Abstract
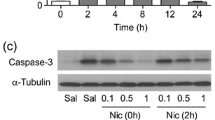
Exposure to ethanol during developmental stages leads to several types of neurological disorders. Apoptotic neurodegeneration due to ethanol exposure is a main feature in alcoholism. Exposure of developing animals to alcohol induces apoptotic neuronal death and causes fetal alcohol syndrome. In the present study, we observed the possible protective effect of pyruvate against ethanol-induced neurodegeneration. Exposure of developing mice to ethanol (2.5 g/kg) induces apoptotic neurodegeneration and widespread neuronal cell death in the cortex and thalamus. Co-treatment of pyruvate (500 mg/kg) protects neuronal cell against ethanol by the reduced expression of caspase-3 in these brain regions. Immunohistochemical analysis and TUNNEL at 24 h showed that apoptotic cell death induced by ethanol in the cortex and thalamus is reduced by pyruvate. Histomorphological analysis at 24 h with cresyl violet staining also proved that pyruvate reduced the number of neuronal cell loss in the cortex and thalamus. The results showed that ethanol increased the expression of caspase-3 and thus induced apoptotic neurodegeneration in the developing mice cortex and thalamus, while co-treatment of pyruvate inhibits the induction of caspase-3 and reduced the cell death in these brain regions. These findings, therefore, showed that treatment of pyruvate inhibits ethanol-induced neuronal cell loss in the postnatal seven (P7) developing mice brain and may appear as a safe neuroprotectant for treating neurodegenerative disorders in newborns and infants.



Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
15 February 2024
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-024-07398-8
References
Jones KL, Smith DW (1973) Recognition of the fetal alcohol syndrome in early infancy. Lancet 302(7836):999–1001
Wozniak DF, Hartman RE, Boyle MP, Vogt SK, Brooks AR, Tenkova T, Young C, Olney JW, Muglia LJ (2004) Apoptotic neurodegeneration induced by ethanol in neonatal mice is associated with profound learning/memory deficits in juveniles followed by progressive functional recovery in adults. Neurobiol Dis 17(3):403–414
Sokol RJ, Delaney-Black V, Nordstrom B (2003) Fetal alcohol spectrum disorder. JAMA 290(22):2996–2999
Eckardt MJ, File SE, Gessa GL, Grant KA, Guerri C, Hoffman PL, Kalant H, Koob GF, Li TK, Tabakoff B (1998) Effects of moderate alcohol consumption on the central nervous system. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 22(5):998–1040
Sun AY, Ingelman-Sundberg M, Neve E, Matsumoto H, Nishitani Y, Minowa Y, Fukui Y, Bailey SM, Patel VB, Cunningham CC, Zima T, Fialova L, Mikulikova L, Popov P, Malbohan I, Janebova M, Nespor K, Sun GY (2001) Ethanol and oxidative stress. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 25(5):237S–243S
Chu J, Tong M, de la Monte SM (2007) Chronic ethanol exposure causes mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in immature central nervous system neurons. Acta Neuropathol 113(6):659–673
Ramachandran V, Watts LT, Maffi SK, Chen J, Schenker S, Henderson G (2003) Ethanol-induced oxidative stress precedes mitochondrially mediated apoptotic death of cultured fetal cortical neurons. J Neurosci Res 74(4):577–588
Andrae U, Singh J, Ziegler-Skylakakis K (1985) Pyruvate and related alpha-ketoacids protect mammalian cells in culture against hydrogen peroxide-induced cytotoxicity. Toxicol Lett 28(2–3):93–98
O’Donnell-Tormey J, Nathan CF, Lanks K, DeBoer CJ, de la Harpe J (1987) Secretion of pyruvate. An antioxidant defense of mammalian cells. J Exp Med 165(2):500–514
Cavallini L, Valente M, Rigobello MP (1990) The protective action of pyruvate on recovery of ischemic rat heart: comparison with other oxidizable substrates. J Mol Cell Cardiol 22(2):143–154
Salahudeen AK, Clark EC, Nath KA (1991) Hydrogen peroxide-induced renal injury. A protective role for pyruvate in vitro and in vivo. J Clin Investig 88(6):1886–1893
Crestanello JA, Kamelgard J, Whitman GJ (1995) The cumulative nature of pyruvate’s dual mechanism for myocardial protection. J Surg Res 59(1):198–204
Desagher S, Glowinski J, Premont J (1997) Pyruvate protects neurons against hydrogen peroxide-induced toxicity. J Neurosci: Off J Soc Neurosci 17(23):9060–9067
Maus M, Marin P, Israel M, Glowinski J, Premont J (1999) Pyruvate and lactate protect striatal neurons against N-methyl-D-aspartate-induced neurotoxicity. Eur J Neurosci 11(9):3215–3224
Sheline CT, Behrens MM, Choi DW (2000) Zinc-induced cortical neuronal death: contribution of energy failure attributable to loss of NAD(+) and inhibition of glycolysis. J Neurosci: Off J Soc Neurosci 20(9):3139–3146
Lee JY, Kim YH, Koh JY (2001) Protection by pyruvate against transient forebrain ischemia in rats. J Neurosci: Off J Soc Neurosci 21(20):1–6
Tsacopoulos M, Magistretti PJ (1996) Metabolic coupling between glia and neurons. J Neurosci: Off J Soc Neurosci 16(3):877–885
Giandomenico AR, Cerniglia GE, Biaglow JE, Stevens CW, Koch CJ (1997) The importance of sodium pyruvate in assessing damage produced by hydrogen peroxide. Free Radic Biol Med 23(3):426–434
Le DA, Wu Y, Huang Z, Matsushita K, Plesnila N, Augustinack JC, Hyman BT, Yuan J, Kuida K, Flavell RA, Moskowitz MA (2002) Caspase activation and neuroprotection in caspase-3- deficient mice after in vivo cerebral ischemia and in vitro oxygen glucose deprivation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99(23):15188–15193
Phillips DE (1989) Effects of limited postnatal ethanol exposure on the development of myelin and nerve fibers in rat optic nerve. Exp Neurol 103(1):90–100
Kumada T, Lakshmana MK, Komuro H (2006) Reversal of neuronal migration in a mouse model of fetal alcohol syndrome by controlling second-messenger signalings. J Neurosci: Off J Soc Neurosci 26(3):742–756
Sowell ER, Thompson PM, Mattson SN, Tessner KD, Jernigan TL, Riley EP, Toga AW (2001) Voxel-based morphometric analyzes of the brain in children and adolescents prenatally exposed to alcohol. Neuro Report 12(3):515–523
Sowell ER, Thompson PM, Mattson SN, Tessner KD, Jernigan TL, Riley EP, Toga AW (2002) Regional brain shape abnormalities persist into adolescence after heavy prenatal alcohol exposure. Cereb Cortex 12(8):856–865
Sowell ER, Thompson PM, Peterson BS, Mattson SN, Welcome SE, Henkenius AL, Riley EP, Jernigan TL, Toga AW (2002) Mapping cortical gray matter asymmetry patterns in adolescents with heavy prenatal alcohol exposure. Neuro Image 17(4):1807–1819
Mattson SN, Riley EP (1998) A review of the neurobehavioral deficits in children with fetal alcohol syndrome or prenatal exposure to alcohol. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 22(2):279–294
Andersen JK (2004) Oxidative stress in neurodegeneration: cause or consequence? Nat Med 10:S18–S25
Goodlett CR, Horn KH, Zhou FC (2005) Alcohol teratogenesis: mechanisms of damage and strategies for intervention. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 230(6):394–406
Bernardi P, Krauskopf A, Basso E, Petronilli V, Blachly-Dyson E, Di Lisa F, Forte MA (2006) The mitochondrial permeability transition from in vitro artifact to disease target. FEBS J 273(10):2077–2099
O’Rourke B, Cortassa S, Aon MA (2005) Mitochondrial ion channels: gatekeepers of life and death. Physiology (Bethesda) 20:303–315
Lazebnik YA, Kaufmann SH, Desnoyers S, Poirier GG, Earnshaw WC (1994) Cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase by a proteinase with properties like ICE. Nature 371(6495):346–347
Fink MP (2003) Ethyl pyruvate: a novel anti-inflammatory agent. Crit Care Med 31(1 Suppl):S51–S56
Varma SD, Hegde KR (2007) Lens thiol depletion by peroxynitrite. Protective effect of pyruvate. Mol Cell Biochem 298(1–2):199–204
Mallet RT, Bunger R (1993) Metabolic protection of post-ischemic phosphorylation potential and ventricular performance. Adv Exp Med Biol 346:233–241
Mallet RT, Sun J, Knott EM, Sharma AB, Olivencia-Yurvati AH (2005) Metabolic cardioprotection by pyruvate: recent progress. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 230(7):435–443
Nicholls DG, Johnson-Cadwell L, Vesce S, Jekabsons M, Yadava N (2007) Bioenergetics of mitochondria in cultured neurons and their role in glutamate excitotoxicity. J Neurosci Res 85(15):3206–3212
Araki T, Sasaki Y, Milbrandt J (2004) Increased nuclear NAD biosynthesis and SIRT1 activation prevent axonal degeneration. Science 305(5686):1010–1013
Mongan PD, Fontana JL, Chen R, Bunger R (1999) Intravenous pyruvate prolongs survival during hemorrhagic shock in swine. Am J Physiol 277(6 Pt 2):H2253–H2263
Zeng J, Yang GY, Ying W, Kelly M, Hirai K, James TL, Swanson RA, Litt L (2007) Pyruvate improves recovery after PARP-1-associated energy failure induced by oxidative stress in neonatal rat cerebrocortical slices. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab: Off J Int Soc Cereb Blood Flow Metab 27(2):304–315
Mukherjee SK, Klaidman LK, Yasharel R, Adams JD Jr (1997) Increased brain NAD prevents neuronal apoptosis in vivo. Eur J Pharmacol 330(1):27–34
Wang X, Perez E, Liu R, Yan LJ, Mallet RT, Yang SH (2007) Pyruvate protects mitochondria from oxidative stress in human neuroblastoma SK-N-SH cells. Brain Res 1132(1):1–9
Ullah N, Naseer MI, Ullah I, Lee HY, Koh PO, Kim MO (2011) Protective effect of pyruvate against ethanol-induced apoptotic neurodegeneration in the developing rat brain. Neuropharmacology 61(8):1248–1255
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Pioneer Research Center Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (2012-0009521).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Najeebullah and Muhammad Imran Naseer contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ullah, N., Naseer, M.I., Ullah, I. et al. Neuroprotective profile of pyruvate against ethanol-induced neurodegeneration in developing mice brain. Neurol Sci 34, 2137–2143 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-013-1350-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-013-1350-8