Abstract
Objective
In this study, we performed analysis of brainstem reflexes and movement disorders using surface polymyogram in L-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria (L2HGA). We also reviewed all cases in the literature with detailed clinical and radiological description to analyze the anatomical correlates of involuntary movements.
Patients and method
We performed surface electromyography of appropriate muscles, long-loop reflexes, and somatosensory evoked potentials and analyzed the neuroimaging findings in patients with L2HGA and recorded blink reflex (BR), auditory startle response (ASR), and startle response after somatosensory stimuli (SSS) in patients and healthy subjects. We also performed a systematic literature search to identify the association of neuroimaging findings and movements disorders in previous patients with L2HGA.
Results
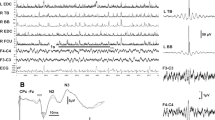
Thirteen patients were enrolled in the study. Among them, ten had low-amplitude postural tremor with a frequency between 4 and 7 Hz. The tremor was predominant on distal parts of the upper extremities. Postural tremor was accompanied by negative myoclonus in one-third. The BR, ASR, and SSS, all, were hypoactive. There was a close association of postural tremor with cerebellar atrophy in patients who participated in this study and by the analysis of the previously reported patients.
Conclusions
Low-amplitude postural tremor is common in L2HGA. It is related with cerebellar atrophy. Although the neuroimaging shows no overt lesions at the brainstem, there is a functional inhibition at this level.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kranendijk M, Struys EA, Salomons GS, Van Der Knaap MS, Jakobs C (2012) Progress in understanding 2-hydroxyglutaric acidurias. J Inherit Metab Dis 35:571–587
Barbot C, Fineza I, Diogo L et al (1997) L-2-Hydroxyglutaric aciduria: clinical, biochemical and magnetic resonance imaging in six Portuguese pediatric patients. Brain Dev 19:268–273
Steenweg ME, Jakobs C, Errami A et al (2010) An overview of L-2-hydroxyglutarate dehydrogenase gene (L2HGDH) variants: a genotype-phenotype study. Hum Mutat 31:380–390
Topçu M, Aydin ÖF, Yalçinkaya C et al (2005) L-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria: a report of 29 patients. Turk J Pediatr 47:1–7
Zübarioğlu T, Yalçınkaya C, Oruç Ç et al (2020) Evaluation of clinical, neuroradiologic, and genotypic features of patients with l-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria. Turk Pediatr Ars 55:290–298
Olgac A, Tekin OL, Ezgü FS, Biberoǧlu G, Tümer L (2019) A 7-year-old boy with hand tremors and a novel mutation for L-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria. Balk J Med Genet 22:93–96
Clerc C, Bataillard M, Richard P, Divry P, Kraehenbuhl J, Rumbach L (2000) An adult form of L-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria revealed by tremor. Eur Neurol 43:119–120
Periasamy V, Rudwan M, Yadav G, Khan RA (2008) Epilepsy in a young adult caused by L-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria: A case report. Med Princ Pract 17:258–261
Termsarasab P, Frucht SJ (2014) Writer’s cramp as a presentation of L-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria. J Clin Mov Disord 1:9
Goffette SM, Duprez TP, Nassogne MCL, Vincent MFA, Jakobs C, Sindic CJ (2006) L-2-Hydroxyglutaric aciduria: Clinical, genetic, and brain MRI characteristics in two adult sisters. Eur J Neurol 13:499–504
Samuraki M, Komai K, Hasegawa Y et al (2008) A successfully treated adult patient with L-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria. Neurology 70:1051–1052
Sass JO, Romrell JS, Vinson SY et al (2009) Tracing the origin of L-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria in a family. Int J Neurosci 119:2118–2123
Fourati H, Ellouze E, Ahmadi M et al (2016) MRI features in 17 patients with L2 hydroxyglutaric aciduria. Eur J Radiol Open 3:245–250
Shah H, Chandarana M, Sheth J, Shah S (2020) A case report of chronic progressive pancerebellar syndrome with leukoencephalopathy:L-2 hydroxyglutaric aciduria. Mov Disord Clin Pract 7:560–563
van der Knaap MS, Valk J, Barth PG, Smit LME, van Engelen BGM, Donati PT (1995) Leukoencephalopathy with swelling in children and adolescents: MRI patterns and differential diagnosis. Neuroradiology 37:679–686
Weimar C, Schlamann M, Krägeloh-Mann I, Schöls L (2013) L-2 hydroxyglutaric aciduria as a rare cause of leukencephalopathy in adults. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 115:765–766
Faiyaz-Ul-Haque M, Al-Sayed MD, Faqeih E et al (2014) Clinical, neuroimaging, and genetic features of L-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria in Arab kindreds. Ann Saudi Med 34:107–114
Saidha S, Murphy S, McCarthy P, Mayne PD, Hennessy M (2010) L-2-Hydroxyglutaric aciduria diagnosed in an adult presenting with acute deterioration. J Neurol 257:146–148
Martin AJ, Morales-Briceño H, Tchan M, Fung VSC (2020) The head retraction reflex in Niemann-Pick type C: a novel diagnostic clue. Mov Disord Clin Pract 7:543–547
Williams DR, Doyle LMF, Lees AJ, Brown P (2008) The auditory startle response in parkinsonism may reveal the extent but not type of pathology. J Neurol 255:628–632
Fujitake J, Ishikawa Y, Fujii H et al (1999) L-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria: two Japanese adult cases in one family. J Neurol 246:378–382
Gökçen C, Isikay S, Yilmaz K (2013) L-2 Hydroxyglutaric aciduria presenting with anxiety symptoms. BMJ Case Rep 2013:bcr2013009512
Yamamoto T, Yoshioka S, Tsurusaki Y et al (2016) White matter abnormalities in an adult patient with l-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria. Brain Dev 38:142–144
Işikay S (2013) L-2 Hydroxyglutaric aciduria presenting with status epilepticus. BMJ Case Rep 2013:bcr2013010164
Isikay S, Carman KB (2013) Contribution of brain MRI in a patient diagnosed with L-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria. BMJ Case Rep 2013:bcr2013008917
Divry P, Jakobs C, Vianey-Saban C et al (1993) L-2-Hydroxyglutaric aciduria: two further cases. J Inherit Metab Dis 16:505–507
Jović NJ, Kosać A, Koprivšek K (2014) L-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria: a case report. Srp Arh Celok Lek 142:337–341
Lee C, Born M, Salomons GS, Jakobs C, Woelfle J (2006) Hemiconvulsion-hemiplegia-epilepsy syndrome as a presenting feature of L-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria. J Child Neurol 21:538–540
Seijo-Martinez M, Navarro C, Castro Del Rio M et al (2005) L-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria: Clinical, neuroimaging, and neuropathological findings. Arch Neurol 62:666–670
Sztriha L, Gururaj A, Vreken P, Nork M, Lestringant GG (2002) L-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria in two siblings. Pediatr Neurol 27:141–144
Yilmaz K (2009) Riboflavin treatment in a case with l-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria. Eur J Paediatr Neurol 13:57–60
Zafeiriou DI, Sewell A, Savvopoulou-Augoustidou P, Gombakis N, Katzos G (2001) L-2-Hydroxyglutaric aciduria presenting as status epilepticus. Brain Dev 23:255–257
Zafeiriou DI, Ververi A, Salomons GS et al (2008) L-2-Hydroxyglutaric aciduria presenting with severe autistic features. Brain Dev 30:305–307
Kamate M, Prashanth GP, Hattiholi V (2014) L-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria: report of two Indian families. Indian J Pediatr 81:296–298
Karatas H, Saygi S, Bastan B et al (2010) L-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria: report of four Turkish adult patients. Neurologist 16:44–46
Marcel C, Mallaret M, Lagha-Boukbiza O, Kremer S, Echaniz-Laguna A, Tranchant C (2012) L-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria diagnosed in a young adult with progressive cerebellar ataxia and facial dyskinesia. Rev Neurol 168:187–191
Mazzei R, Ungaro C, Garreffa G et al (2011) Clinical, genetic and magnetic resonance findings in an Italian patient affected by l-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria. Neurol Sci 32:95–99
Mete A, Isikay S, Sirikci A, Ozkur A, Bayram M (2012) Eyelid myoclonia with absence seizures in a child with L-2 hydroxyglutaric aciduria: findings of magnetic resonance imaging. Pediatr Neurol 46:195–197
Buijink AWG, Van Der Stouwe AMM, Broersma M et al (2015) Motor network disruption in essential tremor: a functional and effective connectivity study. Brain 138:2934–2947
Fang W, Lv F, Luo T et al (2013) Abnormal regional homogeneity in patients with essential tremor revealed by resting-state functional MRI. PLoS 8:e69199
Canda E, Köse M, Yazıcı H et al (2018) Clinical, neuroimaging, and genetic features of the patients with L-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria. J Pediatr Res 5:39–43
Esteban A (1999) A neurophysiological approach to brainstem reflexes. Blink reflex Neurophysiol Clin 29:7–38
Hori A, Yasuhara A, Naito H, Yasuhara M (1986) Blink reflex elicited by auditory stimulation in the rabbit. J Neurol Sci 76:49–59
Koch M (1999) The neurobiology of startle. Prog Neurobiol 59:107–128
Kofler M, Müller J, Seppi K, Wenning GK (2003) Exaggerated auditory startle responses in multiple system atrophy: a comparative study of parkinson and cerebellar subtypes. Clin Neurophysiol 114:541–547
Kofler M, Müller J, Wenning GK et al (2001) The auditory startle reaction in parkinsonian disorders. Mov Disord 16:62–71
Kurul S, Çakmakçi H, Dirik E (2004) Glutaric aciduria type 1: proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy findings. Pediatr Neurol 31:228–231
Jequier Gygax M, Roulet-Perez E, Meagher-Villemure K et al (2009) Sudden unexpected death in an infant with L-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria. Eur J Pediatr 168:957–962
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by the local ethical committee.
Informed consent
None.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gunduz, A., Aktuglu-Zeybek, A.C., Tezer, D. et al. Postural tremor in L-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria is associated with cerebellar atrophy. Neurol Sci 43, 2051–2058 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-021-05555-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-021-05555-x