Abstract
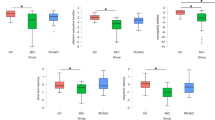
The Ekman 60-Faces (EK-60F) Test is a well-known neuropsychological tool assessing emotion recognition from facial expressions. It is the most employed task for research purposes in psychiatric and neurological disorders, including neurodegenerative diseases, such as the behavioral variant of Frontotemporal Dementia (bvFTD). Despite its remarkable usefulness in the social cognition research field, to date, there are still no normative data for the Italian population, thus limiting its application in a clinical context. In this study, we report procedures and normative data for the Italian version of the test. A hundred and thirty-two healthy Italian participants aged between 20 and 79 years with at least 5 years of education were recruited on a voluntary basis. They were administered the EK-60F Test from the Ekman and Friesen series of Pictures of Facial Affect after a preliminary semantic recognition test of the six basic emotions (i.e., anger, fear, sadness, happiness, disgust, surprise). Data were analyzed according to the Capitani procedure [1]. The regression analysis revealed significant effects of demographic variables, with younger, more educated, female subjects showing higher scores. Normative data were then applied to a sample of 15 bvFTD patients which showed global impaired performance in the task, consistently with the clinical condition. We provided EK-60F Test normative data for the Italian population allowing the investigation of global emotion recognition ability as well as selective impairment of basic emotions recognition, both for clinical and research purposes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Capitani E, Laiacona M (1997) Composite neuropsychological batteries and demographic correction: standardization based on equivalent scores, with a review of published data. The Italian Group for the Neuropsychological Study of Ageing. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 19(6):795–809. doi:10.1080/01688639708403761
Adolphs R (2003) Cognitive neuroscience of human social behaviour. Nat Rev Neurosci 4(3):165–178. doi:10.1038/nrn1056nrn1056
Phan KL, Wager T, Taylor SF, Liberzon I (2002) Functional neuroanatomy of emotion: a meta-analysis of emotion activation studies in PET and fMRI. Neuroimage 16(2):331–348. doi:10.1006/nimg.2002.1087S1053811902910876
Fusar-Poli P, Placentino A, Carletti F, Landi P, Allen P, Surguladze S, Benedetti F, Abbamonte M, Gasparotti R, Barale F, Perez J, McGuire P, Politi P (2009) Functional atlas of emotional faces processing: a voxel-based meta-analysis of 105 functional magnetic resonance imaging studies. J Psychiatry Neurosci 34(6):418–432
Kohler CG, Walker JB, Martin EA, Healey KM, Moberg PJ (2010) Facial emotion perception in schizophrenia: a meta-analytic review. Schizophr Bull 36(5):1009–1019. doi:10.1093/schbul/sbn192sbn192
Unoka Z, Fogd D, Fuzy M, Csukly G (2011) Misreading the facial signs: specific impairments and error patterns in recognition of facial emotions with negative valence in borderline personality disorder. Psychiatry Res 189(3):419–425. doi:10.1016/j.psychres.2011.02.010S0165-1781(11)00102-8
Poljac E, Montagne B, de Haan EH (2011) Reduced recognition of fear and sadness in post-traumatic stress disorder. Cortex 47(8):974–980. doi:10.1016/j.cortex.2010.10.002S0010-9452(10)00243-1
Montagne B, Schutters S, Westenberg HG, van Honk J, Kessels RP, de Haan EH (2006) Reduced sensitivity in the recognition of anger and disgust in social anxiety disorder. Cogn Neuropsychiatry 11(4):389–401. doi:10.1080/13546800444000254
Croker V, McDonald S (2005) Recognition of emotion from facial expression following traumatic brain injury. Brain Inj 19(10):787–799
Rapcsak SZ, Galper SR, Comer JF, Reminger SL, Nielsen L, Kaszniak AW, Verfaellie M, Laguna JF, Labiner DM, Cohen RA (2000) Fear recognition deficits after focal brain damage: a cautionary note. Neurology 54(3):575–581
Meletti S, Benuzzi F, Cantalupo G, Rubboli G, Tassinari CA, Nichelli P (2009) Facial emotion recognition impairment in chronic temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia 50(6):1547–1559. doi:10.1111/j.1528-1167.2008.01978.xEPI1978
Ariatti A, Benuzzi F, Nichelli P (2008) Recognition of emotions from visual and prosodic cues in Parkinson’s disease. Neurol Sci 29(4):219–227. doi:10.1007/s10072-008-0971-9
Zimmerman EK, Eslinger PJ, Simmons Z, Barrett AM (2007) Emotional perception deficits in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Cogn Behav Neurol 20(2):79–82. doi:10.1097/WNN.0b013e31804c700b00146965-200706000-00001
Bediou B, Ryff I, Mercier B, Milliery M, Henaff MA, D’Amato T, Bonnefoy M, Vighetto A, Krolak-Salmon P (2009) Impaired social cognition in mild Alzheimer disease. J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol 22(2):130–140. doi:10.1177/08919887093329390891988709332939
Fernandez-Duque D, Black SE (2005) Impaired recognition of negative facial emotions in patients with frontotemporal dementia. Neuropsychologia 43(11):1673–1687. doi:10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2005.01.005
Lough S, Kipps CM, Treise C, Watson P, Blair JR, Hodges JR (2006) Social reasoning, emotion and empathy in frontotemporal dementia. Neuropsychologia 44(6):950–958. doi:10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2005.08.009
Rosen HJ, Pace-Savitsky K, Perry RJ, Kramer JH, Miller BL, Levenson RW (2004) Recognition of emotion in the frontal and temporal variants of frontotemporal dementia. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 17(4):277–281. doi:10.1159/00007715477154
Diehl-Schmid J, Pohl C, Ruprecht C, Wagenpfeil S, Foerstl H, Kurz A (2007) The Ekman 60 Faces Test as a diagnostic instrument in frontotemporal dementia. Arch Clin Neuropsychol 22(4):459–464. doi:10.1016/j.acn.2007.01.024
Ghosh BC, Rowe JB, Calder AJ, Hodges JR, Bak TH (2009) Emotion recognition in progressive supranuclear palsy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 80(10):1143–1145. doi:10.1136/jnnp.2008.15584680/10/1143
Rohrer JD, Sauter D, Scott S, Rossor MN, Warren JD (2012) Receptive prosody in nonfluent primary progressive aphasias. Cortex 48(3):308–316. doi:10.1016/j.cortex.2010.09.004S0010-9452(10)00238-8
Calabria M, Cotelli M, Adenzato M, Zanetti O, Miniussi C (2009) Empathy and emotion recognition in semantic dementia: a case report. Brain Cogn 70(3):247–252. doi:10.1016/j.bandc.2009.02.009S0278-2626(09)00038-4
Ekman P, Friesen W (1976) Pictures of facial affect. Consulting Psychologists Press, Palo Alto
Rascovsky K, Hodges JR, Knopman D, Mendez MF, Kramer JH, Neuhaus J, van Swieten JC, Seelaar H, Dopper EG, Onyike CU, Hillis AE, Josephs KA, Boeve BF, Kertesz A, Seeley WW, Rankin KP, Johnson JK, Gorno-Tempini ML, Rosen H, Prioleau-Latham CE, Lee A, Kipps CM, Lillo P, Piguet O, Rohrer JD, Rossor MN, Warren JD, Fox NC, Galasko D, Salmon DP, Black SE, Mesulam M, Weintraub S, Dickerson BC, Diehl-Schmid J, Pasquier F, Deramecourt V, Lebert F, Pijnenburg Y, Chow TW, Manes F, Grafman J, Cappa SF, Freedman M, Grossman M, Miller BL (2011) Sensitivity of revised diagnostic criteria for the behavioural variant of frontotemporal dementia. Brain 134(Pt 9):2456–2477. doi:10.1093/brain/awr179awr179
Neary D, Snowden JS, Gustafson L, Passant U, Stuss D, Black S, Freedman M, Kertesz A, Robert PH, Albert M, Boone K, Miller BL, Cummings J, Benson DF (1998) Frontotemporal lobar degeneration: a consensus on clinical diagnostic criteria. Neurology 51(6):1546–1554
Wilks SS (1941) Determination of sample sizes for setting tolerance limits. Ann Math Stat 12:91–96
McClure EB (2000) A meta-analytic review of sex differences in facial expression processing and their development in infants, children, and adolescents. Psychol Bull 126(3):424–453
Lee TM, Liu HL, Hoosain R, Liao WT, Wu CT, Yuen KS, Chan CC, Fox PT, Gao JH (2002) Gender differences in neural correlates of recognition of happy and sad faces in humans assessed by functional magnetic resonance imaging. Neurosci Lett 333(1):13–16. doi:10.1016/S0304-3940(02)00965-5
Sullivan S, Ruffman T (2004) Emotion recognition deficits in the elderly. Int J Neurosci 114(3):403–432. doi:10.1080/00207450490270901H6YBRR4W08PXACL8
Ruffman T, Henry JD, Livingstone V, Phillips LH (2008) A meta-analytic review of emotion recognition and aging: implications for neuropsychological models of aging. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 32(4):863–881. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2008.01.001S0149-7634(08)00010-9
Brothers L (1990) The social brain: a project for integrating primate behaviour and neurophysiology in a new domain. Concepts Neurosci 1:27–51
Hedden T, Gabrieli JDE (2004) Insights into the ageing mind: a view from cognitive neuroscience. Nat Rev Neurosci 5(2):87–96. doi:10.1038/Nrn1323
Bianchi A, Pra MD (2008) Twenty years after Spinnler and Tognoni: new instruments in the Italian neuropsychologist’s toolbox. Neurolo Sci 29(4):209–217. doi:10.1007/s10072-008-0970-x
Acknowledgments
We thank Francesca Cortese, Leonardo Iaccarino and Federica Biotti for their help in the collection of neuropsychological data and Eleonora Catricalà and Pasquale Anthony Della Rosa for the statistical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dodich, A., Cerami, C., Canessa, N. et al. Emotion recognition from facial expressions: a normative study of the Ekman 60-Faces Test in the Italian population. Neurol Sci 35, 1015–1021 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-014-1631-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-014-1631-x