Abstract
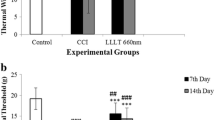
The increase in PGE2 production by microsomal PGE synthase-1 (mPGES-1) in CNS contributes to the severity of the inflammatory and pain responses in the model of edema formation and hyperalgesia induced by carrageenan. PGI2, alike to PGE2, plays an important role in the inflammation. Low-level laser therapy (LLLT) has been used in the treatment of inflammatory pathologies, reducing both pain and the acute inflammatory process. In this work, we studied the effect of LLLT on the expression of both mPGES-1 and IP messenger RNA (mRNA), in either subplantar or total brain tissues obtained from rats submitted to model of edema formation and hyperalgesia induced by carrageenan administration. The test sample consisted of 30 rats divided into five groups: A1 (control—saline), A2 (carrageenan—0.5 mg/paw), A3 (carrageenan—0.5 mg/paw + LLLT), A4 (carrageenan—1.0 mg/paw), and A5 (carrageenan—1.0 mg/paw + LLLT). The animals from groups A3 and A5 were irradiated 1 h after induction of inflammation by carrageenan injection. Continuous-wave red laser with wavelengths of 660 nm and dose of 7.5 J/cm2 was used. Six hours after carrageenan-induced inflammation, mPGES-1 and prostacyclin receptor (IP) mRNA expression were significantly increased both in subplantar and brain tissues. LLLT was able to reduce both mPGES-1 and IP mRNA expression in subplantar and brain tissues. We suggest that LLLT is able to reduce both inflammation and hyperalgesia observed in the model of edema formation and hyperalgesia induced by carrageenan, by a mechanism involving the decrease in the expression of both mPGES-1 and IP.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ibuki T, Matsumura K, Yamazaki Y, Nozaki T, Tanaka Y, Kobayashi S (2003) Cyclooxygenase-2 is induced in the endothelial cells throughout the central nervous system during carrageenan-induced hind paw inflammation; its possible role in hyperalgesia. J Neurochem 86:318–328
Zeilhofer HU, Brune K (2006) Analgesic strategies beyond the inhibition of cyclooxygenases. Trends Pharmacol Sci 27:467–474
Kawabata A (2011) Prostaglandin E2 and pain-an update. Biol Pharm Bull 34:1170–1173
Murakami M, Naraba H, Tanioka T, Semmyo N, Nakatani Y, Kojima F, Ikeda T, Fueki M, Ueno A, Oh S, Kudo I (2000) Regulation of prostaglandin E2 biosynthesis by inducible membrane-associated prostaglandin E2 synthase that acts in concert with cyclooxygenase-2. J Biol Chem 275:32783–32792
Claveau D, Sirinyan M, Guay J, Gordon R, Chan CC, Bureau Y, Riendeau D, Mancini JA (2003) Microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 is a major terminal synthase that is selectively up-regulated during cyclooxygenase-2-dependent prostaglandin E2 production in the rat adjuvant-induced arthritis model. J Immunol 170:4738–4744
Zeilhofer HU (2007) Prostanoids in nociception and pain. Biochem Pharmacol 73:165–174
Guay J, Bateman K, Gordon R, Mancini J, Riendeau D (2004) Carrageenan-induced paw edema in rat elicits a predominant prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) response in the central nervous system associated with the induction of microsomal PGE2 synthase-1. J Biol Chem 279:24866–24872
Pulichino AM, Rowland S, Wu T, Clark P, Xu D, Mathieu MC, Riendeau D, Audoly LP (2006) Prostacyclin antagonism reduces pain and inflammation in rodent models of hyperalgesia and chronic arthritis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 319:1043–1050
Doi Y, Minami T, Nishizawa M, Mabuchi T, Mori H, Ito S (2002) Central nociceptive role of prostacyclin (IP) receptor induced by peripheral inflammation. Neuroreport 13:93–96
Murata T, Ushikubi F, Matsuoka T, Hirata M, Yamasaki A, Sugimoto Y, Ichikawa A, Aze Y, Tanaka T, Yoshida N, Ueno A, Oh-ishi S, Narumiya S (1997) Altered pain perception and inflammatory response in mice lacking prostacyclin receptor. Nature 388:678–682
Walker JB (1983) Relief from chronic pain by low power laser irradiation. Neurosci Lett 43:339–344
Ribas ES, Paiva WS, Pinto NC, Yeng LT, Okada M, Fonoff ET, Chavantes MC, Teixeira MJ (2012) Use of low intensity laser treatment in neuropathic pain refractory to clinical treatment in amputation stumps. Int J Gen Med 5:739–742
Chow R, Armati P, Laakso EL, Bjordal JM, Baxter GD (2011) Inhibitory effects of laser irradiation on peripheral mammalian nerves and relevance to analgesic effects: a systematic review. Photomed Laser Surg 29:365–381
Hagiwara S, Iwasaka H, Okuda K, Noguchi T (2007) GaAlAs (830 nm) low-level laser enhances peripheral endogenous opioid analgesia in rats. Lasers Surg Med 39:797–802
Hagiwara S, Iwasaka H, Hasegawa A, Noguchi T (2008) Pre-Irradiation of blood by gallium aluminum arsenide (830 nm) low-level laser enhances peripheral endogenous opioid analgesia in rats. Anesth Analg 107:1058–1063
Albertini R, Aimbire F, Villaverde AB, Silva JA Jr, Costa MS (2007) COX-2 mRNA expression decreases in the subplantar muscle of rat paw subjected to carrageenan-induced inflammation after low level laser therapy. Inflamm Res 56:228–229
Albertini R, Villaverde AB, Aimbire F, Salgado MA, Bjordal JM, Alves LP, Munin E, Costa MS (2007) Anti-inflammatory effects of low-level laser therapy (LLLT) with two different red wavelengths (660 nm and 684 nm) in carrageenan-induced rat paw edema. J Photochem Photobiol B 89:50–55
Bjordal JM, Lopes-Martins RA, Iversen VV (2006) A randomised, placebo controlled trial of low level laser therapy for activated Achilles tendinitis with microdialysis measurement of peritendinous prostaglandin E2 concentrations. Br J Sports Med 40:76–80
Fukuda TY, Tanji MM, Silva SR, Sato MN, Plapler H (2013) Infrared low-level diode laser on inflammatory process modulation in mice: pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines. Lasers Med Sci 28:1305–1313
Lim W, Lee S, Kim I, Chung M, Kim M, Lim H, Park J, Kim O, Choi H (2007) The anti-inflammatory mechanism of 635 nm light-emitting-diode irradiation compared with existing COX inhibitors. Lasers Surg Med 39:614–621
de Almeida P, Lopes-Martins RÁ, Tomazoni SS, Albuquerque-Pontes GM, Santos LA, Vanin AA, Frigo L, Vieira RP, Albertini R, de Tarso Camillo de Carvalho P, Leal-Junior EC (2013) Low-level laser therapy and sodium diclofenac in acute inflammatory response induced by skeletal muscle trauma: effects in muscle morphology and mRNA gene expression of inflammatory markers. Photochem Photobiol 89:501–507
Assis L, Moretti AI, Abrahão TB, Cury V, Souza HP, Hamblin MR, Parizotto NA (2012) Low-level laser therapy (808 nm) reduces inflammatory response and oxidative stress in rat tibialis anterior muscle after cryolesion. Lasers Surg Med 44(9):726–735
Marcos RL, Leal-Junior EC, Arnold G, Magnenet V, Rahouadj R, Wang X, Demeurie F, Magdalou J, de Carvalho MH, Lopes-Martins RÁ (2012) Low-level laser therapy in collagenase-induced Achilles tendinitis in rats: analyses of biochemical and biomechanical aspects. J Orthop Res 30(12):1945–1951
Pires D, Xavier M, Araújo T, Silva JA Jr, Aimbire F, Albertini R (2011) Low-level laser therapy (LLLT; 780 nm) acts differently on mRNA expression of anti- and pro-inflammatory mediators in an experimental model of collagenase-induced tendinitis in rat. Lasers Med Sci 26(1):85–94
Arganaraz GA, Silva JA Jr, Perosa SR, Pessoa LG, Carvalho FF, Bascands JL, Bader M, da Silva TE, Amado D, Cavalheiro EA, Pesquero JB, da Graça N-MM (2004) The synthesis and distribution of the kinin B1 and B2 receptors are modiied in the hippocampus of rats submitted to pilocarpine model of epilepsy. Brain Res 23:114–125
Narumiya S, Sugimoto Y, Ushikubi F (1999) Prostanoid receptors: structures, properties, and functions. Physiol Rev 79:1193–1226
Funk CD (2001) Prostaglandins and leukotrienes: advances in eicosanoid biology. Science 294:1871–1875
Toriyabe M, Omote K, Kawamata T, Namiki A (2004) Contribution of interaction between nitric oxide and cyclooxygenases to the production of prostaglandins in carrageenan-induced inflammation. Anesthesiology 101:983–990
Barretto SR, de Melo GC, dos Santos JC, de Oliveira MG, Pereira-Filho RN, Alves AV, Ribeiro MA, Lima-Verde IB, Quintans Júnior LJ, de Albuquerque-Júnior RL, Bonjardim LR (2013) Evaluation of anti-nociceptive and anti-inflammatory activity of low-level laser therapy on temporomandibular jointinflammation in rodents. J Photochem Photobiol B 129:135–142
Salmos-Brito JA, de Menezes RF, Teixeira CE, Gonzaga RK, Rodrigues BH, Braz R, Bessa-Nogueira RV, Gerbi ME (2013) Evaluation of low-level laser therapy in patients with acute and chronic temporomandibular disorders. Lasers Med Sci 28(1):57–64
Pallotta RC, Bjordal JM, Frigo L, Leal Junior EC, Teixeira S, Marcos RL, Ramos L, Messias Fde M, Lopes-Martins RA (2012) Infrared (810-nm) low-level laser therapy on rat experimental knee inflammation. Lasers Med Sci 27(1):71–78
Mafra de Lima F, Villaverde AB, Salgado MA, Castro-Faria-Neto HC, Munin E, Albertini R, Aimbire F (2010) Low intensity laser therapy (LILT) in vivo acts on the neutrophils recruitment and chemokines/cytokines levels in a model of acute pulmonary inflammation induced by aerosol of lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia coli in rat. J Photochem Photobiol B 101(3):271–278
de Lima FM, Villaverde AB, Albertini R, Corrêa JC, Carvalho RL, Munin E, Araújo T, Silva JA, Aimbire F (2011) Dual effect of low-level laser therapy (LLLT) on the acute lung inflammation induced by intestinal ischemia and reperfusion: action on anti- and pro-inflammatory cytokines. Lasers Surg Med 43(5):410–420
Mesquita-Ferrari RA, Martins MD, Silva JA Jr, da Silva TD, Piovesan RF, Pavesi VC, Bussadori SK, Fernandes KP (2011) Effects of low-level laser therapy on expression of TNF-α and TGF-β in skeletal muscle during the repair process. Lasers Med Sci 26(3):335–340
Alves AC, Vieira R, Leal-Junior E, dos Santos S, Ligeiro AP, Albertini R, Junior J, de Carvalho P (2013) Effect of low-level laser therapy on the expression of inflammatory mediators and on neutrophils and macrophages in acute joint inflammation. Arthritis Res Ther 15(5):R116
Dos Santos SA, Alves AC, Leal-Junior EC, Albertini R, Vieira RD, Ligeiro AP, Junior JA, de Carvalho PD. Comparative analysis of two low-level laser doses on the expression of inflammatory mediators and on neutrophils and macrophages in acute joint inflammation. Lasers Med Sci. doi: 10.1007/s10103-013-1467-2
Hentschke VS, Jaenisch RB, Schmeing LA, Cavinato PR, Xavier LL, Dal Lago P (2013) Low-level laser therapy improves the inflammatory profile of rats with heart failure. Lasers Med Sci 28(3):1007–1016
de Lima FM, Vitoretti L, Coelho F, Albertini R, Breithaupt-Faloppa AC, de Lima WT, Aimbire F (2013) Suppressive effect of low-level laser therapy on tracheal hyperresponsiveness and lung inflammation in rat subjected to intestinal ischemia and reperfusion. Lasers Med Sci 28(2):551–564
Carlos FP, de Paula Alvesda Silva M, de Lemos Vasconcelos Silva Melo E, Costa MS, Zamuner SR (2014) Protective effect of low-level laser therapy (LLLT) on acute zymosan-induced arthritis. Lasers Med Sci 29(2):757–763
Prianti AC Jr, Silva JA Jr, Dos Santos RF, Rosseti IB, Costa MS (2014) Low-level laser therapy (LLLT) reduces the COX-2 mRNA expression in both subplantar and total brain tissues in the model of peripheral inflammation induced by administration of carrageenan. Lasers Med Sci. doi:10.1007/s10103-014-1543-2
de Paiva Carvalho RL, Leal-Junior EC, Petrellis MC, Marcos RL, de Carvalho MH, De Nucci G, Lopes-Martins RA (2013) Effects of low-level laser therapy (LLLT) and diclofenac (topical and intramuscular) as single and combined therapy in experimental model of controlled muscle strain in rats. Photochem Photobiol 89:508–512
de Almeida P, Tomazoni SS, Frigo L, de Carvalho PT, Vanin AA, Santos LA, Albuquerque-Pontes GM, De Marchi T, Tairova O, Marcos RL, Lopes-Martins RA, Leal-Junior EC (2014) What is the best treatment to decrease pro-inflammatory cytokine release in acute skeletal muscle injury induced by trauma in rats: low-level laser therapy, diclofenac, or cryotherapy? Lasers Med Sci 29:653–658
Koeberle A, Werz O (2009) Inhibitors of the microsomal prostaglandin E(2) synthase-1 as alternative to non steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)—a critical review. Curr Med Chem 16(32):4274–4296
Mbalaviele G, Pauley AM, Shaffer AF, Zweifel BS, Mathialagan S, Mnich SJ, Nemirovskiy OV, Carter J, Gierse JK, Wang JL, Vazquez ML, Moore WM, Masferrer JL (2010) Distinction of microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 (mPGES-1) inhibition from cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition in cells using a novel, selective mPGES-1 inhibitor. Biochem Pharmacol 79(10):1445–1454
Arhancet GB, Walker DP, Metz S, Fobian YM, Heasley SE, Carter JS, Springer JR, Jones DE, Hayes MJ, Shaffer AF, Jerome GM, Baratta MT, Zweifel B, Moore WM, Masferrer JL, Vazquez ML (2013) Discovery and SAR of PF-4693627, a potent, selective and orally bioavailable mPGES-1 inhibitor for the potential treatment of inflammation. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 23(4):1114–1119
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge FAPESP and CNPq, for the grants, under which this research was conducted.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chagas, L.R., Silva, J.A., de Almeida Pires, J. et al. Expression of mPGES-1 and IP mRNA is reduced by LLLT in both subplantar and brain tissues in the model of peripheral inflammation induced by carrageenan. Lasers Med Sci 30, 83–88 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-014-1622-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-014-1622-4