Abstract
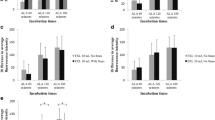
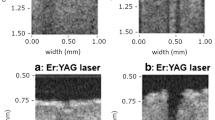
Ablative fractional technology has been used to improve transdermal drug delivery. However, there have been few previous in vivo investigations of the relative potency and methodology of fractional radiofrequency (RF) combined with sonophoresis. The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of fractional RF combined with sonophoresis on 5-aminolevulinic acid (ALA) penetration of the skin. Three male domestic swine were used. The skin of the pigs was exposed to fractional RF and/or sonophoresis, followed by topical ALA application. Fluorescence intensity (FI) of porphyrin fluorescence was measured. In both the epidermis and the dermis, FI increased after fractional RF and increased additionally with the addition of sonophoresis. Fractional RF with sonophoresis effectively enhanced ALA skin penetration. Pre-fractional RF followed by posttreatment with sonophoresis can be used for ALA-photodynamic therapy to achieve higher ALA uptake.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babilas P, Schreml S, Landthaler M, Szeimies RM (2010) Photodynamic therapy in dermatology: state-of-the-art. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed 26:118–132
Lee WR, Shen SC, Wang KH, Hu CH, Fang JY (2002) The effect of laser treatment on skin to enhance and control transdermal delivery of 5-fluorouracil. J Pharm Sci 91:1613–1626
Lee WR, Shen SC, Pai MH, Yang HH, Yuan CY, Fang JY (2010) Fractional laser as a tool to enhance the skin permeation of 5-aminolevulinic acid with minimal skin disruption: a comparison with conventional erbium: YAG laser. J Control Release 145:124–133
Haedersdal M, Sakamoto FH, Farinelli WA, Doukas AG, Tam J, Anderson RR (2010) Fractional CO(2) laser-assisted drug delivery. Lasers Surg Med 42:113–122
Polat BE, Blankschtein D, Langer R (2010) Low-frequency sonophoresis: application to the transdermal delivery of macromolecules and hydrophilic drugs. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 7:1415–1432
Yoo KH, Kim BJ, Kim MN (2009) Enhanced efficacy of photodynamic therapy with methyl 5-aminolevulinic acid in recalcitrant periungual warts after ablative carbon dioxide fractional laser: a pilot study. Dermatol Surg 35:1927–1932
Morton CA, McKenna KE, Rhodes LE (2008) Guidelines for topical photodynamic therapy: update. Br J Dermatol 159:1245–1266
Tsai JC, Chen IH, Wong TW, Lo YL (2002) In vitro/in vivo correlations between transdermal delivery of 5-aminolaevulinic acid and cutaneous protoporphyrin IX accumulation and effect of formulation. Br J Dermatol 146:853–862
Fang JY, Lee WR, Shen SC, Fang YP, Hu CH (2004) Enhancement of topical 5-aminolaevulinic acid delivery by erbium: YAG laser and microdermabrasion: a comparison with iontophoresis and electroporation. Br J Dermatol 151:132–140
Kassuga LE, Issa MC, Chevrand NS (2012) Transepidermal application of medication combined with photodynamic therapy in the treatment of actinic keratosis. Surg Cosmet Dermatol 4:89–92
Suh DH, Lee SJ, Lee JH, Kim HJ, Shin MK, Song KY (2012) Treatment of striae distensae combined enhanced penetration platelet-rich plasma and ultrasound after plasma fractional radiofrequency. J Cosmet Laser Ther 14:272–276
Issa MC, De Britto Pereira Kassuga LE, Chrevrand NS, Do Nascimiento Barbosa L, Luiz RR, Pantelao L, Vilar EG, Rochael MC (2013) Transepidermal retinoic acid delivery using ablative fractional radiofrequency associated with acoustic pressure ultrasound for stretch marks treatment. Lasers Surg Med 45:81–88
Issa MC, Kassuga LE, Chevrand NS, Pires MT (2013) Topical delivery of triamcinolone via skin pretreated with ablative radiofrequency: a new method in hypertrophic scar treatment. Int J Dermatol 52:367–370
Trelles MA, Martínez-Carpio PA (2014) Attenuation of acne scars using high power fractional ablative unipolar radiofrequency and ultrasound for transepidermal delivery of bioactive compounds through microchannels. Lasers Surg Med 46:152–159
Fang JY, Fang CL, Sung KC, Chen HY (1999) Effect of low frequency ultrasound on the in vitro percutaneous absorption of clobetasol 17-propionate. Int J Pharm 191:33–42
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding sources
None
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest
Additional information
Jong Min Park and Ki-Heon Jeong contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, J.M., Jeong, KH., Bae, M.I. et al. Fractional radiofrequency combined with sonophoresis to facilitate skin penetration of 5-aminolevulinic acid. Lasers Med Sci 31, 113–118 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-015-1835-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-015-1835-1