Abstract
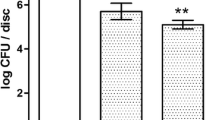
This in vitro study examined (a) the anti-bacterial efficacy of a pulsed erbium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet (Er:YAG) laser applied to Streptococcus sanguinis or Porphyromonas gingivalis adhered to either polished or microstructured titanium implant surfaces, (b) the response of osteoblast-like cells and (c) adhesion of oral bacteria to titanium surfaces after laser irradiation. Thereto, (a) bacteria adhered to titanium disks were irradiated with a pulsed Er:YAG laser (λ = 2,940 nm) at two different power settings: a lower mode (12.74 J/cm2 calculated energy density) and a higher mode (63.69 J/cm2). (b) After laser irradiation with both settings of sterile titanium, disks were seeded with 104 MG-63 cells/cm2. Adhesion and proliferation were determined after 1, 4, and 24 h by fluorescence microscopy and scanning electron microscopy. (c) Bacterial adhesion was also studied on irradiated (test) and non-irradiated (control) surfaces. Adhered P. gingivalis were effectively killed, even at the lower laser setting, independent of the material’s surface. S. sanguinis cells adhered were effectively killed only at the higher setting of 63.69 J/cm2. Laser irradiation of titanium surfaces had no significant effects on (b) adhesion or proliferation of osteoblast-like MG-63 cells or (c) adhesion of both oral bacterial species in comparison to untreated surfaces. An effective decontamination of polished and rough titanium implant surfaces with a Er:YAG laser could only be achieved with a fluence of 63.69 J/cm2. Even though this setting may lead to certain surface alterations, no significant adverse effect on subsequent colonization and proliferation of MG-63 cells or increased bacterial adhesion was found in comparison to untreated control surfaces.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wennerberg A, Albrektsson T (2011) Current challenges in successful rehabilitation with oral implants. J Oral Rehabil 38:286–294
Preston CB, Maggard MB, Lampasso J, Chalabi O (2008) Long-term effectiveness of the continuous and the sectional archwire techniques in leveling the curve of Spee. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 133:550–555. doi:10.1016/j.ajodo.2006.02.039
Furst MM, Salvi GE, Lang NP, Persson GR (2007) Bacterial colonization immediately after installation on oral titanium implants. Clin Oral Implants Res 18:501–508
Lang NP, Berglundh T (2011) Periimplant diseases: where are we now?—consensus of the Seventh European Workshop on Periodontology. J Clin Periodontol 38(Suppl 11):178–181
Lee A, Wang HL (2010) Biofilm related to dental implants. Implant Dent 19:387–393
Berglundh T, Zitzmann NU, Donati M (2011) Are peri-implantitis lesions different from periodontitis lesions? J Clin Periodontol 38(Suppl 11):188–202
Persson LG, Berglundh T, Lindhe J, Sennerby L (2001) Re-osseointegration after treatment of peri-implantitis at different implant surfaces. An experimental study in the dog. Clin Oral Implants Res 12:595–603
Renvert S, Roos-Jansåker AM, Claffey N (2008) Non-surgical treatment of peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis: a literature review. J Clin Periodontol 35(8 Suppl):305–315
Pye AD, Lockhart DE, Dawson MP, Murray CA, Smith AJ (2009) A review of dental implants and infection. J Hosp Infect 72:104–110
Lindhe J, Meyle J (2008) Peri-implant diseases: consensus report of the sixth European Workshop on Periodontology. J Clin Periodontol 35(8 Suppl):282–285
Deppe H, Horch HH (2007) Laser applications in oral surgery and implant dentistry. Lasers Med Sci 22:217–221
Kotsovilis S, Karoussis IK, Trianti M, Fourmousis I (2008) Therapy of peri-implantitis: a systematic review. J Clin Periodontol 35:621–629
Schwarz HP, Dorner F, Mitterer A, Mundt W, Schlokat U, Pichler L, Turecek PL (1999) Preclinical evaluation of recombinant von Willebrand factor in a canine model of von Willebrand disease. Wien Klin Wochenschr 111:181–191
Schwarz HP, Dorner F, Mitterer A, Mundt W, Schlokat U, Pichler L, Turecek PL (1998) Evaluation of recombinant von Willebrand factor in a canine model of von Willebrand disease. Haemophilia Off J World Fed Hemophilia 4(Suppl 3):53–62
Schwarz F, Bieling K, Nuesry E, Sculean A, Becker J (2006) Clinical and histological healing pattern of peri-implantitis lesions following non-surgical treatment with an Er:YAG laser. Lasers Surg Med 38:663–671
Stübinger S, Etter C, Miskiewicz M, Homann F, Saldamli B, Wieland M, Sader R (2010) Surface alterations of polished and sandblasted and acid-etched titanium implants after Er:YAG, carbon dioxide, and diode laser irradiation. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 25:104–111
Hauser-Gerspach I, Kulik EM, Weiger R, Decker E-M, Von Ohle C, Meyer J (2007) Adhesion of Streptococcus sanguinis to dental implant and restorative materials. Dent Mater J 26:361–366
Hauser-Gerspach I, Vadaszan J, Deronjic I, Gass C, Meyer J, Dard M, Waltimo T, Stübinger S, Mauth C (2012) Influence of gaseous ozone in peri-implantitis: bactericidal efficacy and cellular response. An in vitro study using titanium and zirconia. Clin Oral Investig 16:1049–1059
Hauser-Gerspach I, Stübinger S, Meyer J (2010) Bactericidal effects of different laser systems on bacteria adhered to dental implant surfaces: an in vitro study comparing zirconia with titanium. Clin Oral Implants Res 21:277–283
Kato T, Kusakari H, Hoshino E (1998) Bactericidal efficacy of carbon dioxide laser against bacteria-contaminated titanium implant and subsequent cellular adhesion to irradiated area. Lasers Surg Med 23:299–309
Kreisler M, Kohnen W, Marinello C, Götz H, Duschner H, Jansen B, d’Hoedt B (2002) Bactericidal effect of the Er:YAG laser on dental implant surfaces: an in vitro study. J Periodontol 73:1292–1298
Prates RA, Yamada AMJ, Suzuki LC, Eiko Hashimoto MC, Cai S, Gouw-Soares S, Gomes L, Riberio MS (2007) Bactericidal effect of malachite green and red laser on Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. J Photochem Photobiol B 86:70–76
Kojima T, Shimada K, Iwasaki H, Ito K (2005) Inhibitory effects of a super pulsed carbon dioxide laser at low energy density on periodontopathic bacteria and lipopolysaccharide in vitro. J Periodont Res 40:469–473
Ando Y, Aoki A, Watanabe H, Ishikawa I (1996) Bactericidal effect of erbium YAG laser on periodontopathic bacteria. Lasers Surg Med 19:190–200
Noiri Y, Katsumoto T, Azakami H, Ebisu S (2008) Effects of Er:YAG laser irradiation on biofilm-forming bacteria associated with endodontic pathogens in vitro. J Endod 34:826–839
Sennhenn-Kirchner S, Schwarz P, Schliephake H, Konietschke F, Brunner E, Borg-von Zepelin M (2009) Decontamination efficacy of erbium:yttrium-aluminium-garnet and diode laser light on oral Candida albicans isolates of a 5-day in vitro biofilm model. Lasers Med Sci 24:313–320
Quaranta A, Maida C, Scrascia A, Campus G, Quaranta M (2009) Er:YAG laser application on titanium implant surfaces contaminated by Porphyromonas gingivalis: an histomorphometric evaluation. Minerva Stomatol 58:317–330
Schwarz F, Sculean A, Romanos G, Herten M, Horn N, Scherbaum W, Becker J (2005) Influence of different treatment approaches on the removal of early plaque biofilms and the viability of SAOS2 osteoblasts grown on titanium implants. Clin Oral Investig 9:111–117
Romeo E, Ghisolfi M, Carmagnola D (2004) Peri-implant diseases. a systematic review of the literature. Minerva Stomatol 53:215–230
Johnson JD, Chen R, Lenton PA, Zhang G, Hinrichs JE, Rudney JD (2008) Persistence of extracrevicular bacterial reservoirs after treatment of aggressive periodontitis. J Periodontol 79:2305–2312
Duarte PM, Reis AF, de Freitas PM, Ota-Tsuzuki C (2009) Bacterial adhesion on smooth and rough titanium surfaces after treatment with different instruments. J Periodontol 80:1824–1832
Shin SI, Min HK, Park BH, Kwon YH, Park JB, Herr Y, Heo SJ, Chung JH (2011) The effect of Er:YAG laser irradiation on the scanning electron microscopic structure and surface roughness of various implant surfaces: an in vitro study. Lasers Med Sci 26:767–776
Kim JH, Herr Y, Chung JH, Shin SI, Kwon YH (2011) The effect of erbium-doped: yttrium, aluminium and garnet laser irradiation on the surface microstructure and roughness of double acid-etched implants. J Periodont Imlant Sci 41:234–241
Galli C, Macaluso GM, Elezi E, Ravanetti F, Cacchioli A, Gualini G, Passeri G (2011) The effects of Er:YAG laser treatment on titanium surface profile and osteoblastic cell activity: an in vitro study. J Periodontol 82:1169–1177
Acknowledgments
We thank the ITI Foundation (grant no. 518/2007) and the SSO Funds (grant no.: 248–09) for financial support. The authors also thank Catiana Gass for doing some of the in vitro cell experiments at Straumann laboratories.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hauser-Gerspach, I., Mauth, C., Waltimo, T. et al. Effects of Er:YAG laser on bacteria associated with titanium surfaces and cellular response in vitro. Lasers Med Sci 29, 1329–1337 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-013-1303-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-013-1303-8