Abstract
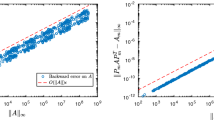
Given an n × n symmetric possibly indefinite matrix A, a modified Cholesky algorithm computes a factorization of the positive definite matrix A + E, where E is a correction matrix. Since the factorization is often used to compute a Newton-like downhill search direction for an optimization problem, the goals are to compute the modification without much additional cost and to keep A + E well-conditioned and close to A. Gill, Murray and Wright introduced a stable algorithm, with a bound of ||E||2 = O(n 2). An algorithm of Schnabel and Eskow further guarantees ||E||2 = O(n). We present variants that also ensure ||E||2 = O(n). Moré and Sorensen and Cheng and Higham used the block LBL T factorization with blocks of order 1 or 2. Algorithms in this class have a worst-case cost O(n 3) higher than the standard Cholesky factorization. We present a new approach using a sandwiched LTL T-LBL T factorization, with T tridiagonal, that guarantees a modification cost of at most O(n 2).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aasen J.O. (1971). On the reduction of a symmetric matrix to tridiagonal form. BIT 11(3): 233–242
Ashaft C., Grimes R.G. and Lewis J.G. (1998). Accurate symmetric indefinite linear equation solvers. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 20(2): 513–561
Bunch J.R. and Kaufman L. (1977). Some stable methods for calculating inertia and solving symmetric linear systems. Math. Comp. 31: 163–179
Bunch J.R. and Parlett B.N. (1971). Direct methods for solving symmetric indefinite systems of linear equations. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 8(4): 639–655
Cheng, S.H.: Symmetric Indefinite Matrices: Linear System Solvers and Modified Inertia Problems. PhD thesis, University of Manchester (1998)
Cheng S.H. and Higham N.J. (1998). A modified Cholesky algorithm based on a symmetric indefinite factorization. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 19(4): 1097–1110
Cuppen J.J.M. (1980). A divide and conquer method for the symmetric tridiagonal eigenproblem. Numer. Math. 36(2): 177–195
Demmel, J.W.: Applied Numerical Linear Algebra. SIAM (1997)
Fang, H.-r.: Matrix Factorization, Triadic Matrices, and Modified Cholesky Factorizations for Optiimization. PhD thesis, University of Maryland (2006)
Fang, H.-r., O’Leary, D.P.: Modified Cholesky algorithms: A catalog with new approaches. Technical Report CS-TR-4807, Computer Science Department, University of Maryland (2006)
Fang H.-r. and O’Leary D.P. (2006). Stable factorizations of symmetric tridiagonal and triadic matrices. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 28(2): 576–595
Forsgren A., Gill P.E. and Murray W. (1995). Computing modified Newton directions using a partial Cholesky factorization. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 16(1): 139–150
Gill P.E. and Murray W. (1974). Newton-type methods for unconstrained and linearly constrained optimization. Math. Program. 28: 311–350
Gill P.E., Murray W. and Wright M.H. (1981). Practical Optimization. Academic, New York
Horn R.A. and Johnson C.R. (1985). Matrix Analysis. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Moré J.J. and Sorensen D.C. (1979). On the use of directions of negative curvature in a modified Newton method. Math. Program. 16: 1–20
Parlett B.N. and Reid J.K. (1970). On the solution of a system of linear equations whose matrix is symmetric but not definite. BIT 10(3): 386–397
Schnabel R.B. and Eskow E. (1990). A new modified Cholesky factorization. SIAM J. Sci. Stat. Comput. 11: 1136–1158
Schnabel R.B. and Eskow E. (1999). A revised modified Cholesky factorization algorithm. SIAM J. Optim. 9(4): 1135–1148
Stewart G.W. (1980). The efficient generation of random orthogonal matrices with an application to condition estimation. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 17: 403–409
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
H.-r. Fang’s work was supported by National Science Foundation Grant CCF 0514213.
D. P. O’Leary’s work was supported by National Science Foundation Grant CCF 0514213 and Department of Energy Grant DEFG0204ER25655.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, Hr., O’Leary, D.P. Modified Cholesky algorithms: a catalog with new approaches. Math. Program. 115, 319–349 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10107-007-0177-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10107-007-0177-6