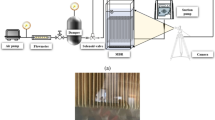
Abstract
The performance of a vibratory shear-enhanced membrane process for dewatering of freshwater microalgae, Chlorella vulgaris, has been studied. Chlorella vulgaris is a potential renewable feedstock for biofuel and bioproduct production. The efficient dewatering of the algal biomass is crucial for scale-up and sustainable design. This dynamic filtration system achieves high shear rates desirable for microfiltration by high-frequency torsional oscillations of the membrane unit. A 0.05 µm (nominal pore size) polyethersulfone microfiltration membrane was evaluated for the separation of suspended algae (0.5–100 g/L). The effect of process parameters such as trans-membrane pressure, surface shear rate, and solute concentration on permeate flux was evaluated and quantified. Algal biomass mixtures were dewatered with high algae rejections for all studies. The effect of trans-membrane pressure on permeate flux showed a classic pattern of a pressure-controlled region at lower pressures transforming to a mass transfer gel layer-controlled region at higher pressures, with quicker transitions at higher algae feed concentrations. The shear rate at the membrane surface was varied by changing the vibrational frequency of the unit. Permeate flux values observed in dynamic filtration mode, compared to those in cross-flow filtration (CFF) mode, were greater by a factor of 4.2–4.9. This process could provide a greener alternative to conventional mechanical and thermal separation systems, as high values of permeate flux and separation efficiency can be maintained with an energy consumption of 1.6 kWh/m3 of water removed.












Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A :
-
Membrane permeability constant [L/m2 h Pa]
- b :
-
Fouling decay rate constant [dimensionless]
- CFF:
-
Cross-flow filtration
- d :
-
Displacement caused by oscillations [m]
- EOM:
-
Extracellular organic matter
- F :
-
Oscillation frequency [Hz]
- h :
-
Vertical distance along the axial line of symmetry in membrane module [m]
- h t :
-
Total vertical distance of membrane module assembly [m]
- J :
-
Permeate flux [L/m2 h]
- J 0 :
-
Initial flux constant [L/m2 h]
- NOM:
-
Natural organic matter
- ΔP :
-
Pressure gradient across membrane [kPa]
- PES:
-
Polyethersulfone
- R 1 :
-
Inner radius of membrane [m]
- R 2 :
-
Outer radius of membrane [m]
- R m :
-
Membrane resistance [m2 hr/L s] 3
- R f :
-
Fouling resistance [m2 hr/L s]
- Re :
-
Reynolds number [dimensionless]
- TMP:
-
Trans-membrane pressure [kPa]
- V :
-
Transverse fluid velocity, [m/s]
- Ω :
-
Amplitude of angular velocity [rad/s]
- μ :
-
Viscosity of the fluid [N s/m2]
- ν :
-
Kinematic viscosity of the fluid [m2/s])
- γ :
-
Wall shear rate [s−1]
- γ max :
-
Maximum shear rate [s−1]
References
Akoum O, Jaffrin MY, Ding L, Paullier P, Vanhoutte C (2002) An hydrodynamic investigation of microfiltration and ultrafiltration in a vibrating membrane module. J Membr Sci 197:37–52
Akoum O, Jaffrin MY, Ding L (2005) Concentration of total milk proteins by high shear ultrafiltration in a vibrating membrane module. J Membr Sci 247:211–220
Akoum O, Richfield D, Jaffrin MY, Ding LH, Swart P (2006) Recovery of trypsin inhibitor and soy milk protein concentration by dynamic filtration. J Membr Sci 279:291–300
Babel S, Takizawa S (2010) Microfiltration membrane fouling and cake behavior during algal filtration. Desalination 261:46–51
Babel S, Takizawa S (2011) Chemical pretreatment for reduction of membrane fouling caused by algae. Desalination 274:171–176
Babel S, Takizawa S, Ozaki H (2002) Factors affecting seasonal variation of membrane filtration resistance caused by Chlorella algae. Water Res 36:1193–1202
Batan L, Quinn J, Willson B, Bradley T (2010) Net energy and greenhouse gas emissions evaluation of biodiesel derived from microalgae. Environ Sci Technol 44:7975–7980
Beier SP, Jonsson G (2007) Separation of enzymes and yeast cells with a vibrating hollow fiber membrane module. Sep Purif Technol 53:111–118
Beier SP, Jonsson G (2009) A vibrating membrane bioreactor (VMBR): macromolecular transmission—influence of extracellular polymeric substances. Chem Eng Sci 64:1436–1444
Beier SP, Guerra M, Garde A, Jonsson G (2006) Dynamic microfiltration with a vibrating hollow fiber membrane module: filtration of yeast suspensions. J Membr Sci 281:281–287
Bilad MR, Vandamme D, Foubert I, Muylaert K, Vankelecom IFJ (2012) Harvesting microalgal biomass using submerged microfiltration membranes. Bioresour Technol 111:343–352
Brondani M, Hoffmann R, Mayer FD, Kleinert JS (2014) Environmental and energy analysis of biodiesel production in Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. Clean Technol Environ Policy. doi:10.1007/s10098-014-0768-x
Campbell PK, Beer T, Batten D (2011) Life cycle assessment of biodiesel production from microalgae in ponds. Bioresour Technol 102:50–56
Castaing J-B, Massé A, Pontié M, Séchet V, Haure J, Jaouen P (2010) Investigating submerged ultrafiltration (UF) and microfiltration (MF) membranes for seawater pre-treatment dedicated to total removal of undesirable micro-algae. Desalination 253:71–77
Cavalett O, Junqueira TL, Dias MOS, Jesus CDF, Mantelatto PE, Cunha MP, Franco HCJ, Cardoso TF, Filho RM, Rossell CEV, Bonomi A (2012) Environmental and economic assessment of sugarcane first generation biorefineries in Brazil. Clean Technol Environ Policy 14:399–410
Cheryan M (1998) Ultrafiltration and microfiltration handbook, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Chiou Y-T, Hsieh M-L, Yeh H-H (2010) Effect of algal extracellular polymer substances on UF membrane fouling. Desalination 250:648–652
Danquah MK, Li A, Uduman N, Moheimani N, Forde GM (2009) Dewatering of microalgal culture for biodiesel production: exploring polymer flocculation and tangential flow filtration. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 84:1078–1083
De Baerdemaeker T, Lemmens B, Dotremont C, Fret J, Roef L, Goiris K, Diels L (2013) Benchmark study on algae harvesting with backwashable submerged flat panel membranes. Bioresour Technol 129:582–591
Discart V, Bilad MR, Vandamme D, Foubert I, Muylaert K, Vankelecom IFJ (2013) Role of transparent exopolymeric particles in membrane fouling: Chlorella vulgaris broth filtration. Bioresour Technol 129:18–25
Gabriel KJ, El-Halwagi MM (2013) Modeling and optimization of a bioethanol production facility. Clean Technol Environ Policy 15:931–944
Garcia A, Alriols MG, Wukovits W, Friedl A, Labidi J (2014) Assessment of biorefinery process intensification by ultrasound technology. Clean Technol Environ Policy 16:1403–1410
Gomaa HG, Rao S, Al Taweel M (2011) Flux enhancement using oscillatory motion and turbulence promoters. J Membr Sci 381:64–73
Grima EM, Belarbi E-H, Acien Fernandez FG, Robles MA, Chisti Y (2003) Recovery of microalgal biomass and metabolites: process options and economics. Biotechnol Adv 20:491–515
Ho WSW, Sirkar KK (1992) Membrane handbook. Van Nostrand-Reinhold, New York
Jaffrin MY (2008) Dynamic shear-enhanced membrane filtration: a review of rotating disks, rotating membranes and vibrating systems. J Membr Sci 324:7–25
Jaffrin MY, Akoum O, Ding LH (2002) Microfiltration and ultrafiltration of UHT skim milk with a vibrating membrane module. Sep Purif Technol 28:219–234
Jaffrin MY, Ding LH, Akoum O, Brou A (2004) A hydrodynamic comparison between rotating disk and vibratory dynamic filtration systems. J Membr Sci 242:155–167
Kola A, Ye Y, Ho A, Le-Clech P, Chen V (2012) Application of low frequency transverse vibration on fouling limitation in submerged hollow fiber membranes. J Membr Sci 409–410:54–65
Kravanja P, Konighofer K, Canella L, Jungmeier G, Friedl A (2012) Perspectives for the production of bioethanol from wood and straw in Austria: technical, economic, and ecological aspects. Clean Technol Environ Policy 14:411–425
Kwon B, Park N, Cho J (2005) Effect of algae on fouling and efficiency of UF membranes. Desalination 179:203–214
Ladner DA, Vardona DR, Clark MM (2010) Effects of shear on microfiltration and ultrafiltration fouling by marine bloom-forming algae. J Membr Sci 356:33–43
Lardon L, Helias A, Sialve B, Stayer JP, Bernard O (2009) Lifecycle assessment of biodiesel production from microalgae. Environ Sci Technol 43:6475–6481
Lee N, Amy G, Croue J-P, Buisson H (2004) Identification and understanding of fouling in low-pressure membrane (MF/UF) filtration by natural organic matter (NOM). Water Res 38:4511–4523
Lee N, Amy G, Croue J-P (2006) Low-pressure membrane (MF/UF) fouling associated with allochthonous versus autochthonous natural organic matter. Water Res 40:2357–2368
Lee D-J, Liao G-Y, Chang Y-R, Chang J-S (2012) Chitosan coagulation-membrane filtration of Chorella vulgaris. Int J Hydrogen Energy 37:15643–15647
Li T, Law AW-K, Cetin M, Fane AG (2013) Fouling control of submerged hollow fibre membranes by vibrations. J Membr Sci 427:230–239
Mezohegyi G, Bilad MR, Vankelecom IFJ (2012) Direct sewage up-concentration by submerged aerated and vibrated membranes. Bioresour Technol 118:1–7
Mulder M (1996) Basic principles of membrane technology, 2nd edn. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht
New Logic (2014) Application note: algae dewatering with VSEP. http://www.vsep.com/pdf/Membrane-Filtration-of-Algae-Application-Note.pdf. Accessed October 1 2014
Nurra C, Clavero E, Salvado J, Torras C (2014a) Vibrating membrane filtration as improved technology for microalgae dewatering. Bioresour Technol 157:247–253
Nurra C, Torras C, Clavero E, Rios S, Rey M, Lorente E, Farriol X, Salvado J (2014b) Biorefinery concept in a microalgae pilot plant. Culturing, dynamic filtration, and steam explosion fractionation. Bioresour Technol 163:136–142
O’Connell D, Savelski M, Slater CS (2013) Life cycle assessment of dewatering routes for algae derived biodiesel processes. Clean Technol Environ Policy 15:567–577
Petala MD, Zouboulis AI (2006) Vibratory shear enhanced processing membrane filtration applied for the removal of natural organic matter from surface waters. J Membr Sci 269:1–14
Postlethwaite J, Lamping SR, Leach GC, Hurwitz MF, Lye GJ (2004) Flux and transmission characteristics of a vibrating microfiltration system operated at high biomass loading. J Membr Sci 228:89–101
Qu F, Liang H, Tian J, Yu H, Chen Z, Li G (2012) Ultrafiltration (UF) membrane fouling caused by cyanobateria: fouling effects of cells and extracellular organics matter (EOM). Desalination 293:30–37
Rickman M, Pellegrino J, Davis R (2012) Fouling phenomena during membrane filtration of microalgae. J Membr Sci 423–424:33–42
Rios SD, Salvado J, Farriol X, Torras C (2012) Antifouling microfiltration strategies to harvest microalgae for biofuel. Bioresour Technol 119:406–418
Rosenblat S (1960) Flow between torsionally oscillating disks. J Fluid Mech 8:388–399
Sander K, Murthy GS (2010) Life cycle analysis of algae biodiesel. Int J Life Cycle Assess 15:704–714
Santos DT, Albarelli JQ, Rostagno MA, Ensinas AV, Marechal F, Meireles MAA (2014) New proposal for production of bioactive compounds by supercritical technology integrated to a sugarcane biorefinery. Clean Technol Environ Policy 16:1455–1468
Shi W, Benjamin MM (2008) Membrane interactions with NOM and an adsorbent in a vibratory shear enhanced filtration process (VSEP) system. J Membr Sci 312:23–33
Shi W, Benjamin MM (2009) Fouling of RO membranes in a vibratory shear enhanced filtration process (VSEP) system. J Membr Sci 331:11–20
Sioutopoulos DC, Yiantsios SG, Karabelas AJ (2010) Relation between fouling characteristics of RO and UF membranes in experiments with colloidal organic and inorganic species. J Membr Sci 350:62–82
Stephenson AL, Kazamina E, Dennis JS, Howe CJ, Scott SA, Smith AG (2010) Assessment of potential algal biodiesel production in the United Kingdom: a comparison of raceways and air-lift tubular bioreactors. Energy Fuels 24:4062–4077
Subramani A, DeCarolis J, Pearce W, Jacangelo JG (2012) Vibratory shear enhanced process (VSEP) for treating brackish water reverse osmosis concentrate with high silica content. Desalination 29(1):15–22
Tang MC, Chin MWS, Lim KM, Mun YS, Ng RTL, Tay DHS, Ng DKS (2013) Systematic approach for conceptual design of an integrated biorefinery with uncertainties. Clean Technol Environ Policy 15:783–799
Wicaksana F, Fane AG, Pongpairoj P, Field R (2012) Microfiltration of algae (Chlorella sorokiniana): critical flux, fouling and transmission. J Membr Sci 387–388:83–92
Zamani F, Law AWK, Fane AG (2013) Hydrodynamic analysis of vibrating hollow fibre membranes. J Membr Sci 429:304–312
Acknowledgments
Support for this research is provided by a Grant from the U.S. Department of Energy—#EE0003113. We acknowledge Rowan University Chemical Engineering students: Joseph Garrett, Kevin Rodier, Matthew van der Wielen, and Allyson White for their assistance with the experimental studies. We also would like to thank Mr. Mark Galimberti of New Logic Research for his help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Slater, C.S., Savelski, M.J., Kostetskyy, P. et al. Shear-enhanced microfiltration of microalgae in a vibrating membrane module. Clean Techn Environ Policy 17, 1743–1755 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-015-0907-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-015-0907-z