Abstract
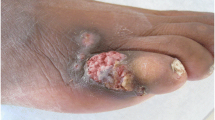
An immunosuppressed patient who presented with unusual clinical signs of cutaneous alternariosis, including papular, nodular and verrucous lesions of the forearms, is reported. In spite of continuous treatment with oral itraconazole for 6 months, a large, progressive, necrotic ulcer appeared on the patient's left leg. Liposomal amphotericin B was then administered (total dose, 750 mg) with excellent clinical results.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vartivarian SE, Anaissie EJ, Bodey GP (1993) Emerging fungal pathogens in immunocompromised patients: classification, diagnosis and management. Clin Infect Dis 17 (Suppl 2):487–491
Halaby T, Boots H, Vermeulen A, van der Ven A, Beguin H, van Hooff H, Jacobs J (2001) Phaeohyphomycosis caused byAlternaria infectoria in a renal transplant recipient. J Clin Microbiol 39:1952–1955
Benito N, Moreno A, Puig J, Rimola A (2001) Alternariosis after liver transplantation. Transplantation 72:1840–1843
Jha V, Krishna VS, Chakrabarti A, Sharma PK, Sud K, Kohli HS, Sakhuja V (1996) Subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis in a renal transplant recipient: a case report and review of the literature. Am J Kidney Dis 28:137–139
Gilmour TK, Rytina E, O'Connell PB, Sterling JC (2001) Cutaneous alternariosis in a cardiac transplant recipient. Australas J Dermatol 42:46–49
Laumaille C, Le Gall F, Degeilh B, Gueho E, Huerre M (1998) CutaneousAlternaria infectoria infection after liver transplantation. Ann Pathol 18:192–194
Baykal C, Kazancioglu R, Buyukbabani N, Celik AV, Yegenoglu Y, Kayacan SM, Satana D, Sever MS (2000) Simultaneous cutaneous and ungual alternariosis in a renal transplant recipient. Br J Dermatol 143:910–912
Bécherel PA, Chosidow O, Francés C (1995) Cutaneous alternariosis after renal transplantation. Ann Intern Med 122:171
Mirza SH, Hannan A, Ahmad A, Ahmad M (1993) Subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis. J Infect 27:75–78
Acland KM, Hay RJ, Groves R (1998) Cutaneous infection withAlternaria alternata complicating immunosuppression: successful treatment with itraconazole. Br J Dermatol 138:354–356
Foulet F, Duvoux C, Bièvre C, Hèzode C, Bretagne S (1999) Cutaneous phaeohyphomycosis caused byVeronaea bothryosa in a liver transplant recipient successfully treated with itraconazole. Clin Infect Dis 29:689–690
Altomare GF, Capella GL, Boneschi V, Viviani MA (2000) Effectiveness of terbinafine in cutaneous alternariosis. Br J Dermatol 142:840–841
McGinnis MR, Pasarell L (1998) In vitro testing of susceptibilities of filamentous ascomycetes to voriconazole, itraconazole and amphotericin B, with consideration of phylogenetic implications. J Clin Microbiol 36:2353–2355
Shearer C, Chandrasekar PH (1993) Cutaneous alternariosis and regional lymphadenitis during allogenic BMT. Bone Marrow Transplant 11:497–499
Pauzner R, Goldschmied-Reovuen A, Hay I, Vered Z, Ziskind Z, Hassin N, Farfel Z (1997) Phaeohyphomycosis following cardiac surgery: case report and review of serious infection due toBipolaris and Exserohilum species. Clin Infect Dis 25:921–923
Luber AD, Maa L, Lam M, Guglielmo J (1999) Risk factors for amphotericin B-induced nephrotoxicity. J Antimicrob Chemother 43:267–271
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Merino, E., Bañuls, J., Boix, V. et al. Relapsing Cutaneous Alternariosis in a Kidney Transplant Recipient Cured with Liposomal Amphotericin B. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 22, 51–53 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-002-0856-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-002-0856-4