitive adsorption of heavy metal by extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) extracted from sulfate reducing bacteria. Bioresour Technol 163:374–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.04.073
Weber WJ, Morris JC (1963) Kinetics of adsorption on carbon from solution. J Sanit Eng Div 89:31–60
World Health Organization, International Programme on Chemical Safety. The public health impact of chemicals: knowns and unknowns; 2016. Available at http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/206553/1/WHO_FWC_PHE_EPE_16. 01_eng.pdf?ua¼1. Accessed October 28, 2022
Xavier JC, Costa PES, Hissa DC, Melo VMM, Falcão RM, Balbino VQ, Verde LCL (2019) Evaluation of the microbial diversity and heavy metal resistance genes of a microbial community on contaminated environment. Appl Geochem 105:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2019.04.012
Xie S, Yang J, Chen C, Zhang X, Wang Q, Zhang C (2008) Study on biosorption kinetics and thermodynamics of uranium by Citrobacter freudii. J Environ Radioactiv 99:126–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2007.07.003
Xu S, Xing Y, Liu S, Hao X, Chen W, Huang Q (2020) Characterization of Cd2+ biosorption by Pseudomonas sp strain 375, a novel biosorbent isolated from soil polluted with heavy metals in Southern China. Chemosphere 240:124893. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124893
Yao J, Zhang M, Han F, Liu Z, Han Y, Li Q, Zhou W (2022) Thermophilic adsorption of Pb2+ onto bacterium from deep-sea hydrothermal vent. J Environ Chem Eng 10(2):107364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2022.107364
Yi YJ, Lim JM, Gu S, Lee WK, Oh E, Lee SM, Oh BT (2017) Potential use of lactic acid bacteria Leuconostoc mesenteroides as a probiotic for the removal of Pb(II) toxicity. J Microbiol 55:296–303. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-017-6642-x
Yin K, Wang Q, Lv M, Chen L (2019) Microorganism remediation strategies towards heavy metals. Chem Eng J 360:1553–1563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.10.226
Yusuf I, Ahmad SA, Phang LY, Syed MA, Shamaan NA, Khalil KA, Shukor MY (2016) Keratinase production and biodegradation of polluted secondary chicken feather wastes by a newly isolated multi heavy metal tolerant bacterium-Alcaligenes sp. AQ05-001. J Environ Manage 183:182–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.08.059
Funding
This research was funded by CINVESTAV, CONACyT-163235 INFR-2011–01, México.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the present study. Cervantes-González E, designed the study, helped to laboratory work, and wrote the draft manuscript. Silva-Aguilar performed the laboratory data collection of the metal removal. Garcia-Mena J, Murugesan Selvasankar, and Nirmalkar Khemlal carried out the experimentation analysis and discussion of the data on bacterial diversity and dynamics. All authors confirmed and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
All authors are available for it.
Consent for publication
All authors agree to the publication of the results contained in this paper.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Silva-Aguilar, F.J., García-Mena, J., Murugesan, S. et al. Characterization of bacterial diversity and capacity to remove lead of a consortium from mining soil. Int Microbiol 26, 705–722 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10123-022-00313-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10123-022-00313-1