Abstract
Purpose
High fasting plasma glucose (HFPG) has been identified as a risk factor for drug-resistant tuberculosis incidence and mortality. However, the epidemic characteristics of HFPG-attributable multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) and extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis (XDR-TB) remain unclear. We aimed to analyze the global spatial patterns and temporal trends of HFPG-attributable MDR-TB and XDR-TB from 1990 to 2019.
Methods
Utilizing data from the Global Burden of Disease 2019 project, annual deaths and disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) of HFPG-attributable MDR-TB and XDR-TB were conducted from 1990 to 2019. Joinpoint regression was employed to quantify trends over time.
Results
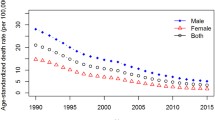
From 1990 to 2019, the deaths and DALYs due to HFPG-attributable MDR-TB and XDR-TB globally showed an overall increasing trend, with a significant increase until 2003 to 2004, followed by a gradual decline or stability thereafter. The low sociodemographic index (SDI) region experienced the most significant increase over the past 30 years. Regionally, Sub-Saharan Africa, Central Asia and Oceania remained the highest burden. Furthermore, there was a sex and age disparity in the burden of HFPG-attributable MDR-TB and XDR-TB, with young males in the 25–34 age group experiencing higher mortality, DALYs burden and a faster increasing trend than females. Interestingly, an increasing trend followed by a stable or decreasing pattern was observed in the ASMR and ASDR of HFPG-attributable MDR-TB and XDR-TB with SDI increasing.
Conclusion
The burden of HFPG-attributable MDR-TB and XDR-TB rose worldwide from 1990 to 2019. These findings emphasize the importance of routine bi-directional screening and integrated management for drug-resistant TB and diabetes.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available in the [Global Health Data Exchange GBD Results Tool] repository, [http://ghdx.healthdata.org/gbd-results-tool].
References
Dheda K, Barry CE 3rd, Maartens G (2016) Tuberculosis Lancet 387(10024):1211–1226
World Health Organization (2022) Global tuberculosis report 2022. Geneva: World health organization. licence: cc bY-Nc-sa 3.0 iGo. https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/363752/9789240061729-eng.pdf?sequence=1
World Health Organization (2012) Drug-resistant tuberculosis. https://www.who.int/news/item/13-01-2012-drug-resistant-tuberculosis
GBD 2019 Tuberculosis Collaborators (2022) Global, regional, and national sex differences in the global burden of tuberculosis by HIV status, 1990–2019: results from the global burden of disease study 2019. Lancet Infect Dis 22(2):222–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00449-7
Magee MJ, Blumberg HM, Narayan KM (2011) Commentary: Co-occurrence of tuberculosis and diabetes: new paradigm of epidemiological transition. Int J Epidemiol 40(2):428–431
World Health Organization (2022) Rapid communication: Key changes to treatment of multidrug- and rifampicin-resistant tuberculosis. WHO/UCN/TB/2022.2. Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO. https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/353743/WHO-UCN-TB-2022.2-eng.pdf?sequence=1
Ahmad E, Lim S, Lamptey R, Webb DR, Davies MJ (2022) Type 2 diabetes. Lancet 400(10365):1803–1820
Saeedi P, Petersohn I, Salpea P, Malanda B, Karuranga S, Unwin N, Colagiuri S, Guariguata L, Motala AA, Ogurtsova K, Shaw JE, Bright D, Williams R (2019) Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9(th) edition. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 157:107843
Riza AL, Pearson F, Ugarte-Gil C, Alisjahbana B, van de Vijver S, Panduru NM, Hill PC, Ruslami R, Moore D, Aarnoutse R, Critchley JA, van Crevel R (2014) Clinical management of concurrent diabetes and tuberculosis and the implications for patient services. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2(9):740–753
Lu P, Zhang Y, Liu Q, Ding X, Kong W, Zhu L, Lu W (2021) Association of BMI, diabetes, and risk of tuberculosis: a population-based prospective cohort. Int J Infect Dis 109:168–173
van Crevel R, Dockrell HM (2014) TANDEM: understanding diabetes and tuberculosis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2(4):270–272
Ruesen C, Chaidir L, Ugarte-Gil C, van Ingen J, Critchley JA, Hill PC, Ruslami R, Santoso P, Huynen MA, Dockrell HM, Moore DAJ, Alisjahbana B, van Crevel R (2020) Diabetes is associated with genotypically drug-resistant tuberculosis. Eur Respir J 55(3):1901891
Baker MA, Harries AD, Jeon CY, Hart JE, Kapur A, Lönnroth K, Ottmani SE, Goonesekera SD, Murray MB (2011) The impact of diabetes on tuberculosis treatment outcomes: a systematic review. BMC Med 9:81
Asadollahi K, Beeching N, Gill G (2007) Hyperglycaemia and mortality. J R Soc Med 100(11):503–507
Liang R, Feng X, Shi D, Yang M, Yu L, Liu W, Zhou M, Wang X, Qiu W, Fan L, Wang B, Chen W (2022) The global burden of disease attributable to high fasting plasma glucose in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: An updated analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 38(8):e3572
Danaei G, Finucane MM, Lu Y, Singh GM, Cowan MJ, Paciorek CJ, Lin JK, Farzadfar F, Khang YH, Stevens GA, Rao M, Ali MK, Riley LM, Robinson CA, Ezzati M (2011) National, regional, and global trends in fasting plasma glucose and diabetes prevalence since 1980: systematic analysis of health examination surveys and epidemiological studies with 370 country-years and 2·7 million participants. Lancet 378(9785):31–40
Tegegne BS, Mengesha MM, Teferra AA, Awoke MA, Habtewold TD (2018) Association between diabetes mellitus and multi-drug-resistant tuberculosis: evidence from a systematic review and meta-analysis. Syst Rev 7(1):161
Xu G, Hu X, Lian Y, Li X (2023) Diabetes mellitus affects the treatment outcomes of drug-resistant tuberculosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Infect Dis 23(1):813
Liu Q, Li W, Xue M, Chen Y, Du X, Wang C, Han L, Tang Y, Feng Y, Tao C, He JQ (2017) Diabetes mellitus and the risk of multidrug resistant tuberculosis: a meta-analysis. Sci Rep 7(1):1090
Viswanathan V, Kumpatla S, Aravindalochanan V, Rajan R, Chinnasamy C, Srinivasan R, Selvam JM, Kapur A (2012) Prevalence of diabetes and pre-diabetes and associated risk factors among tuberculosis patients in India. PLoS One 7(7):e41367
Bashar M, Alcabes P, Rom WN, Condos R (2001) Increased incidence of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis in diabetic patients on the Bellevue Chest Service, 1987 to 1997. Chest 120(5):1514–1519
Fisher-Hoch SP, Whitney E, McCormick JB, Crespo G, Smith B, Rahbar MH, Restrepo BI (2008) Type 2 diabetes and multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. Scand J Infect Dis 40(11–12):888–893
Song WM, Shao Y, Liu JY, Tao NN, Liu Y, Zhang QY, Xu TT, Li SJ, Yu CB, Gao L, Cui LL, Li YF, Li HC (2019) Primary drug resistance among tuberculosis patients with diabetes mellitus: a retrospective study among 7223 cases in China. Infect Drug Resist 12:2397–2407
Baghaei P, Tabarsi P, Javanmard P, Farnia P, Marjani M, Moniri A, Masjedi MR, Velayati AA (2016) Impact of diabetes mellitus on tuberculosis drug resistance in new cases of tuberculosis. J Glob Antimicrob Resist 4:1–4
Lyu M, Wang D, Zhao J, Yang Z, Chong W, Zhao Z, Ming L, Ying B (2020) A novel risk factor for predicting anti-tuberculosis drug resistance in patients with tuberculosis complicated with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int J Infect Dis 97:69–77
Mehta S, Yu EA, Ahamed SF, Bonam W, Kenneth J (2015) Rifampin resistance and diabetes mellitus in a cross-sectional study of adult patients in rural South India. BMC Infect Dis 15:451
Lönnroth K, Roglic G, Harries AD (2014) Improving tuberculosis prevention and care through addressing the global diabetes epidemic: from evidence to policy and practice. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2(9):730–739
GBD 2019 Risk Factors Collaborators (2020) Global burden of 87 risk factors in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet. 396(10258):1223–1249. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30752-2
Singh GM, Danaei G, Farzadfar F, Stevens GA, Woodward M, Wormser D, Kaptoge S, Whitlock G, Qiao Q, Lewington S, Di Angelantonio E, Vander Hoorn S, Lawes CM, Ali MK, Mozaffarian D, Ezzati M (2013) The age-specific quantitative effects of metabolic risk factors on cardiovascular diseases and diabetes: a pooled analysis. PLoS One 8(7):e65174
GBD Tuberculosis Collaborators (2018) Global, regional, and national burden of tuberculosis, 1990-2016: results from the Global Burden of Diseases, injuries, and risk factors 2016 Study. Lancet Infect Dis 18(12):1329–1349. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(18)30625-X
GBD 2019 Tuberculosis Collaborators (2022) Global, regional, and national sex differences in the global burden of tuberculosis by HIV status, 1990–2019: results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Infect Dis. 22(2):222–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00449-7
World Health Organization (2021) Meeting report of the WHO expert consultation on the definition of extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis. CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO. https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/338776/9789240018662-eng.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y
World Health Organization (2021) WHO announces updated definitions of extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis. https://www.who.int/news/item/27-01-2021-who-announces-updated-definitions-of-extensively-drug-resistant-tuberculosis
Skrahina A, Hurevich H, Zalutskaya A, Sahalchyk E, Astrauko A, Hoffner S, Rusovich V, Dadu A, de Colombani P, Dara M, van Gemert W, Zignol M (2013) Multidrug-resistant tuberculosis in Belarus: the size of the problem and associated risk factors. Bull World Health Organ 91(1):36–45
Liu C, Wang B, Liu S, Li S, Zhang K, Luo B, Yang A (2021) Type 2 diabetes attributable to PM(2.5): A global burden study from 1990 to 2019. Environ Int 156:106725
GBD 2019 Diseases and Injuries Collaborators (2020) Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 396(10258):1204–1222. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30925-9
Liu J, Yuan M, Chen Y, Wang Y, Wang Q, Zhang Q, Chai L, Li D, Qiu Y, Chen H, Wang J, Xie X, Li M (2022) Global burden of asthma associated with high body mass index from 1990 to 2019. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 129(6):720-730.e728
Zhang J, Ma B, Han X, Ding S, Li Y (2022) Global, regional, and national burdens of HIV and other sexually transmitted infections in adolescents and young adults aged 10–24 years from 1990 to 2019: a trend analysis based on the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Child Adolesc Health 6(11):763–776
Chen Y, Liu J, Zhang Q, Wang Q, Chai L, Chen H, Li D, Qiu Y, Wang Y, Shen N, Wang J, Xie X, Li S, Li M (2023) Epidemiological features and temporal trends of HIV-negative tuberculosis burden from 1990 to 2019: a retrospective analysis based on the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. BMJ Open 13(9):e074134
Bu Q, Qiang R, Fang L, Peng X, Zhang H, Cheng H (2023) Global trends in the incidence rates of MDR and XDR tuberculosis: Findings from the global burden of disease study 2019. Front Pharmacol 14:1156249
Ou ZJ, Yu DF, Liang YH, He WQ, Li YZ, Meng YX, Xiong HS, Zhang MY, He H, Gao YH, Wu F, Chen Q (2021) Trends in burden of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis in countries, regions, and worldwide from 1990 to 2017: results from the Global Burden of Disease study. Infect Dis Poverty 10(1):24
Stevenson CR, Forouhi NG, Roglic G, Williams BG, Lauer JA, Dye C, Unwin N (2007) Diabetes and tuberculosis: the impact of the diabetes epidemic on tuberculosis incidence. BMC Public Health 7:234
Dooley KE, Tang T, Golub JE, Dorman SE, Cronin W (2009) Impact of diabetes mellitus on treatment outcomes of patients with active tuberculosis. Am J Trop Med Hyg 80(4):634–639
Mushtaq A (2019) Tuberculosis in diabetes: insidious and neglected. Lancet Respir Med 7(6):483
Marais BJ, Raviglione MC, Donald PR, Harries AD, Kritski AL, Graham SM, El-Sadr WM, Harrington M, Churchyard G, Mwaba P, Sanne I, Kaufmann SH, Whitty CJ, Atun R, Zumla A (2010) Scale-up of services and research priorities for diagnosis, management, and control of tuberculosis: a call to action. Lancet 375(9732):2179–2191
Dooley KE, Chaisson RE (2009) Tuberculosis and diabetes mellitus: convergence of two epidemics. Lancet Infect Dis 9(12):737–746
The Lancet Diabetes E (2014) Diabetes and tuberculosis–a wake-up call. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2(9):677
World Health Organization (2016) WHO director-general launches diabetes report. https://www.who.int/director-general/speeches/detail/who-director-general-launches-diabetes-report.
World Health Organization. Communicable Diseases Cluster. (2001) Guidelines for drug susceptibility testing for second-line anti-tuberculosis drugs for dots-plus. WHO/CDS/TB/2001.288. https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/83807/WHO_CDS_TB_2001.288_eng.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y
Anderson LF, Tamne S, Watson JP, Cohen T, Mitnick C, Brown T, Drobniewski F, Abubakar I (2013) Treatment outcome of multi-drug resistant tuberculosis in the United Kingdom: retrospective-prospective cohort study from 2004 to 2007. Euro Surveill 18(40):20601. https://doi.org/10.2807/1560-7917.es2013.18.40.20601
Moadebi S, Harder CK, Fitzgerald MJ, Elwood KR, Marra F (2007) Fluoroquinolones for the treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis. Drugs 67(14):2077–2099
Kim SJ (2005) Drug-susceptibility testing in tuberculosis: methods and reliability of results. Eur Respir J 25(3):564–569
World Health Organization (2006) Guidelines for the programmatic management of drug-resistant tuberculosis, WHO/CDS/TB/2001.288. https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/246249/9789241546959-eng.pdf?sequence=2&isAllowed=y
World Health Organization & Stop TB Partnership. Task Force on Retooling (2008) New laboratory diagnostic tools for tuberculosis control. https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/44036/9789241597487_eng.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y
World Health Organization & International Union against Tuberculosis and Lung Disease (2011) Collaborative framework for care and control of tuberculosis and diabetes. https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/44698/9789241502252_eng.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y
Zhang T, Zhang J, Wei L, Liang H, Zhang J, Shi D, Wang Z (2023) The global, regional, and national burden of tuberculosis in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019. J Infect Public Health 16(3):368–375
Duarte R, Lönnroth K, Carvalho C, Lima F, Carvalho ACC, Muñoz-Torrico M, Centis R (2018) Tuberculosis, social determinants and co-morbidities (including HIV). Pulmonology 24(2):115–119
Moss AR, Hahn JA, Tulsky JP, Daley CL, Small PM, Hopewell PC (2000) Tuberculosis in the homeless. A prospective study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 162(1):460–464
Dara M, Acosta CD, Melchers NV, Al-Darraji HA, Chorgoliani D, Reyes H, Centis R, Sotgiu G, D’Ambrosio L, Chadha SS, Migliori GB (2015) Tuberculosis control in prisons: current situation and research gaps. Int J Infect Dis 32:111–117
Safaev K, Parpieva N, Liverko I, Yuldashev S, Dumchev K, Gadoev J, Korotych O, Harries AD (2021) Trends, Characteristics and Treatment Outcomes of Patients with Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis in Uzbekistan: 2013–2018. Int J Environ Res Public Health 18(9):4663
Dheda K, Gumbo T, Gandhi NR, Murray M, Theron G, Udwadia Z, Migliori GB, Warren R (2014) Global control of tuberculosis: from extensively drug-resistant to untreatable tuberculosis. Lancet Respir Med 2(4):321–338
Faustini A, Hall AJ, Perucci CA (2006) Risk factors for multidrug resistant tuberculosis in Europe: a systematic review. Thorax 61(2):158–163
GBD 2019 Diabetes Mortality Collaborators (2022) Diabetes mortality and trends before 25 years of age: an analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 10(3):177–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00349-1
Viner R, White B, Christie D (2017) Type 2 diabetes in adolescents: a severe phenotype posing major clinical challenges and public health burden. Lancet 389(10085):2252–2260
Shang WJ, Jing WZ, Wang YP, Kang LY, Du M, Liu J, Liu M (2022) Epidemic situation of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis and change trend in Belt and Road countries. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi 43(7):1060–1065
Dadu A, Hovhannesyan A, Ahmedov S, van der Werf MJ, Dara M (2020) Drug-resistant tuberculosis in eastern Europe and central Asia: a time-series analysis of routine surveillance data. Lancet Infect Dis 20(2):250–258
Gautam S, Shrestha N, Mahato S, Nguyen TPA, Mishra SR, Berg-Beckhoff G (2021) Diabetes among tuberculosis patients and its impact on tuberculosis treatment in South Asia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep 11(1):2113
Corbett EL, Marston B, Churchyard GJ, De Cock KM (2006) Tuberculosis in sub-Saharan Africa: opportunities, challenges, and change in the era of antiretroviral treatment. Lancet 367(9514):926–937
Bainomugisa A, Lavu E, Pandey S, Majumdar S, Banamu J, Coulter C, Marais B, Coin L, Graham SM, du Cros P (2022) Evolution and spread of a highly drug resistant strain of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in Papua New Guinea. BMC Infect Dis 22(1):437
Ley SD, Harino P, Vanuga K, Kamus R, Carter R, Coulter C, Pandey S, Feldmann J, Ballif M, Siba PM, Phuanukoonnon S, Gagneux S, Beck HP (2014) Diversity of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and drug resistance in different provinces of Papua New Guinea. BMC Microbiol 14:307
Global, regional, and national burden of diabetes from (1990) to 2021, with projections of prevalence to 2050: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet 402(10397):203–234
Falzon D, Mirzayev F, Wares F, Baena IG, Zignol M, Linh N, Weyer K, Jaramillo E, Floyd K, Raviglione M (2015) Multidrug-resistant tuberculosis around the world: what progress has been made? Eur Respir J 45(1):150–160
Lange C, Chesov D, Heyckendorf J, Leung CC, Udwadia Z, Dheda K (2018) Drug-resistant tuberculosis: An update on disease burden, diagnosis and treatment. Respirology 23(7):656–673
GBD 2017 DALYs and HALE Collaborators (2022) Global, regional, and national disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs) for 359 diseases and injuries and healthy life expectancy (HALE) for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 392(10159):1859–1922. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32335-3
Acknowledgements
Thanks to Xiao Ming (Xiaoming_room@hotmail.com) for his work in the GBD database. His excellent sharing of GBD database analysis procedure and other public database, makes it easier for us to explore the GBD database.
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province (Grant No. 2020JO-508).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YC: collecting data, analyzing data, writing the manuscript. JL, QZ, QW, LC, HC, JZ, YQ, YW, YS, JW, SL, ML: writing the manuscript, submitting to the publication. revising the manuscript. All authors contributed to manuscript revision, read and approved the submitted version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The present study was based on published data from the GBD 2019 study, which does not require specific institutional ethics approval.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Liu, J., Zhang, Q. et al. Global burden of MDR-TB and XDR-TB attributable to high fasting plasma glucose from 1990 to 2019: a retrospective analysis based on the global burden of disease study 2019. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 43, 747–765 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-024-04779-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-024-04779-x