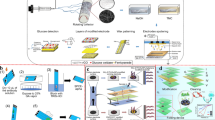
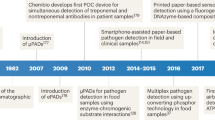
Abstract
Paper-based devices provide an alternative technology for simple, low-cost, portable, and disposable or recyclable diagnostic tools for many applications, including clinical diagnosis, food quality control, and environmental monitoring. The present review focuses on new paper-based tests for point-of-care (POC) infectious disease testing. This review provides a brief presentation of the fabrication techniques and the main sample preparation procedures. Recent immunological and molecular testing formats based on new paper-based solutions which go beyond conventional lateral flow formats are also added. Emphasis is placed on how paper systems could be used for detecting whole and viable bacteria associated to infectious diseases. Paper has recently become attractive, since it is a ubiquitous and extremely cheap material. It is easy to store, easy to use, and is compatible with many (bio)chemical and (bio)medical applications. Paper absorbs and transports liquids by capillary force without additional mechanical assistance. Hence, paper-based analytical devices are promising and possibly game-changing, even if they still suffer from limitations, including accuracy and sensitivity. It is anticipated that, in the near future, with advances in fabrication procedures and associated analytical techniques, there will be a continuous flow of innovative paper-based diagnostics kits.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liana DD, Raguse B, Gooding JJ, Chow E (2012) Recent advances in paper-based sensors. Sensors (Basel) 12:11505–11526
Martinez AW, Phillips ST, Whitesides GM, Carrilho E (2010) Diagnostics for the developing world: microfluidic paper-based analytical devices. Anal Chem 82:3–10
Shah P, Zhu X, Li CZ (2013) Development of paper-based analytical kit for point-of-care testing. Expert Rev Mol Diagn 13:83–91
Parolo C, Merkoçi A (2013) Paper-based nanobiosensors for diagnostics. Chem Soc Rev 42:450–457
Fu E, Liang T, Houghtaling J, Ramachandran S, Ramsey SA, Lutz B, Yager P (2011) Enhanced sensitivity of lateral flow tests using a two-dimensional paper network format. Anal Chem 83:7941–7946
Hagerstwon M (2002) Goals, guidelines and principles for point-of-care testing. In: Kost GJ (ed) Principles and practice of point-of-care testing. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 3–12
Tolonen U, Kallio M, Ryhänen J, Raatikainen T, Honkala V, Lesonen V (2007) A handheld nerve conduction measuring device in carpal tunnel syndrome. Acta Neurol Scand 115:390–397
Martinez AW, Phillips ST, Carrilho E, Thomas SW 3rd, Sindi H, Whitesides GM (2008) Simple telemedicine for developing regions: camera phones and paper-based microfluidic devices for real-time, off-site diagnosis. Anal Chem 80:3699–3707
Crowley TA, Pizziconi V (2005) Isolation of plasma from whole blood using planar microfilters for lab-on-a-chip applications. Lab Chip 5:922–929
VanDelinder V, Groisman A (2006) Separation of plasma from whole human blood in a continuous cross-flow in a molded microfluidic device. Anal Chem 78:3765–3771
Songjaroen T, Dungchai W, Chailapakul O, Henry CS, Laiwattanapaisal W (2012) Blood separation on microfluidic paper-based analytical devices. Lab Chip 12:3392–3398
Chin CD, Linder V, Sia SK (2007) Lab-on-a-chip devices for global health: past studies and future opportunities. Lab Chip 7:41–57
Dungchai W, Chailapakul O, Henry CS (2011) A low-cost, simple, and rapid fabrication method for paper-based microfluidics using wax screen-printing. Analyst 136:77–82
Li X, Ballerini DR, Shen W (2012) A perspective on paper-based microfluidics: current status and future trends. Biomicrofluidics 6:11301–1130113
Lu Y, Shi W, Jiang L, Qin J, Lin B (2009) Rapid prototyping of paper-based microfluidics with wax for low-cost, portable bioassay. Electrophoresis 30:1497–1500
Carrilho E, Martinez AW, Whitesides GM (2009) Understanding wax printing: a simple micropatterning process for paper-based microfluidics. Anal Chem 81:7091–7095
Yang X, Forouzan O, Brown TP, Shevkoplyas SS (2012) Integrated separation of blood plasma from whole blood for microfluidic paper-based analytical devices. Lab Chip 12:274–280
Abbas A, Brimer A, Slocik JM, Tian L, Naik RR, Singamaneni S (2013) Multifunctional analytical platform on a paper strip: separation, preconcentration, and subattomolar detection. Anal Chem 85:3977–3983
Chamoles NA, Blanco MB, Gaggioli D, Casentini C (2001) Hurler-like phenotype: enzymatic diagnosis in dried blood spots on filter paper. Clin Chem 47:2098–2102
Zlateva KT, Maes P, Rahman M, Van Ranst M (2005) Chromatography paper strip sampling of enteric adenoviruses type 40 and 41 positive stool specimens. Virol J 2:6
Mohammed MI, Desmulliez MP (2011) Lab-on-a-chip based immunosensor principles and technologies for the detection of cardiac biomarkers: a review. Lab Chip 11:569–595
Fu E, Liang T, Spicar-Mihalic P, Houghtaling J, Ramachandran S, Yager P (2012) Two-dimensional paper network format that enables simple multistep assays for use in low-resource settings in the context of malaria antigen detection. Anal Chem 84:4574–4579
Peeling RW, Holmes KK, Mabey D, Ronald A (2006) Rapid tests for sexually transmitted infections (STIs): the way forward. Sex Transm Infect 82(Suppl 5):v1–v6
Posthuma-Trumpie GA, Korf J, van Amerongen A (2009) Lateral flow (immuno)assay: its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. A literature survey. Anal Bioanal Chem 393:569–582
Fu E, Lutz B, Kauffman P, Yager P (2010) Controlled reagent transport in disposable 2D paper networks. Lab Chip 10:918–920
Osborn JL, Lutz B, Fu E, Kauffman P, Stevens DY, Yager P (2010) Microfluidics without pumps: reinventing the T-sensor and H-filter in paper networks. Lab Chip 10:2659–2665
Apilux A, Ukita Y, Chikae M, Chailapakul O, Takamura Y (2013) Development of automated paper-based devices for sequential multistep sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays using inkjet printing. Lab Chip 13:126–135
Martinez AW, Phillips ST, Whitesides GM (2008) Three-dimensional microfluidic devices fabricated in layered paper and tape. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:19606–19611
Martinez AW, Phillips ST, Butte MJ, Whitesides GM (2007) Patterned paper as a platform for inexpensive, low-volume, portable bioassays. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 46:1318–1320
Fenton EM, Mascarenas MR, López GP, Sibbett SS (2009) Multiplex lateral-flow test strips fabricated by two-dimensional shaping. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 1:124–129
Abe K, Kotera K, Suzuki K, Citterio D (2010) Inkjet-printed paperfluidic immuno-chemical sensing device. Anal Bioanal Chem 398:885–893
Li X, Tian J, Shen W (2010) Quantitative biomarker assay with microfluidic paper-based analytical devices. Anal Bioanal Chem 396:495–501
Dungchai W, Chailapakul O, Henry CS (2010) Use of multiple colorimetric indicators for paper-based microfluidic devices. Anal Chim Acta 674:227–233
Wang W, Wu WY, Wang W, Zhu JJ (2010) Tree-shaped paper strip for semiquantitative colorimetric detection of protein with self-calibration. J Chromatogr A 1217:3896–3899
Carrilho E, Phillips ST, Vella SJ, Martinez AW, Whitesides GM (2009) Paper microzone plates. Anal Chem 81:5990–5998
Veigas B, Jacob JM, Costa MN, Santos DS, Viveiros M, Inácio J, Martins R, Barquinha P, Fortunato E, Baptista PV (2012) Gold on paper-paper platform for Au-nanoprobe TB detection. Lab Chip 12:4802–4808
Cheng CM, Martinez AW, Gong J, Mace CR, Phillips ST, Carrilho E, Mirica KA, Whitesides GM (2010) Paper-based ELISA. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 49:4771–4774
He Y, Zhang S, Zhang X, Baloda M, Gurung AS, Xu H, Zhang X, Liu G (2011) Ultrasensitive nucleic acid biosensor based on enzyme-gold nanoparticle dual label and lateral flow strip biosensor. Biosens Bioelectron 26:2018–2024
Silva LB, Veigas B, Doria G, Costa P, Inácio J, Martins R, Fortunato E, Baptista PV (2011) Portable optoelectronic biosensing platform for identification of mycobacteria from the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex. Biosens Bioelectron 26:2012–2017
Hossain SM, Ozimok C, Sicard C, Aguirre SD, Ali MM, Li Y, Brennan JD (2012) Multiplexed paper test strip for quantitative bacterial detection. Anal Bioanal Chem 403:1567–1576
Funes-Huacca M, Wu A, Szepesvari E, Rajendran P, Kwan-Wong N, Razgulin A, Shen Y, Kagira J, Campbell R, Derda R (2012) Portable self-contained cultures for phage and bacteria made of paper and tape. Lab Chip 12:4269–4278
Jorgensen JH, Ferraro MJ (1998) Antimicrobial susceptibility testing: general principles and contemporary practices. Clin Infect Dis 26:973–980
Cira NJ, Ho JY, Dueck ME, Weibel DB (2012) A self-loading microfluidic device for determining the minimum inhibitory concentration of antibiotics. Lab Chip 12:1052–1059
Martinez AW (2011) Microfluidic paper-based analytical devices: from POCKET to paper-based ELISA. Bioanalysis 3:2589–2592
Tian J, Jarujamrus P, Li L, Li M, Shen W (2012) Strategy to enhance the wettability of bioacive paper-based sensors. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4:6573–6578
Whitesides GM, Wilding P (2012) Lab on a stamp: paper-based diagnostic tools. Interview by Molly Webster and Vikram Sheel Kumar. Clin Chem 58:956–958
Acknowledgments
The author would like to warmly thank Catherine Saunier for her secretarial assistance and Pr. Alex Van Belkum for his external peer review.
Funding
None.
Conflict of interest
None.
Ethical approval
Not required.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rozand, C. Paper-based analytical devices for point-of-care infectious disease testing. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 33, 147–156 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-013-1945-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-013-1945-2