Abstract
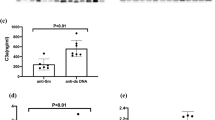
Fibrinogen-like protein 2 (FGL2), a member of the fibrinogen-related superfamily of proteins, is expressed on the surface of macrophages, T cells, and endothelial cells and directly cleaves prothrombin to thrombin. The aim of this study is to determine the serum FGL2 level and its association with clinical parameters in patients with systemic sclerosis (SSc). Serum FGL2 level was examined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in 61 patients with SSc, 24 patients with systemic lupus erythematosus, and 24 healthy individuals. In a retrospective longitudinal study, sera from 13 patients with SSc were analyzed. The serum FGL2 level was increased in patients with SSc compared with healthy individuals (P < 0.001) and patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (P < 0.01). Among patients with SSc, there were no differences in serum FGL2 level between limited cutaneous SSc and diffuse cutaneous SSc. In the longitudinal study, the FGL2 level was generally unchanged at follow-up. The results show that the serum FGL2 level was increased in patients with SSc but not in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus or healthy individuals. Therefore, FGL2 possibly contribute to the development of SSc.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
White B (1996) Immunopathogenesis of systemic sclerosis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 32:695–708
Okano Y (1996) Antinuclear antibody in systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). Rheum Dis Clin North Am 22:709–735
Fleischmajer R, Perlish JS, Reeves JRT (1977) Cellular infiltrates in scleroderma skin. Arthritis Rheum 20:975–984
Scharffetter K, Lankat-Buttgereit B, Krieg T (1988) Localization of collagen mRNA in normal and scleroderma skin by in-situ hybridization. Eur J Clin Invest 18:9–17
Hasegawa M, Sato S (2008) The roles of chemokines in leukocyte recruitment and fibrosis in systemic sclerosis. Front Biosci 13:3637–3647
Koyama T, Hall LR, Haser WG, Tonegawa S, Saito H (1987) Structure of a cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-specific gene shows a strong homology to fibrinogen beta and gamma chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:1609–1613
Ghanekar A, Mendicino M, Liu H et al (2004) Endothelial induction of fgl2 contributes to thrombosis during acute vascular xenograft rejection. J Immunol 172:5693–5701
Marazzi S, Blum S, Hartmann R et al (1998) Characterization of human fibroleukin, a fibrinogen-like protein secreted by T lymphocytes. J Immunol 161:138–147
Ning Q, Sun Y, Han M et al (2005) Role of fibrinogen-like protein 2 prothrombinase/fibroleukin in experimental and human allograft rejection. J Immunol 174:7403–7411
Marsden PA, Ning Q, Fung LS et al (2003) The Fgl2/fibroleukin prothrombinase contributes to immunologically mediated thrombosis in experimental and human viral hepatitis. J Clin Invest 112:58–66
Li C, Fung LS, Chung S et al (1992) Monoclonal antiprothrombinase (3D4.3) prevents mortality from murine hepatitis virus (MHV-3) infection. J Exp Med 176:689–697
Melnyk MC, Shalev I, Zhang J et al (2011) The prothrombinase activity of FGL2 contributes to the pathogenesis of experimental arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol 40:269–278
Subcommittee for Scleroderma Criteria of the American Rheumatism Association Diagnostic and Therapeutic Criteria Committee (1980) Preliminary criteria for the classification of systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). Arthritis Rheum 23:581–590
LeRoy EC, Krieg T, Black C et al (1988) Scleroderma (systemic sclerosis): classification, subsets, and pathogenesis. J Rheumatol 15:202–205
Tan EM, Cohen AS, Fries JF et al (1982) The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 25:1271–1277
Steen VD, Powell DL, Medsger TAJ (1988) Clinical correlations and prognosis based on serum autoantibodies in patients with systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum 31:196–203
Sato S, Ihn H, Kikuchi K, Takehara K (1994) Antihistone antibodies in systemic sclerosis: association with pulmonary fibrosis. Arthritis Rheum 37:391–394
Clements PJ, Lachenbruch PA, Seibold JR et al (1993) Skin thickness score in systemic sclerosis: an assessment of interobeservar variability in 3 independent studies. J Rheumatol 20:1892–1896
Generini S, Matucci Cerinic M (1999) Raynaud’s phenomenon and vascular disease in systemic sclerosis. Adv Exp Med Biol 455:93–100
Suematsu M, Wakabayashi Y, Ishimura Y (1996) Gaseous monoxides: a new class of microvascular regulator in the liver. Cardiovasc Res 32:679–686
Butler AR, Flitney FW, Williams DL (1995) NO, nitrosonium ions, nitroxide ions, nitrosothiols and iron-nitrosyls in biology: a chemist’s perspective. Trends Pharmacol Sci 16:18–22
Selzner N, Liu H, Boehnert MU et al (2012) FGL2/fibroleukin mediates hepatic reperfusion injury by induction of sinusoidal endothelial cell and hepatocyte apoptosis in mice. J Hepatol 56:153–159
Famularo G, Procopio A, Giacomelli R et al (1990) Soluble interleukin-2 receptor, interleukin-2 and interleukin-4 in sera and supernatants from patients with progressive systemic sclerosis. Clin Exp Immunol 81:368–372
Hasegawa M, Fujimoto M, Kikuchi K, Takehara K (1997) Elevated serum levels of interleukin 4 (IL-4), IL-10, and IL-13 in patients with systemic sclerosis. J Rheumatol 24:328–332
Needleman BW, Wigley FM, Stair RW (1992) Interleukin-1, interleukin-2, interleukin-4, interleukin-6, tumor necrosis factor-a, and interferon-g levels in sera from patients with scleroderma. Arthritis Rheum 35:67–72
Matsushita T, Hasegawa M, Hamaguchi Y, Takehara K, Sato S (2006) Longitudinal analysis of serum cytokine concentrations in systemic sclerosis: association of interleukin 12 elevation with spontaneous regression of skin sclerosis. J Rheumatol 33:275–284
Chan CW, Kay LS, Khadaroo RG et al (2003) Soluble fibrinogen-like protein 2/fibroleukin exhibits immunosuppressive properties: suppressing T cell proliferation and inhibiting maturation of bone marrow-derived dendritic cells. J Immunol 170:4036–4044
Shalev I, Liu H, Koscik C et al (2008) Targeted deletion of fgl2 leads to impaired regulatory T cell activity and development of autoimmune glomerulonephritis. J Immunol 180:249–260
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant for Research on Intractable Diseases from the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare of Japan.
Disclosures
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yanaba, K., Asano, Y., Noda, S. et al. Increased circulating fibrinogen-like protein 2 in patients with systemic sclerosis. Clin Rheumatol 32, 43–47 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-012-2089-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-012-2089-y