Abstract
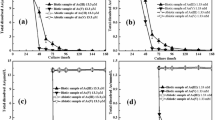
Arsenic, a toxic element in the environment, has seriously threatened the health of hundreds of millions of people in the world. Meanwhile, microorganisms play an important role in the adsorption and bio-transformation of arsenic. Here, we compared the biological characteristics of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans BY3 in different media systems, such as arsenic bio-adsorption and bio-transformation capacities. We show that arsenic stress significantly affected the pH and Eh of the culture systems, as well as the oxidation rates of Fe2+ and bacteria numbers. Furthermore, arsenic influenced bacterial structure and composition of the cell membrane, caused volume decreased and changed the vibration conditions of characteristic peaks of surface groups (-CH2, -NH, and –OH) on cell membranes. In addition, At.f-BY3 shows high bio-adsorption abilities and certain bio-transformation abilities for iAsIII. Bio-adsorption and conversion efficiency was also shown to be significantly affected by Fe2+ concentrations in the reaction systems. Statistic analysis revealed 10.07-fold increase of the transformation ability of iAsIII into iAsV in the 9 K growth media containing 1600 mg/L NaAsO2 compared with that in the 1 K growth media. Our findings contribute to understand the applications and microbiological mechanisms of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans in arsenic pollution.

Bio-adsorption and bio-transformation are used as a biological method of heavy metals pollution, such as Cu2+, Ni2+, Pb2+, Cr2+, Zn2+, Cd2+, As3+ and As5+ in acid mine water. The aim of this investigation was to assess the performance of arsenite (iAsIII) to adsorption and transformation by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans BY3, and application of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans BY3 on the aspect of arsenic pollution has great potential of exploration.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas SZ, Riaz M, Ramzan N, Zahid MT, Shakoori FR, Rafatullah M (2015) Isolation and characterization of arsenic resistant bacteria from wastewater. Braz J Microbiol 45:1309–1315
Adebayo AO, Zandbergen F, Kozul-Horvath CD, Gruppuso PA, Hamilton JW (2014) Chronic exposure to low-dose arsenic modulates lipogenic gene expression in mice. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 29:1–9
Baillet F, Magnin JP, Cheruy A, Ozil P (1997) Cadmium tolerance and uptake by a Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans biomass. Environ Technol Lett 18:631–637
Bellenberg S, Diaz M, Noel N, Sand W, Poetsch A, Guiliani N, Vera M (2014) Biofilm formation, communication and interactions of leaching bacteria during colonization of pyrite and sulfur surfaces. Res Microbiol 165:773–781
Chen P, Yan L, Wang Q, Li Y, Li HY (2012) Surface alteration of realgar (As4S4) by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Int Microbiol Off J Spanish Soc Microbiol 15:9–15
Choong TSY, Chuah TG, Robiah Y, Koay FLG, Azni I (2007) Arsenic toxicity, health hazards and removal techniques from water: an overview. Desalination 127:139–166
Das A, Modak JM, Natarajan KA (1998) Surface chemical studies of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans with reference to copper tolerance. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 73:215–222
Dilda PJ, Hogg PJ (2007) Arsenical-based cancer drugs. Cancer Treat Rev 33:542–564
Gattepaille LM, Engström K, Vahter M, Jakobsson M, Broberg K (2015) Human adaptation to arsenic-rich environments. Mol Biol Evol 32:1544–1555
Govarthanan M, Park JH, Praburaman L, Yi YJ, Min C, Myung H, Gnanendra S, Kamala-Kannan S, Oh BT (2015) Relative expression of low molecular weight protein, tyrosine phosphatase (wzb, gene) of Herbaspirillumsp. GW103 toward arsenic stress and molecular modeling. Curr Microbiol 71:311–316
Hallberg KB, Johnson DB (2001) Biodiversity of acidophilic prokaryotes. Adv Appl Microbiol 49:37–84
Harneit K, Göksel A, Kock D, Klock JH, Gehrke T, SandW (2006) Adhesion to metal sulfide surfaces by cells of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans, Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans, and Leptospirillum ferrooxidans. Hydrometallurgy 83: 245–254
Hettick BE, Cañascarrell JE, French AD, Klein DM (2015) Arsenic: a review of the element’s toxicity, plant interactions, and potential methods of remediation. J Agric Food Chem 63:7097–7107
Jomova K, Jenisova Z, Feszterova M, Baros S, Liska J, Hudecova D, Rhodes CJ, Valko M (2011) Arsenic: toxicity, oxidative stress and human disease. J Appl Toxicol 31:95–107
Latorre M, Cortés MP, Travisany D, Di GA, Budinich M, Reyesjara A (2016) The bioleaching potential of a bacterial consortium. Bioresour Technol 218:659–666
Lett MC, Muller D, Lièvremont D, Silver S, Santini J (2012) Unified nomenclature for genes involved in prokaryotic aerobic arsenite oxidation. J Bacteriol 194:207–208
Li YQ, Wan DS, Huang SS, Leng FF, Yan L, Ni YQ, Li HY (2010) Type IV pili of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans are necessary for sliding, twitching motility, and adherence. Curr Microbiol 60:17–24
Malasarn D, Saltikov CW, Campbell KM, Santini JM, Hering JG, Newman DK (2004) Arra is a reliable marker for as(v) respiration. Science 306:455–455
Marrero J, Coto O, Goldmann S, Graupner T, Schippers A (2015) Recovery of nickel and cobalt from laterite tailings by reductive dissolution under aerobic conditions using Acidithiobacillus species. Environ Sci Technol 49:6674–6682
Mestrot A, Feldmann J, Krupp EM, Hossain MS, Romanross G, Meharg AA (2011) Field fluxes and speciation of arsines emanating from soils. Environ Sci Technol 45:1798–1804
Orellana LH, Jerez CA (2011) A genomic island provides Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans ATCC 53993 additional copper resistance: a possible competitive advantage. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 92:761–767
Oremland RS, Stolz JF (2005) Arsenic, microbes and contaminated aquifers. Trends Microbiol 13:45–49
Park J, Han Y, Lee E, Choi U, Yoo K, Song Y, Kim H (2014) Bioleaching of highly concentrated arsenic mine tailings by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Sep Purif Technol 133:291–296
Satyapal GK, Mishra SK, Srivastava A, Ranjan RK, Prakash K, Haque R, Kumar N (2018) Possible bioremediation of arsenic toxicity by isolating indigenous bacteria from the middle gangetic plain of Bihar, India. Biotechnol Rep 17: 117-125Schlebusch CM, 125,
Smedley PL, Kinniburgh DG (2002) A review of the source, behaviour and distribution of arsenic in natural waters. Appl Geochem 17:517–568
Song B, Leff LG (2006) Influence of magnesium ions on biofilm formation by Pseudomonas fluorescens. Microbiol Res 161:355–361
Stolz JF, Basu P, Oremland RS (2002) Microbial transformation of elements: the case of arsenic and selenium. Int Microbiol 5:201–207
Tang D, Gao Q, Zhao Y, Li Y, Chen P, Zhou J, Xu R, Wu Z, Xu Y, Li H (2018) Mg2+ reduces biofilm quantity in Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans through inhibiting type IV pili formation. FEMS Microbiol Lett 365:e29408987
Wang PP, Yan GX, Jia Y, Andrew AM, Zhu YG (2014) A review on completing arsenic biogeochemicalcycle: microbial volatilization of arsines in environment. Acta Sci Circumst 26:371–381
Welch AH, Westjohn DB, Helsel DR, Wanty RB (2000) Arsenic in ground water of the United States: occurrence and geochemistry. Ground Water 38:589–604
Wu JT, Chiang YR, Huang WY, Jane WN (2006) Cytotoxic effects of free fatty acids on Phytoplankton algae and Cyanobacteria. Aquat Toxicol 80:338–345
Wu L, Yi H, Zhang H (2013) Reactive oxygen species and Ca2+ are involved in sodium arsenite-induced cell killing in yeast cells. FEMS Microbiol Lett 343:57–63
Wu X, Zhang Z, Liu L, Deng F, Liu X, Qiu G (2014) Metal resistance-related genes are differently expressed in response to copper and zinc ion in six Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans strains. Curr Microbiol 69:775–784
Yamamura S, Amachi S (2014) Microbiology of inorganic arsenic: from metabolism to bioremediation. J Biosci Bioeng 118:1–9
Yan L, Yin HH, Zhang SA, Duan JG, Li YQ, Chen P, Li HY (2010) Organoarsenic resistance and bioremoval of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Bioresour Technol 101:6572–6575
Yin XX, Zhang YY, Yang J, Zhu YG (2011) Rapid biotransformation of arsenic by a model protozoan Tetrahymenathermophila. Environ Pollut 159:837–840
Zhao FJ, McGrath SP, Meharg AA (2010) Arsenic as a food-chain contaminant: mechanisms of plant uptake and metabolism and mitigation strategies. Annu Rev Plant Biol 61:535–559
Zhong T, Lv Y, Fei C, Zhang W, Rosen BP, Zhao FJ (2016) Arsenic methylation in Arabidopsis thaliana, expressing an algal arsenite methyltransferase gene increases arsenic phytotoxicity. J Agric Food Chem 64:2674–2681
Zhu YG, Yoshinaga M, Zhao FJ, Rosen BP (2014) Earth abides arsenic biotransformations. Earth Planet Sci 42:443–467
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31660026). The Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of China (lzujbky-2016-152) and the Gansu Province Science Foundation for Distinguished Young Scholars (Grant No. 1308RJDA014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, Q., Tang, D., Song, P. et al. Bio-adsorption and Bio-transformation of Arsenic by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans BY3. Int Microbiol 21, 207–214 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10123-018-0017-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10123-018-0017-y