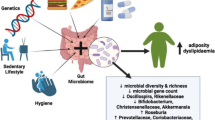
Abstract
The potential role of the gut microbiota in various human diseases has attracted considerable attention worldwide. Here, we discuss the vital role of the intestinal microbiota in the development of obesity. First, we describe how the gut microbiota promotes fat accumulation. Additionally, a high-fat diet leads to structural instability among in the gut microbiota, further leading to an increase in endotoxins, which aggravates obesity. We then discuss how gut microbiota metabolites, including short-chain fatty acids and lipopolysaccharides, affect the host. Finally, we review several strategies for regulating the intestinal flora.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- LPS:
-
lipopolysaccharides
- TNF-α:
-
tumor necrosis factor-α
- IL-1β:
-
interleukin 1β
- LPL:
-
lipoprotein lipase
- AMPK:
-
adenosine monophosphate–activated protein kinase
- SCFAs:
-
short-chain fatty acids
- FIAF:
-
fasting-induced adipocyte factor
- Cpt1:
-
carnitine palmitoyl transferase-1
- GPCRs:
-
G protein–coupled receptors
- TLR:
-
Toll-like receptor
- GLP:
-
glucagon-like peptide
- CD:
-
clusters of differentiation
- PGC-1α:
-
receptor-gamma coactivator-1α
- UCP-1:
-
mitochondrial uncoupling protein-1
- PYY:
-
peptide YY
- HFD:
-
high-fat diet
- TCA cycle:
-
tricarboxylic acid cycle
- LCFAs:
-
long-chain fatty acids
- Th.:
-
T helper
References
Williams EP, Mesidor M, Winters K, Dubbert PM, Wyatt SB (2015) Overweight and obesity: prevalence, consequences, and causes of a growing public health problem. Curr Obes Rep 4(3):363–370. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13679-015-0169-4
Cani PD, Osto M, Geurts L, Everard A (2012) Involvement of gut microbiota in the development of low-grade inflammation and type 2 diabetes associated with obesity. Gut Microbes 3(4):279–288. https://doi.org/10.4161/gmic.19625
Carvalho BM, Guadagnini D, Tsukumo DML, Schenka AA, Latuf-Filho P, Vassallo J, Dias JC, Kubota LT, Carvalheira JBC, Saad MJA (2012) Modulation of gut microbiota by antibiotics improves insulin signalling in high-fat fed mice. Diabetologia 55(10):2823–2834. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-012-2648-4
Guarner F, Malagelada J-R (2003) Gut flora in health and disease. Lancet 361(9356):512–519. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(03)12489-0
Eckburg PB, Bik EM, Bernstein CN, Purdom E, Dethlefsen L, Sargent M, Gill SR, Nelson KE, Relman DA (2005) Diversity of the human intestinal microbial flora. Science 308(5728):1635–1638. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1110591
James SL, Muir JG, Curtis SL, Gibson PR (2003) Dietary fibre: a roughage guide. Intern Med J 33(7):291–296
Piya MK, Harte AL, McTernan PG (2013) Metabolic endotoxaemia: is it more than just a gut feeling? Curr Opin Lipidol 24(1):78–85. https://doi.org/10.1097/MOL.0b013e32835b4431
Teixeira TF, Collado MC, Ferreira CL, Bressan J, Peluzio Mdo C (2012) Potential mechanisms for the emerging link between obesity and increased intestinal permeability. Nutr Res 32(9):637–647. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nutres.2012.07.003
Nieto-Vazquez I, Fernandez-Veledo S, Kramer DK, Vila-Bedmar R, Garcia-Guerra L, Lorenzo M (2008) Insulin resistance associated to obesity: the link TNF-alpha. Arch Physiol Biochem 114(3):183–194. https://doi.org/10.1080/13813450802181047
Zhao L (2013) The gut microbiota and obesity: from correlation to causality. Nat Rev Microbiol 11(9):639–647. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro3089
Tabatabaei-Malazy O, Hasani-Ranjbar S, Amoli MM, Heshmat R, Sajadi M, Derakhshan R, Amiri P, Namakchian M, Rezazadeh E, Tavakkoly-Bazzaz J, Keshtkar A, Larijani B (2010) Gender-specific differences in the association of adiponectin gene polymorphisms with body mass index. Rev Diab Stud : RDS 7(3):241–246. https://doi.org/10.1900/rds.2010.7.241
Tavakkoly Bazzaz J, Shojapoor M, Nazem H, Amiri P, Fakhrzadeh H, Heshmat R, Parvizi M, Hasani Ranjbar S, Amoli MM (2010) Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene polymorphism in diabetes and obesity. Mol Biol Rep 37(1):105–109. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-009-9545-z
Ramdas M, Harel C, Armoni M, Karnieli E (2015) AHNAK KO mice are protected from diet-induced obesity but are glucose intolerant. Hormone Metab Res = Hormon- und Stoffwechselforschung = Hormones et metabolisme 47(4):265–272. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0034-1387736
Moreno-Indias I, Cardona F, Tinahones FJ, Queipo-Ortuno MI (2014) Impact of the gut microbiota on the development of obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Front Microbiol 5:190. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2014.00190
Turnbaugh PJ, Ley RE, Mahowald MA, Magrini V, Mardis ER, Gordon JI (2006) An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature 444(7122):1027–1031. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05414
Ley RE, Backhed F, Turnbaugh P, Lozupone CA, Knight RD, Gordon JI (2005) Obesity alters gut microbial ecology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102(31):11070–11075. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0504978102
Heimann E, Nyman M, Degerman E (2015) Propionic acid and butyric acid inhibit lipolysis and de novo lipogenesis and increase insulin-stimulated glucose uptake in primary rat adipocytes. Adipocyte 4(2):81–88. https://doi.org/10.4161/21623945.2014.960694
Chimerel C, Emery E, Summers DK, Keyser U, Gribble FM, Reimann F (2014) Bacterial metabolite indole modulates incretin secretion from intestinal enteroendocrine L cells. Cell Rep 9(4):1202–1208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2014.10.032
Backhed F, Ding H, Wang T, Hooper LV, Koh GY, Nagy A, Semenkovich CF, Gordon JI (2004) The gut microbiota as an environmental factor that regulates fat storage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101(44):15718–15723. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0407076101
Backhed F, Manchester JK, Semenkovich CF, Gordon JI (2007) Mechanisms underlying the resistance to diet-induced obesity in germ-free mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104(3):979–984. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0605374104
Matsuo K, Matsusue K, Aibara D, Takiguchi S, Gonzalez FJ, Yamano S (2017) Insulin represses fasting-induced expression of hepatic fat-specific protein 27. Pharm Soc Japn 40(6):888–893
Hardie DG, Ross FA, Hawley SA (2012) AMPK: a nutrient and energy sensor that maintains energy homeostasis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 13(4):251–262. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3311
Kahn BB, Alquier T, Carling D, Hardie DG (2005) AMP-activated protein kinase: ancient energy gauge provides clues to modern understanding of metabolism. Cell Metab 1(1):15–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2004.12.003
Le Poul E, Loison C, Struyf S, Springael JY, Lannoy V, Decobecq ME, Brezillon S, Dupriez V, Vassart G, Van Damme J, Parmentier M, Detheux M (2003) Functional characterization of human receptors for short chain fatty acids and their role in polymorphonuclear cell activation. J Biol Chem 278(28):25481–25489. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M301403200
Samuel BS, Shaito A, Motoike T, Rey FE, Backhed F, Manchester JK, Hammer RE, Williams SC, Crowley J, Yanagisawa M, Gordon JI (2008) Effects of the gut microbiota on host adiposity are modulated by the short-chain fatty-acid binding G protein-coupled receptor, Gpr41. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105(43):16767–16772. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0808567105
Karra E, Chandarana K, Batterham RL (2009) The role of peptide YY in appetite regulation and obesity. J Physiol 587(1):19–25. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2008.164269
McNeil NI (1984) The contribution of the large intestine to energy supplies in man. Am J Clin Nutr 39(2):338–342. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/39.2.338
Popovich DG, Jenkins DJ, Kendall CW, Dierenfeld ES, Carroll RW, Tariq N, Vidgen E (1997) The western lowland gorilla diet has implications for the health of humans and other hominoids. J Nutr 127(10):2000–2005. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/127.10.2000
Frost GS, Walton GE, Swann JR, Psichas A, Costabile A, Johnson LP, Sponheimer M, Gibson GR, Barraclough TG (2014) Impacts of plant-based foods in ancestral hominin diets on the metabolism and function of gut microbiota in vitro. mBio 5(3):e00853–e00814. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.00853-14
Cummings JH, Pomare EW, Branch WJ, Naylor CP, Macfarlane GT (1987) Short chain fatty acids in human large intestine, portal, hepatic and venous blood. Gut 28(10):1221–1227
Levrat MA, Remesy C, Demigne C (1991) High propionic acid fermentations and mineral accumulation in the cecum of rats adapted to different levels of inulin. J Nutr 121(11):1730–1737. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/121.11.1730
Donohoe DR, Garge N, Zhang X, Sun W, O’Connell TM, Bunger MK, Bultman SJ (2011) The microbiome and butyrate regulate energy metabolism and autophagy in the mammalian colon. Cell Metab 13(5):517–526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2011.02.018
De Vadder F, Kovatcheva-Datchary P, Goncalves D, Vinera J, Zitoun C, Duchampt A, Backhed F, Mithieux G (2014) Microbiota-generated metabolites promote metabolic benefits via gut-brain neural circuits. Cell 156(1–2):84–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2013.12.016
Frost G, Sleeth ML, Sahuri-Arisoylu M, Lizarbe B, Cerdan S, Brody L, Anastasovska J, Ghourab S, Hankir M, Zhang S, Carling D, Swann JR, Gibson G, Viardot A, Morrison D, Louise Thomas E, Bell JD (2014) The short-chain fatty acid acetate reduces appetite via a central homeostatic mechanism. Nat Commun 5:3611. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms4611
Blad CC, Tang C, Offermanns S (2012) G protein-coupled receptors for energy metabolites as new therapeutic targets. Nat Rev Drug Discov 11(8):603–619. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd3777
Offermanns S (2014) Free fatty acid (FFA) and hydroxy carboxylic acid (HCA) receptors. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 54:407–434. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-011613-135945
Leurs R, Bakker RA, Timmerman H, de Esch IJ (2005) The histamine H3 receptor: from gene cloning to H3 receptor drugs. Nat Rev Drug Discov 4(2):107–120. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd1631
Hansen AH, Sergeev E, Pandey SK, Hudson BD, Christiansen E, Milligan G, Ulven T (2017) Development and characterization of a fluorescent tracer for the free fatty acid receptor 2 (FFA2/GPR43). J Med Chem 60(13):5638–5645. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b00338
Muredda L, Kepczynska MA, Zaibi MS, Alomar SY, Trayhurn P (2018) IL-1beta and TNFalpha inhibit GPR120 (FFAR4) and stimulate GPR84 (EX33) and GPR41 (FFAR3) fatty acid receptor expression in human adipocytes: implications for the anti-inflammatory action of n-3 fatty acids. Arch Physiol Biochem 124(2):97–108. https://doi.org/10.1080/13813455.2017.1364774
Tang C, Offermanns S (2017) FFA2 and FFA3 in metabolic regulation. Handb Exp Pharmacol 236:205–220. https://doi.org/10.1007/164_2016_50
Priyadarshini M, Wicksteed B, Schiltz GE, Gilchrist A, Layden BT (2016) SCFA receptors in pancreatic beta cells: novel diabetes targets? Trends Endocrinol Metab 27(9):653–664. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2016.03.011
Chambers ES, Morrison DJ, Frost G (2015) Control of appetite and energy intake by SCFA: what are the potential underlying mechanisms? Proc Nutr Soc 74(3):328–336. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0029665114001657
Cani PD, Neyrinck AM, Maton N, Delzenne NM (2005) Oligofructose promotes satiety in rats fed a high-fat diet: involvement of glucagon-like Peptide-1. Obes Res 13(6):1000–1007. https://doi.org/10.1038/oby.2005.117
Holmes E, Li JV, Marchesi JR, Nicholson JK (2012) Gut microbiota composition and activity in relation to host metabolic phenotype and disease risk. Cell Metab 16(5):559–564. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2012.10.007
Chambers ES, Viardot A, Psichas A, Morrison DJ, Murphy KG, Zac-Varghese SE, MacDougall K, Preston T, Tedford C, Finlayson GS, Blundell JE, Bell JD, Thomas EL, Mt-Isa S, Ashby D, Gibson GR, Kolida S, Dhillo WS, Bloom SR, Morley W, Clegg S, Frost G (2015) Effects of targeted delivery of propionate to the human colon on appetite regulation, body weight maintenance and adiposity in overweight adults. Gut 64(11):1744–1754. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2014-307913
Qin J, Li R, Raes J, Arumugam M, Burgdorf KS, Manichanh C, Nielsen T, Pons N, Levenez F, Yamada T, Mende DR, Li J, Xu J, Li S, Li D, Cao J, Wang B, Liang H, Zheng H, Xie Y, Tap J, Lepage P, Bertalan M, Batto JM, Hansen T, Le Paslier D, Linneberg A, Nielsen HB, Pelletier E, Renault P, Sicheritz-Ponten T, Turner K, Zhu H, Yu C, Li S, Jian M, Zhou Y, Li Y, Zhang X, Li S, Qin N, Yang H, Wang J, Brunak S, Dore J, Guarner F, Kristiansen K, Pedersen O, Parkhill J, Weissenbach J, Meta HITC, Bork P, Ehrlich SD, Wang J (2010) A human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic sequencing. Nature 464(7285):59–65. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08821
Mondot S, de Wouters T, Dore J, Lepage P (2013) The human gut microbiome and its dysfunctions. Dig Dis 31(3–4):278–285. https://doi.org/10.1159/000354678
Xu J, Gordon JI (2003) Honor thy symbionts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100(18):10452–10459. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1734063100
Devkota S, Wang Y, Musch MW, Leone V, Fehlner-Peach H, Nadimpalli A, Antonopoulos DA, Jabri B, Chang EB (2012) Dietary-fat-induced taurocholic acid promotes pathobiont expansion and colitis in Il10-/- mice. Nature 487(7405):104–108. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11225
Lam V, Su J, Koprowski S, Hsu A, Tweddell JS, Rafiee P, Gross GJ, Salzman NH, Baker JE (2012) Intestinal microbiota determine severity of myocardial infarction in rats. FASEB J : official publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology 26(4):1727–1735. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.11-197921
Cani PD, Amar J, Iglesias MA, Poggi M, Knauf C, Bastelica D, Neyrinck AM, Fava F, Tuohy KM, Chabo C, Waget A, Delmee E, Cousin B, Sulpice T, Chamontin B, Ferrieres J, Tanti JF, Gibson GR, Casteilla L, Delzenne NM, Alessi MC, Burcelin R (2007) Metabolic endotoxemia initiates obesity and insulin resistance. Diabetes 56(7):1761–1772. https://doi.org/10.2337/db06-1491
Santos NCSAC, Castanho MA et al (2003) Evaluation of lipopolysaccharide aggregation by light scattering spectroscopy. Chembiochem 4(1):96–100
Furet JP, Kong LC, Tap J et al (2010) Differential adaptation of human gut microbiota to bariatric surgery-induced weight loss: links with metabolic and low-grade inflammation markers. Diabetes 59(12):3049–3057
Louis S, Tappu RM, Damms-Machado A, Huson DH, Bischoff SC (2016) Characterization of the gut microbial community of obese patients following a weight-loss intervention using whole metagenome shotgun sequencing. PLoS One 11(2):e0149564. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0149564
Medzhitov R, Horng T (2009) Transcriptional control of the inflammatory response. Nat Rev Immunol 9(10):692–703. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri2634
Taira RYS, Shimizu K et al (2015) Bacterial cell wall components regulate adipokine secretion from visceral adipocytes. J Clin Biochem Nutr 56(2):149–154. https://doi.org/10.3164/jcbn.14/74
Everard A, Belzer C, Geurts L, Ouwerkerk JP, Druart C, Bindels LB, Guiot Y, Derrien M, Muccioli GG, Delzenne NM, de Vos WM, Cani PD (2013) Cross-talk between Akkermansia muciniphila and intestinal epithelium controls diet-induced obesity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110(22):9066–9071. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1219451110
Laugerette F, Vors C, Geloen A, Chauvin MA, Soulage C, Lambert-Porcheron S, Peretti N, Alligier M, Burcelin R, Laville M, Vidal H, Michalski MC (2011) Emulsified lipids increase endotoxemia: possible role in early postprandial low-grade inflammation. J Nutr Biochem 22(1):53–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2009.11.011
Blaut M (2015) Gut microbiota and energy balance: role in obesity. Proc Nutr Soc 74(3):227–234. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0029665114001700
Cani PD, Bibiloni R, Knauf C, Waget A, Neyrinck AM, Delzenne NM, Burcelin R (2008) Changes in gut microbiota control metabolic endotoxemia-induced inflammation in high-fat diet-induced obesity and diabetes in mice. Diabetes 57(6):1470–1481. https://doi.org/10.2337/db07-1403
Suzuki T (2013) Regulation of intestinal epithelial permeability by tight junctions. Cell Mol Life Sci : CMLS 70(4):631–659. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-012-1070-x
Chaudhry KK, Samak G, Shukla PK, Mir H, Gangwar R, Manda B, Isse T, Kawamoto T, Salaspuro M, Kaihovaara P, Dietrich P, Dragatsis I, Nagy LE, Rao RK (2015) ALDH2 deficiency promotes ethanol-induced gut barrier dysfunction and fatty liver in mice. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 39(8):1465–1475. https://doi.org/10.1111/acer.12777
Vijay-Kumar M, Aitken JD, Carvalho FA, Cullender TC, Mwangi S, Srinivasan S, Sitaraman SV, Knight R, Ley RE, Gewirtz AT (2010) Metabolic syndrome and altered gut microbiota in mice lacking toll-like receptor 5. Science 328(5975):228–231. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1179721
Rocha DM, Caldas AP, Oliveira LL, Bressan J, Hermsdorff HH (2016) Saturated fatty acids trigger TLR4-mediated inflammatory response. Atherosclerosis 244:211–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2015.11.015
Fasano A (2011) Zonulin and its regulation of intestinal barrier function: the biological door to inflammation, autoimmunity, and cancer. Physiol Rev 91(1):151–175
Drucker DJ (2001) Glucagon-like peptide 2. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86(4):1759
Delzenne NM, Neyrinck AM, Backhed F, Cani PD (2011) Targeting gut microbiota in obesity: effects of prebiotics and probiotics. Nat Rev Endocrinol 7(11):639–646. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrendo.2011.126
Cox AJ, West NP, Cripps AW (2015) Obesity, inflammation, and the gut microbiota. Lancet Diab Endocrinol 3(3):207–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2213-8587(14)70134-2
Creely S, Mc Ternan PG, Kusminski CM et al (2007) Lipopolysaccharide activates an innate immune system response in human adipose tissue in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 292(3):E740. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00302.2006.-Type
Pussinen PJ, Havulinna AS, Lehto M, Sundvall J, Salomaa V (2011) Endotoxemia is associated with an increased risk of incident diabetes. Diabetes Care 34(2):392–397. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc10-1676
Bibbo S, Ianiro G, Gasbarrini A, Cammarota G (2017) Fecal microbiota transplantation: past, present and future perspectives. Minerva Gastroenterol Dietol 63(4):420–430. https://doi.org/10.23736/s1121-421x.17.02374-1
Eiseman B, Silen W, Bascom GS, Kauvar AJ (1958) Fecal enema as an adjunct in the treatment of pseudomembranous enterocolitis. Surgery 44(5):854–859
Kassam Z, Lee CH, Yuan Y, Hunt RH (2013) Fecal microbiota transplantation for Clostridium difficile infection: systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Gastroenterol 108(4):500–508. https://doi.org/10.1038/ajg.2013.59
Vrieze A, Van Nood E, Holleman F, Salojarvi J, Kootte RS, Bartelsman JF, Dallinga-Thie GM, Ackermans MT, Serlie MJ, Oozeer R, Derrien M, Druesne A, Van Hylckama Vlieg JE, Bloks VW, Groen AK, Heilig HG, Zoetendal EG, Stroes ES, de Vos WM, Hoekstra JB, Nieuwdorp M (2012) Transfer of intestinal microbiota from lean donors increases insulin sensitivity in individuals with metabolic syndrome. Gastroenterology 143(4):913–916 e917. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2012.06.031
Zhang H, DiBaise JK, Zuccolo A, Kudrna D, Braidotti M, Yu Y, Parameswaran P, Crowell MD, Wing R, Rittmann BE, Krajmalnik-Brown R (2009) Human gut microbiota in obesity and after gastric bypass. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106(7):2365–2370. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0812600106
Duboc H, Nguyen CC, Cavin JB, Ribeiro-Parenti L, Jarry AC, Rainteau D, Humbert L, Coffin B, Le Gall M, Bado A, Sokol H (2018) Roux-en-Y Gastric-Bypass and sleeve gastrectomy induces specific shifts of the gut microbiota without altering the metabolism of bile acids in the intestinal lumen. Int J Obes 43(2):428–431 (2005) undefined (undefined):undefined
Cani PD (2018) Severe obesity and gut microbiota: does bariatric surgery really reset the system? Gut 68(1):5–6. gutjnl-2018-316815. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2018-316815
Trehan I, Goldbach HS, LaGrone LN, Meuli GJ, Wang RJ, Maleta KM, Manary MJ (2016) Antibiotics as part of the management of severe acute malnutrition. Malawi Med J : the journal of Medical Association of Malawi 28(3):123–130
Hernandez E, Bargiela R, Diez MS, Friedrichs A, Perez-Cobas AE, Gosalbes MJ, Knecht H, Martinez-Martinez M, Seifert J, von Bergen M, Artacho A, Ruiz A, Campoy C, Latorre A, Ott SJ, Moya A, Suarez A, Martins dos Santos VA, Ferrer M (2013) Functional consequences of microbial shifts in the human gastrointestinal tract linked to antibiotic treatment and obesity. Gut Microbes 4(4):306–315. https://doi.org/10.4161/gmic.25321
Nguyen SG, Kim J, Guevarra RB, Lee JH, Kim E, Kim SI, Unno T (2016) Laminarin favorably modulates gut microbiota in mice fed a high-fat diet. Food Funct 7(10):4193–4201. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6fo00929h
Zheng J, Yuan X, Cheng G, Jiao S, Feng C, Zhao X, Yin H, Du Y, Liu H (2018) Chitosan oligosaccharides improve the disturbance in glucose metabolism and reverse the dysbiosis of gut microbiota in diabetic mice. Carbohydr Polym 190:77–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.02.058
Chang CJ, Lin CS, Lu CC, Martel J, Ko YF, Ojcius DM, Tseng SF, Wu TR, Chen YY, Young JD, Lai HC (2015) Ganoderma lucidum reduces obesity in mice by modulating the composition of the gut microbiota. Nat Commun 6:7489. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms8489
Delzenne NM, Bindels LB (2015) Gut microbiota: Ganoderma lucidum, a new prebiotic agent to treat obesity? Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 12(10):553–554. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2015.137
Roopchand DE, Carmody RN, Kuhn P et al (2015) Dietary polyphenols promote growth of the gut bacterium Akkermansia muciniphila and attenuate high-fat diet-induced metabolic syndrome. Diabetes 64(8):2847–2858. https://doi.org/10.2337/db14-1916/-/DC1
Yoo JY, Kim SS (2016) Probiotics and prebiotics: present status and future perspectives on metabolic disorders. Nutrients 8(3):173. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8030173
Anselmo AC, McHugh KJ, Webster J, Langer R, Jaklenec A (2016) Layer-by-layer encapsulation of probiotics for delivery to the microbiome. Adv Mater (Deerfield Beach, Fla) 28(43):9486–9490. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201603270
Moya-Perez A, Neef A, Sanz Y (2015) Bifidobacterium pseudocatenulatum CECT 7765 reduces obesity-associated inflammation by restoring the lymphocyte-macrophage balance and gut microbiota structure in high-fat diet-fed mice. PLoS One 10(7):e0126976. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0126976
Fontane L, Benaiges D, Goday A, Llaurado G, Pedro-Botet J (2018) Influence of the microbiota and probiotics in obesity. Clinica e investigacion en arteriosclerosis : publicacion oficial de la Sociedad Espanola de Arteriosclerosis. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arteri.2018.03.004
Okubo T, Takemura N, Yoshida A, Sonoyama K (2013) KK/Ta mice administered Lactobacillus plantarum strain no. 14 have lower adiposity and higher insulin sensitivity. Biosci Microbiota Food Health 32(3):93–100. https://doi.org/10.12938/bmfh.32.93
Million M, Angelakis E, Paul M, Armougom F, Leibovici L, Raoult D (2012) Comparative meta-analysis of the effect of Lactobacillus species on weight gain in humans and animals. Microb Pathog 53(2):100–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2012.05.007
Conlon MA, Bird AR (2014) The impact of diet and lifestyle on gut microbiota and human health. Nutrients 7(1):17–44. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu7010017
Mariat D, Firmesse O, Levenez F, Guimaraes V, Sokol H, Dore J, Corthier G, Furet JP (2009) The Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio of the human microbiota changes with age. BMC Microbiol 9:123. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2180-9-123
Wu GD, Chen J, Hoffmann C, Bittinger K, Chen YY, Keilbaugh SA, Bewtra M, Knights D, Walters WA, Knight R, Sinha R, Gilroy E, Gupta K, Baldassano R, Nessel L, Li H, Bushman FD, Lewis JD (2011) Linking long-term dietary patterns with gut microbial enterotypes. Science 334(6052):105–108. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1208344
Ley RE, Turnbaugh PJ, Klein S, Gordon JI (2006) Microbial ecology: human gut microbes associated with obesity. Nature 444(7122):1022–1023. https://doi.org/10.1038/4441022a
Sonnenburg ED, Smits SA, Tikhonov M, Higginbottom SK, Wingreen NS, Sonnenburg JL (2016) Diet-induced extinctions in the gut microbiota compound over generations. Nature 529(7585):212–215. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature16504
Haghikia A, Jorg S, Duscha A, Berg J, Manzel A, Waschbisch A, Hammer A, Lee DH, May C, Wilck N, Balogh A, Ostermann AI, Schebb NH, Akkad DA, Grohme DA, Kleinewietfeld M, Kempa S, Thone J, Demir S, Muller DN, Gold R, Linker RA (2016) Dietary fatty acids directly impact central nervous system autoimmunity via the small intestine. Immunity 44(4):951–953. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2016.04.006
Semova I, Carten JD, Stombaugh J, Mackey LC, Knight R, Farber SA, Rawls JF (2012) Microbiota regulate intestinal absorption and metabolism of fatty acids in the zebrafish. Cell Host Microbe 12(3):277–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2012.08.003
Gauffin Cano P, Santacruz A, Moya A, Sanz Y (2012) Bacteroides uniformis CECT 7771 ameliorates metabolic and immunological dysfunction in mice with high-fat-diet induced obesity. PLoS One 7(7):e41079. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0041079
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Industry University Research Collaborative Innovation Major Projects of Guangzhou Science Technology Innovation Commission, China (201604020164), Guangdong Provincial University Engineering Technology Research Center of Natural Products and Drugs (2017GCZX002), Technology Planning Project of Guangzhou, China (201806040009, 201804010349, 201804010329), and the National Science Foundation of China (no. 81173107).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Cuiting Zhi had the idea for the article and drafted it. Jingqing Huang and Jin Wang performed the literature search. Cuiting Zhi, Yan Bai, Jiao Guo, and Zhengquan Su critically revised the work.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhi, C., Huang, J., Wang, J. et al. Connection between gut microbiome and the development of obesity. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 38, 1987–1998 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-019-03623-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-019-03623-x