Abstract
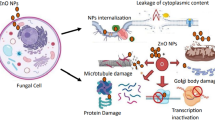
Silver nanoparticles (SN) have been recently developed as a new class of antimicrobial agents against numerous pathogenic microorganisms. SN have also been used as efficient drug delivery systems and have been linked with increasing drug potency. Here, we demonstrated the enhanced antifungal efficacy of nystatin (NYT) and fluconazole (FLU) after conjugation with SN. The antifungal bioactivity of NYT- and FLU-coated SN was evaluated against Candida albicans ATCC 10231 and Aspergillus brasiliensis ATCC 16404 by the agar tube dilution method. The aim of this study was to determine and compare the antifungal efficacy of NYT and FLU with their SN and, finally, the combination of both nanoparticles as NYT-SN + FLU-SN against pathogenic fungi. The results indicated that all test samples showed a dose-dependent response against tested fungi. SN significantly enhanced the antifungal effects of NYT and FLU as compared to drugs alone. We observed a remarkable increase in the percent inhibition of both fungi (90–100%) when treated with a combination of both nanoparticles NYT-SN + FLU-SN at 200 μg/mL only. Furthermore, the morphological modifications occurred at the surface of fungal species were also analyzed by atomic force microscopy (AFM) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). While tested against primary human cell line, all SN showed negligible cytotoxicity. Hence, these results suggest that the combination of SN with NYT and FLU may have clinical implications in the treatment of fungal infections. However, in vivo studies are needed before recommending the use of these nanoparticles safely in clinical situations.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander BD, Johnson MD, Pfeiffer CD, Jiménez-Ortigosa C, Catania J, Booker R, Castanheira M, Messer SA, Perlin DS, Pfaller MA (2013) Increasing echinocandin resistance in Candida glabrata: clinical failure correlates with presence of FKS mutations and elevated minimum inhibitory concentrations. Clin Infect Dis 56(12):1724–1732
Anwar A, Siddiqui R, Hussain MA, Ahmed D, Shah MR, Khan NA (2018) Silver nanoparticle conjugation affects antiacanthamoebic activities of amphotericin B, nystatin, and fluconazole. Parasitol Res 117(1):265–271
Araiza J, Canseco P, Bonifaz A (2006) Otomycosis: clinical and mycological study of 97 cases. Rev Laryngol Otol Rhinol 127(4):251–254
Arendrup MC, Dzajic E, Jensen RH, Johansen HK, Kjaeldgaard P, Knudsen JD, Kristensen L, Leitz C, Lemming LE, Nielsen L, Olesen B (2013) Epidemiological changes with potential implication for antifungal prescription recommendations for fungaemia: data from a nationwide fungaemia surveillance programme. Clin Microbiol Infect 19(8):E343–E353
Atta-ur-Rahman SA, Abbas FN, Ahmed G, Choudhary MI, Alvi KA, De Silva KTD, Arambewela LSR (1991) Chemical constituents of Alstonia macrophylla. J Nat Prod 54:750–754
Carlson C, Hussain SM, Schrand AMK, Braydich-Stolle L, Hess KL, Jones RL, Schlager JJ (2008) Unique cellular interaction of silver nanoparticles: size-dependent generation of reactive oxygen species. J Phys Chem B 112(43):13608–13619
Espinel-Ingroff A, Shadomy S (1989) In vitro and in vivo evaluation of antifungal agents. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 8(4):352–361
Fianchi L, Picardi M, Cudillo L, Corvatta L, Mele L, Trape G, Girmenia C, Pagano L (2004) Aspergillus niger infection in patients with haematological diseases: a report of eight cases. Mycoses 47:163–167
Hayden NJ, Maude RB, Proctor FJ (1994) Studies on the biology of black mould (Aspergillus niger) on temperate and tropical onions. 1. A comparison of sources of the disease in temperate and tropical field crops. Plant Pathol 43(3):562–569
Hoppe JE, Hahn H, Antimycotics Study Group (1996) Randomized comparison of two nystatin oral gels with miconazole oral gel for treatment of oral thrush in infants. Infection 24(2):136–139
Huh AJ, Kwon YJ (2011) “Nanoantibiotics”: a new paradigm for treating infectious diseases using nanomaterials in the antibiotics resistant era. J Control Release 156(2):128–145
Hussein-Al-Ali SH, El Zowalaty ME, Kura AU, Geilich B, Fakurazi S, Webster TJ, Hussein MZ (2014) Antimicrobial and controlled release studies of a novel nystatin conjugated iron oxide nanocomposite. Biomed Res Int 2014:651831
Khan NA, Siddiqui R (2009) Acanthamoeba affects the integrity of human brain microvascular endothelial cells and degrades the tight junction proteins. Int J Parasitol 39(14):1611–1616
Kim KJ, Sung WS, Moon SK, Choi JS, Kim JG, Lee DG (2008) Antifungal effect of silver nanoparticles on dermatophytes. J Microbiol Biotechnol 18(8):1482–1484
Kumar CG, Poornachandra Y (2015) Biodirected synthesis of Miconazole-conjugated bacterial silver nanoparticles and their application as antifungal agents and drug delivery vehicles. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces 125:110–119
Loudon KW, Coke AP, Burnie JP, Shaw AJ, Oppenheim BA, Morris CQ (1996) Kitchens as a source of Aspergillus niger infection. J Hosp Infect 32(3):191–198
Lumbreras C, Cuervas-Mons V, Jara P, Del Palacio A, Turrion VS, Barrios C, Moreno E, Noriega AR, Paya CV (1996) Randomized trial of fluconazole versus nystatin for the prophylaxis of Candida infection following liver transplantation. J Infect Dis 174(3):583–588
Malhotra S, Singh S, Rana N, Tomar S, Bhatnagar P, Gupta M, Singh SK, Singh BK, Chhillar AK, Prasad AK, Len C (2017) Chemoenzymatic synthesis, nanotization and anti-Aspergillus activity of optically enriched fluconazole analogues. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 61:e00273–17.
Moazeni M, Kelidari HR, Saeedi M, Morteza-Semnani K, Nabili M, Gohar AA, Akbari J, Lotfali E, Nokhodchi A (2016) Time to overcome fluconazole resistant Candida isolates: solid lipid nanoparticles as a novel antifungal drug delivery system. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces 142:400–407
Mohammadi G, Shakeri A, Fattahi A, Mohammadi P, Mikaeili A, Aliabadi A, Adibkia K (2017) Preparation, physicochemical characterization and anti-fungal evaluation of nystatin-loaded PLGA-glucosamine nanoparticles. Pharm Res 34:301–309
Monteiro DR, Gorup LF, Silva S, Negri M, De Camargo ER, Oliveira R, Barbosa DD, Henriques M (2011) Silver colloidal nanoparticles: antifungal effect against Candida albicans and Candida glabrata adhered cells and biofilms. Biofouling 27(7):711–719
Monteiro DR, Silva S, Negri M, Gorup LF, De Camargo ER, Oliveira R, Barbosa DD, Henriques M (2012) Silver nanoparticles: influence of stabilizing agent and diameter on antifungal activity against Candida albicans and Candida glabrata biofilms. Lett Appl Microbiol 54(5):383–391
Monteiro DR, Silva S, Negri M, Gorup LF, De Camargo ER, Oliveira R, Barbosa DB, Henriques M (2013) Antifungal activity of silver nanoparticles in combination with nystatin and chlorhexidine digluconate against Candida albicans and Candida glabrata biofilms. Mycoses 56(6):672–680
Naglik JR, Moyes DL, Wächtler B, Hube B (2011) Candida albicans interactions with epithelial cells and mucosal immunity. Clin Microbiol Infect 13(12–13):963–976
Panáček A, Kolář M, Večeřová R, Prucek R, Soukupová J, Kryštof V, Hamal P, Zbořil R, Kvítek L (2009) Antifungal activity of silver nanoparticles against Candida spp. Biomaterials 30(31):6333–6340
Patterson TF (2007) Treatment and prevention of fungal infections. Focus on candidemia. Appl Clin Edu, New York, pp VII–VIII
Person AK, Chudgar SM, Norton BL, Tong BC, Stout JE (2010) Aspergillus niger: an unusual cause of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. J Med Microbiol 59(7):834–838
Pfaller MA, Diekema DJ (2007) Epidemiology of invasive candidiasis: a persistent public health problem. Clin Microbiol Rev 20(1):133–163
Pfaller MA, Pappas PG, Wingard JR (2006) Invasive fungal pathogens: current epidemiological trends. Clin Infect Dis 43(Supplement_1):S3–S14
Prabhu S, Poulose EK (2012) Silver nanoparticles: mechanism of antimicrobial action, synthesis, medical applications, and toxicity effects. Int Nano Lett 2(1):32
Rai M, Yadav A, Gade A (2009) Silver nanoparticles as a new generation of antimicrobials. Biotechnol Adv 27(1):76–83
Rajendran K, Anwar A, Khan NA, Siddiqui R (2017) Brain-eating amoebae: Silver nanoparticle conjugation enhanced efficacy of anti-amoebic drugs against Naegleria fowleri. ACS Chem Neurosci 8(12):2626–2630
Roemer T, Krysan DJ (2014) Antifungal drug development: challenges, unmet clinical needs, and new approaches. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 4(5):A019703
Sarrafha MR, Hashemi SJ, Rezaei S, Bayat M (2018) In vitro evaluation of the effects of fluconazole and nano-fluconazole on Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus fumigatus isolates. Jundishapur J Microbiol 11(6):e57875
Silva S, Pires P, Monteiro DR, Negri M, Gorup LF, Camargo ER, Barbosa DB, Oliveira R, Williams DW, Henriques M, Azeredo J (2013) The effect of silver nanoparticles and nystatin on mixed biofilms of Candida glabrata and Candida albicans on acrylic. Med Mycol 51(2):178–184
Sondi I, Salopek-Sondi B (2004) Silver nanoparticles as antimicrobial agent: a case study on E. coli as a model for Gram-negative bacteria. J Colloid Interfac Sci 275(1):177–182
Vermeulen E, Maertens J, Meersseman P, Saegeman V, Dupont L, Lagrou K (2014) Invasive Aspergillus niger complex infections in a Belgian tertiary care hospital. Clin Microbiol Infect 20(5):O333–O335
Zhang L, Pornpattananangkul D, Hu CM, Huang CM (2010) Development of nanoparticles for antimicrobial drug delivery. Curr Med Chem 17(6):585–594
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the Higher Education Commission of Pakistan, and the International Center for Chemical and Biological Sciences, Karachi, Pakistan, and Sunway University, Selangor, Malaysia, for their support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hussain, M.A., Ahmed, D., Anwar, A. et al. Combination Therapy of Clinically Approved Antifungal Drugs Is Enhanced by Conjugation with Silver Nanoparticles. Int Microbiol 22, 239–246 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10123-018-00043-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10123-018-00043-3