Abstract
Objective
Our aim is to assess the types and frequency of seizure-related injuries and to determine their effects on Quality of Life (QoL).
Methods
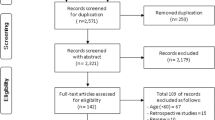
Fifty-seven patients with epilepsy were included to our study. The demographic and clinical data of all the participants were recorded. All patients completed the Quality of Life in Epilepsy Inventory 89 (QOLIE-89). Injury types were classified as burns, head trauma, dental traumas, fractures, body injuries, penetrating traumas, road injuries, and drowning.
Results
Forty-two patients had seizure-related physical injury history whereas 15 of them declared no history of injury. Lower education levels and more frequent seizures were associated with higher seizure-related injury rates (p < 0.05). The most common types of seizure-related injuries were head trauma (22%) and fractures (17%). Fifty-seven (64%)of the injuries took place at home. There was no difference in QOLIE-89 scores between patients with or without seizure-related injury. Multiple injuries, admission to emergency, older than 20 years of the first seizure-related injury, and shorter than 10 years after last seizure-related injury are negatively effective on the QoL scores.
Conclusion
Patients with epilepsy are likely to have seizure-related injuries which may be severe but do not affect the patients’ QoL. Seizure-related injuries most commonly occur at home and therefore simple precautions (supervised bathing, using microwave ovens instead of classical stoves, avoiding electric irons and electric heaters, and sleeping close to the floor to avoid falling) taken to reduce the incidence of seizure-related injuries will help reduce hospitalizations and will also be cost-effective.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wiebe S, Bellhouse DR, Fallahay C, Eliasziw M (1999) Burden of epilepsy: the Ontario Health Survey. Can J Neurol Sci 26:263–270
Devinsky O, Vickrey BG, Cramer J, Perrine K, Hermann B, Meador K, Hays RD (1995) Development of the quality of life in epilepsy inventory. Epilepsia 36(11):1089–1104
Scheffer IE, Berkovic S, Capovilla G, Connolly MB, French J, Guilhoto L, Hirsch E, Jain S, Mathern GW, Moshé SL, Nordli DR, Perucca E, Tomson T, Wiebe S, Zhang YH, Zuberi SM (2017) ILAE classification of the epilepsies: position paper of the ILAE Commission for Classification and Terminology. Epilepsia 58:512–521
Mokdad AH, Forouzanfar MH, Daoud F, Mokdad AA, El Bcheraoui C, Moradi-Lakeh M et al (2016) Global burden of diseases, injuries, and risk factors for young people's health during 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2013. Lancet 387:2383–2401
Jacoby A, Snape D, Baker GA (2009) Determinants of quality of life in people with epilepsy. Neurol Clin 27:843–863
Senol V, Soyuer F, Arman F, Ozturk A (2007) Influence of fatigue, depression, and demographic, socioeconomic, and clinical variables on quality of life of patients with epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav 10:96–104
Sherman EM, Wiebe S, Fay-McClymont TB, Tellez-Zenteno J, Metcalfe A, Hernandez-Ronquillo L et al (2011) Neuropsychological outcomes after epilepsy surgery: systematic review and pooled estimates. Epilepsia 52:857–869
Auriel E, Landov H, Blatt I, Theitler J, Gandelman-Marton R, Chistik V, Margolin N, Gross B, Parmet Y, Andelman F, Neufeld MY (2009) Quality of life in seizure-free patients with epilepsy on monotherapy. Epilepsy Behav 14:130–133
Grant AC, Prus N, Nakhutina L (2013) Factors affecting quality of life in epilepsy in a multi- ethnic urban population. Epilepsy Behav 27:283–285
Spencer SS, Berg AT, Vickrey BG, Sperling MR, Bazil CW, Haut S, Langfitt JT, Walczak TS, Devinsky O, Multicenter Study of Epilepsy Surgery (2007) Health-related quality of life over time since resective epilepsy surgery. Ann Neurol 62:327–334
Barry JJ (2003) The recognition and management of mood disorders as a comorbidity of epilepsy. Epilepsia 44(Suppl 4):30–40
Camfield C, Camfield P (2015) Injuries from seizures are a serious, persistent problem in childhood onset epilepsy: a population-based study. Seizure 27:80–83
Asadi-Pooya AA, Nikseresht A, Yaghoubi E, Nei M (2012) Physical injuries in patients with epilepsy and their associated risk factors. Seizure 21:165–168
Friedman DE, Tobias RS, Akman CI, Smith EO, Levin HS (2010) Recurrent seizure-related injuries in people with epilepsy at a tertiary epilepsy center: a 2-year longitudinal study. Epilepsy Behav 19:400–404
Prasad V, Kendrick D, Sayal K, Thomas SL, West J (2014) Injury among children and young adults with epilepsy. Pediatrics 133:827–835
Buck D, Baker GA, Jacoby A, Smith DF, Chadwick DW (1997) Patients’ experiences of injury as a result of epilepsy. Epilepsia 38:439–444
Kwon CS, Liu M, Quan H, Wiebe S, McChesney J, Wirrell E et all. The incidence of injuries in persons with and without epilepsy-a population-based study. Epilepsia 2010;51: 2247–2253
Lagunju IA, Oyinlade AO, Babatunde OD (2016) Seizure-related injuries in children and adolescents with epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav 54:131–134
Neufeld MY, Vishne T, Chistik V, Korczyn AD (1999) Life-long history of injuries related to seizures. Epilepsy Res 34:123–127
Persson HB, Alberts KA, Farahmand BY, Tomson T (2002) Risk of extremity fractures in adult outpatients with epilepsy. Epilepsia 43:768–772
Gawlak D, Luniewska J, Stojak W, Hovhannisyan A, Strozynska A, Manka-Malara K et al (2017) The prevalence of orodental trauma during epileptic seizures in terms of dental treatment - survey study. Neurol Neurochir Pol 51:361–365
Mollaoglu M, Bolayir E (2013) Injuries in patients with epilepsy and some factors associated with injury. Noro Psikiyatr Ars 50:269–273
van den Broek M, Beghi E (2004) Accidents in patients with epilepsy: types, circumstances, and complications: a European cohort study. Epilepsia 45:667–672
Fisher RS, Cross JH, French JA, Higurashi N, Hirsch E, Jansen FE, Lagae L, Moshé SL, Peltola J, Roulet Perez E, Scheffer IE, Zuberi SM (2017) Operational classification of seizure types by the international league against epilepsy: position paper of the ILAE Commission for Classification and Terminology. Epilepsia 58:522–530
Spitz MC (1998) Injuries and death as a consequence of seizures in people with epilepsy. Epilepsia 39:904–907
Unglaub F, Woodruff S, Demir E, Pallua N (2005) Patients with epilepsy: a high-risk population prone to severe burns as a consequence of seizures while showering. J Burn Care Rehabil 26:526–528
Sheth SG, Krauss G, Krumholz A, Li G (2004) Mortality in epilepsy: driving fatalities vs other causes of death in patients with epilepsy. Neurology 63:1002–1007
Willems LM, Watermann N, Richter S et al (2018) Incidence, risk factors and consequences of epilepsy-related injuries and accidents: a retrospective, single center study. Front Neurol 414(9):1–9
Noble AJ, McCrone P, Seed PT, Goldstein LH, Ridsdale L (2014) Clinical- and cost- effectiveness of a nurse led self-management intervention to reduce emergency visits by people with epilepsy. PLoS One 9(3):e90789
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Written informed consents were obtained from all participants. Local ethics committee approval was received for the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• Seizure-related injuries have no effect on the individuals’ Quality of Life (QoL).
• The main locale of these injuries is at home.
• The most common seizure-related injury at home is dental trauma; fractures outdoors.
• It is important to take precautions at home to minimize the risk.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cengiz, O., Atalar, A.Ç., Tekin, B. et al. Impact of seizure-related injuries on quality of life. Neurol Sci 40, 577–583 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-018-3697-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-018-3697-3