Abstract
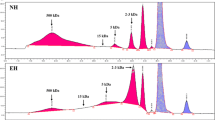
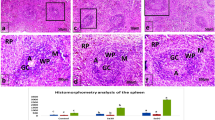
Tuna cooking drip (TCD) is a protein rich by-product of canned tuna processing that is typically discarded. In this study, the immune-enhancing activities of TCD and its enzymatic hydrolysate (EH-TCD) were investigated by intraperitoneally administering Balb/c male mice with TCD and EH-TCD for 2 weeks. This administration resulted in an increase in the weight of the spleen and thymus (200–800 mg/kg) and enhanced the proliferation rates of splenocytes (200–800 mg/kg). TCD and EH-TCD significantly increased the production of immunostimulatory cytokines (interleukin-10 and interleukin-2). In addition, TCD and EH-TCD increased serum IgG1 and IgG2a levels in a concentration-dependent manner. Particularly, EH-TCD had a greater immune-enhancing effect than TCD. These results suggest that TCD and EH-TCD exert immune-enhancing effects through an IgG antibody response and T cell activation, and EH-TCD can be used as an immunostimulatory agent.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang R., Zhang Z, Pei X, Han X, Wang J, Wang L, Long Z, Shen X, Li Y. Immunomodulatory effects of marine oligopeptide preparation from Chum Salmon (Oncorhynchus keta) in mice. Food Chem. 113: 464–470 (2009)
Yang MP, Eoum HY, Na KJ, Araki S, El-Abasy M, Motobu M, Hirota Y. Enhanced phagocytic activity of neutrophils caused by administration of egg white derivatives (EWD) in cats injected with cyclophosphamide (CPA). J. Vet. Med. Sci. 63: 269–274 (2001)
Gildberg A, Bøgwald J, Johansen A, Stenberg E. Isolation of acid peptide fractions from a fish protein hydrolysate with strong stimulatory effect on Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) head kidney leucocytes. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 114B: 97–101 (1996)
Food and agriculture organization of the united nations. The state of world fisheries and aquaculture (2014)
Chalamaiah M, Narsing Rao G, Rao DG, Jyothirmayi T. Protein hydrolysates from meriga (Cirrhinus mrigala) egg and evaluation of their functional properties. Food Chem. 120: 652–657 (2010)
Kim SK, Byun HG, Jeon YJ. Desalination of tuna boiled extract by electrodialysis. Korean J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 32: 68–74 (1999)
Oh HS, Kim JS, Kim HS, Jee SJ, Lee JH, Chung IK, Kang KT, Heu MS. Improvement on the quality and functionality of skipjack tuna cooking drip using commercial enzymes. J. Korean Soc. Food Sci. Nutr. 36: 881–888 (2007)
In MJ, Chae HJ, Oh NS. Process development for heme-enriched peptide by enzymatic hydrolysis of hemoglobin. Bioresour. Technol. 84: 63–68 (2002)
Liceaga-Gesualdo AM, Li-Chan ECY. Functional properties of fish protein hydrolysate from herring (Clupea harengus). J. Food Sci. 64: 1000–1004 (1999)
Kim YM, Kim EY, Kim IH, Nam TJ. Peptide derived from desalinated boiled tuna extract inhibits adipogenesis through the downregulation of C/EBP-α and PPAR-γ in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Int. J. Mol. Med. 35: 1362–1368 (2015)
Kang BK, Kim KBWR, Ahn NK, Choi YU, Kim MJ, Bark SW, Pak WM, Kim BR, Park JH, Bae NY, Ahn DH. Immuno-stimulating activities of skipjack tuna Katsuwonus pelamis cooking juice concentrates on mouse macrophages and spleen cells. Korean J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 47: 776–784 (2014)
Park YM, Won JH, Yun KJ, Ryu JH, Han YN, Choi SK, Lee KT. Preventive effect of ginkgo biloba extract (GBB) on the lipopolysaccharide-induced expressions of inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 via suppression of nuclear factor-κB in RAW 264.7 cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 29: 985–990 (2006)
Duarte J, Vinderola G, Ritz B, Perdigón G, Matar C. Immunomodulating capacity of commercial fish protein hydrolysate for diet supplementation. Immunobiology 211: 341–350 (2006)
Yu ZP, Xu DD, Lu LF, Zheng XD, Chen W. Immunomodulatory effect of a formula developed from American ginseng and Chinese jujube extracts in mice. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. 17: 147–157 (2016)
Huang WC, Kuo ML, Li ML, Yang RC, Liou CJ, Shen JJ. Extract of Gynostemma pentaphyllum enhanced the production of antibodies and cytokines in mice. Yakugaku Zasshi 127: 889–896 (2007)
Smith KA. Interleukin-2: inception, impact, and implications. Science 240: 1169–1176 (1988)
Johansen FE, Brandtzaeg P. Transcriptional regulation of the mucosal IgA system. Trends Immunol. 25: 150–157 (2004)
Bluesotne JA, Abbas AK. Natural versus adaptive regulatory T cells. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 3: 253–257 (2003)
Ni WY, Wu MF, Liao NC, Yeh MY, Lu HF, Hsueh SC, Liu JY, Huang YP, Chang CH, Chung JG. Extract of medicinal mushroom Agaricus blazei Murill enhances the non-specific and adaptive immune activities in Balb/c mice. In Vivo 27: 779–786 (2013)
Hsu KC. Purification of antioxidative peptides prepared from enzymatic hydrolysates of tuna dark muscle by-product. Food Chem. 122: 42–48 (2010)
Sarmadi BH, Ismail A. Antioxidative peptides from food proteins: a review. Peptides 31: 1949–1956 (2010)
Samaranayaka AG, Kitts DD, Li-Chan EC. Antioxidative and angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibitory potential of a Pacific Hake (Merluccius productus) fish protein hydrolysate subjected to simulated gastrointestinal digestion and Caco-2 cell permeation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 58: 1535–1542 (2010)
Balti R, Bougatef A, El-Hadj Ali N, Zekri D, Barkia A, Nasri N. Influence of degree of hydrolysis on functional properties and angiotensin I-converting enzyme-inhibitory activity of protein hydrolysates from cuttlefish (Sepia officinalis) by-products. J. Sci. Food Agric. 90: 2006–2014 (2010)
Cook MT, Hayball PJ, Birdseye L, Bagley C, Nowake BF, Hayball JC. Isolation and partial characterization of a pentraxin-like protein with complement-fixing activity from snapper (Pagrus auratus, Sparidae) serum. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 27: 579–588 (2003)
De Leo F, Panarese S, Gallerani R, Ceci LR. Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides: production and implementation of functional food. Curr. Pharm. Des. 15: 3622–3643 (2009)
Glimcher LH, Murphy KM. Lineage commitment in the immune system: the T helper lymphocyte grows up. Genes Dev. 14: 1693–1711 (2000)
Ravetch JV, Bolland S. IgG Fc receptors. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 19: 275–290 (2001)
Acknowledgements
This study was a part of the project entitled ‘Functional materials and foods using fisheries by-products’, funded by the Ministry of Oceans and Fisheries, Korea (20130279).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, MJ., Kim, KBWR., Sung, NY. et al. Immune-enhancement effects of tuna cooking drip and its enzymatic hydrolysate in Balb/c mice. Food Sci Biotechnol 27, 131–137 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-017-0278-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-017-0278-9