Abstract
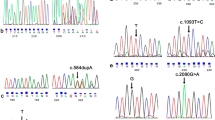
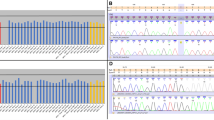
Niemann–Pick C, the autosomal recessive neuro-visceral disease resulting from a failure of cholesterol trafficking within the endosomal–lysosomal pathway, is due to mutations in NPC1 or NPC2 genes. We characterized 34 unrelated patients including 32 patients with mutations in NPC1 gene and two patients in NPC2 gene. Overall, 33 distinct genotypes were encountered. Among the 21 unpublished NPC1 alleles, 15 were due to point mutations resulting in 13 codon replacements (p.C100S, p.P237L, p.R389L, p.L472H, p.Y634C, p.S636F, p.V780G, p.Q921P, p.Y1019C, p.R1077Q, p.L1102F, p.A1187V, and p.L1191F) and in two premature stop codons (p.R934X and p.Q447X); a new mutant carried two in cis mutations, p.[L648H;M1142T] and four other NPC1 alleles were small deletions/insertions leading both to frame shifts and premature protein truncations (p.C31WfsX26, p.F284LfsX26, p.E1188fsX54, and p.T1205NfsX53). Finally, the new intronic c.464-2A>C change at the 3′ acceptor splice site of intron 4 affected NPC1 messenger RNA processing. We also found a new NPC2 mutant caused by a change of the first codon (p.M1L). The novel missense mutations were further investigated by two bioinformatics approaches. Panther proein classification system computationally predicted the detrimental effect of all new missense mutations occurring at evolutionary conserved positions. The other bioinformatics approach was based on prediction of structural alterations induced by missense mutations on the NPC1 atomic models. The in silico analysis predicted protein malfunctioning and/or local folding alteration for most missense mutations. Moreover, the effects of the missense mutations (p.Y634C, p.S636F, p.L648H, and p.V780G) affecting the sterol-sensing domain (SSD) were evaluated by docking simulation between the atomic coordinates of SSD model and cholesterol.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vanier MT, Millat G (2003) Niemann–Pick disease type C. Clin Genet 64:269–281. doi:10.1034/j.1399-0004.2003.00147.x
Patterson MC, Vanier MT, Suzuki K, Morris JA, Carstea E, Neufeld EB, Blanchette-Mackie JE, Pentchev P (2001) Niemann–Pick Disease type C: a lipid trafficking disorder. In: Scriver CR, Beaudet AL, Valle D (eds) The metabolic and molecular bases of inherited disease. McGraw Hill, New York, pp 3611–3634
Garver W, Francis GA, Jelinek D, Sheperd G, Flynn J, Castro G, Walsh Vockely C, Coppock DL, Pettit KM, Heidenreich RA, Meaney JF (2007) The National Niemann–Pick C1 disease database: report of clinical features and health problems. Am J Med Genet A 143:1204–1211
Sevin M, Lesca G, Baumann N, Millat G, Caen-Lyon O, Vanier MT, Sedel F (2007) The adult form of Niemann–Pick disease type C. Brain 130:120–133. doi:10.1093/brain/awl260
Imrie J, Dasgupta S, Besley GTN, Harris C, Heptinstall L, Knight S, Vanier MT, Fensom AH, Ward C, Jacklin E, Whitehouse C, Wraith JE (2007) The natural history of Niemann–Pick disease type C in the UK. J Inherit Metab Dis 30:51–59. doi:10.1007/s10545-006-0384-7
Verot L, Chikh K, Freydière E, Honoré R, Vanier MT, Millat G (2007) Niemann–Pick C disease. functional characterization of three NPC2 mutations and clinical and molecular update on patients with NPC2. Clin Genet 71:320–330. doi:10.1111/j.1399-0004.2007.00782.x
Brown MS, Goldstein JL (1997) The SREBP pathway: regulation of cholesterol metabolism by proteolysis of a membrane bound transcription factor. Cell 89:331–340. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80213-5
Chang TY, Reid PC, Sugii S, Ohgami N, Cruz JC, Chang CC (2005) Niemann–Pick type C disease and intracellular cholesterol trafficking. J Biol Chem 280:20917–20920. doi:10.1074/jbc.R400040200
Vanier MT, Rodriguez-Lafrasse C, Rousson R, Gazzah N, Juge MC, Pentchev PG, Revol A, Louisot P (1991) Type C Niemann–Pick disease: spectrum of phenotypic variation in disruption of intracellular LDL-derived cholesterol processing. Biochim Biophys Acta 1096:328–337
Scott C, Ioannou YA (2004) The NPC1 protein: structure implies function. Biochim Biophys Acta 1685:8–13
Infante RE, Abi-Mosleh L, Radhakrishnan A, Dale JD, Brown MS, Golstein JL (2008) Purified NPC1 protein: I. Binding of cholesterol and oxysterols to a 1278-amino acid membrane protein. J Biol Chem 283:1052–1063. doi:10.1074/jbc.M707943200
Infante RE, Radhakrishnan A, Abi-Mosleh L, Kinch LN, Wang ML, Grishin NV, Goldstein JL, Brown MS (2008) Purified NPC1 protein: II. Localization of sterol binding to a 240-amino acid soluble luminal loop. J Biol Chem 283:1064–1075. doi:10.1074/jbc.M707944200
Vanier MT, Millat G (2004) Structure and function of the NPC2 protein. Biochim Biophys Acta 1685:14–21
Cheruku SR, Xu Z, Dutia R, Lobel P, Storch J (2006) Mechanism of cholesterol transfer from the Niemann–Pick type C2 protein to model membranes supports a role in lysosomal cholesterol transport. J Biol Chem 281:31594–31604. doi:10.1074/jbc.M602765200
Liou HL, Dixit SS, Xu S, Tint GS, Stock AM, Lobel P (2006) NPC2, the protein deficient in Niemann–Pick C2 disease, consists of multiple glycoforms that bind a variety of sterols. J Biol Chem 281:36710–36723. doi:10.1074/jbc.M608743200
Runz H, Dolle D, Schlitter AM, Zschocke J (2008) NPC-db, a Niemann–Pick type C disease gene variation database. Hum Mutat 29:345–350. doi:10.1002/humu.20636
Tarugi P, Ballarini G, Bembi B, Battisti C, Palmeri S, Panzani F, Di Leo E, Martini C, Federico A, Calandra S (2002) Niemann–Pick type C disease. Mutations in NPC1 gene and evidence of abnormal expression of some mutant alleles in fibroblasts. J Lipid Res 43:1908–1919. doi:10.1194/jlr.M200203-JLR200
Di Leo E, Panico F, Tarugi P, Battisti C, Federico A, Calandra S (2004) A point mutation in the lariat branch point of intron 6 of NPC1 as the cause of abnormal pre-mRNA splicing in Niemann–Pick type C disease. Hum Mutat 24:44b. doi:10.1002/humu.9287
Millat G, Bailo N, Molinero S, Rodriguez C, Chikh K, Vanier MT (2005) Niemann–Pick C disease: use of denaturing high performance liquid chromatography for the detection of NPC1 and NPC2 genetic variations and impact on management of patients and families. Mol Genet Metab 86:220–232. doi:10.1016/j.ymgme.2005.07.007
Blanchette-Mackie EJ, Dwyer NK, Amende LM, Kruth HS, Butler JD, Sokol J, Comly ME, Vanier MT, August JT, Brady RO, Pentchev PG (1988) Type-C Niemann–Pick disease: low density lipoprotein uptake is associated with premature cholesterol accumulation in the Golgi complex and excessive cholesterol storage in lysosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:8022–8026. doi:10.1073/pnas.85.21.8022
Thomas PD, Campbell MJ, Kejariwal A, Mi H, Karlak B, Daverman R, Diemer K, Muruganujan A, Narechania A (2003) PANTHER: A library of protein families and subfamilies indexed by function. Genome Res 13:2129–2141. doi:10.1101/gr.772403
Pieper U, Eswar N, Davis FP, Braberg H, Madhusudhan MS, Rossi A, Marti-Renom M, Karchin R, Webb BM, Eramian D, Shen MY, Kelly L, Melo F, Sali A (2006) MODBASE: a database of annotated comparative protein structure models and associated resources. Nucleic Acids Res 34:D291–D295. doi:10.1093/nar/gkj059
Jones TA, Zou JY, Cowan SW, Kjeldgaard M (1991) Improved methods for building protein models in electron density maps and the location of errors in these models. Acta Crystallogr A 47:110–119. doi:10.1107/S0108767390010224
Morris GM, Goodsell DS, Halliday RS, Huey R, Hart WE, Belew RK, Olson AJ (1998) Automated docking using a Lamarkian genetic algorithm and empirical binding free energy function. J Comput Chem 19:1639–1662. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1096-987X(19981115)19:14<1639::AID-JCC10>3.0.CO;2-B
Sanner MF, Duncan BS, Carillo CJ, Olson AJ (1999) Integrating computation and visualization for biomolecular analysis: an example using Python and AVS. Pac Symp Biocomput 4:392–400
den Dunnen JT, Antonarakis SE (2000) Mutation nomenclature extensions and suggestions to describe complex mutations: a discussion. Hum Mutat 15:7–12. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1098-1004(200001)15:1<7::AID-HUMU4>3.0.CO;2-N
den Dunnen JT, Paalman MH (2003) Standardizing mutation nomenclature: why bother? Hum Mutat 22:181–182. doi:10.1002/humu.10262
Garver WS, Francis GA, Jelinek D, Shepherd G, Flynn J, Castro G, Walsh Vockley C, Coppock DL, Pettit KM, Heidenreich RA, Meaney FJ (2007) The National Niemann–Pick C1 disease database: report of clinical features and health problems. Am J Med Genet A 1:1204–1211. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.31735
Sévin M, Lesca G, Baumann N, Millat G, Lyon-Caen O, Vanier MT, Sedel F (2007) The adult form of Niemann–Pick disease type C. Brain 130:120–133. doi:10.1093/brain/awl260
Patterson MC, Vecchio D, Prady H, Abel L, Wraith JE (2007) Miglustat for treatment of Niemann–Pick C disease: a randomised controlled study. Lancet Neurol 6:765–772. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(07)70194-1
Park WD, O’Brien JE, Lundquist PA, Kraft DL, Vockley CW, Karnes PS, Patterson MC, Snow K (2003) Identification of 58 novel mutations in Niemann–Pick disease type C: correlation with biochemical phenotype and importance of PTC1-like domains in NPC1. Hum Mutat 22:313–325. doi:10.1002/humu.10255
Bauer P, Knoblich R, Bauer C, Finckh U, Hufen A, Kropp J, Braun S, Kustermann-Kuhn B, Schmidt D, Harzer K, Rolfs A (2002) NPC1: complete genomic sequence, mutation analysis, and characterization of haplotypes. Hum Mutat 19:30–38. doi:10.1002/humu.10016
Sun X, Marks DL, Park W, Wheatley CL, Puri V, O’Brien JF, Kraft DL, Lundquist PA, Patterson MC, Pagano RE, Snow K (2001) Niemann–Pick C variant detection by altered shingolipid trafficking and correlation with mutations within specific domain of NPC1. Am J Hum Genet 68:1361–1372. doi:10.1086/320599
Fernandez-Valero EM, Ballart A, Iturriaga C, Lluch M, Macias J, Vanier MT, Pineda M, Coll JM (2005) Identification of 25 new mutations in 40 unrelated Spanish Niemann–Pick type C patients: genotype–phenotype correlations. Clin Genet 68:245–254. doi:10.1111/j.1399-0004.2005.00490.x
Millat G, Marcais C, Tomasetto C, Chikh K, Fensom AH, Harzer K, Wenger DA, Ohono K, Vanier MT (2001) Niemann–Pick C1 disease: correlations between NPC1 mutations, levels of NPC1 protein, and phenotypes emphasize the functional significance of the putative sterol-sensing domain and of the cysteine-rich luminal loop. Am J Hum Genet 68:1373–1385. doi:10.1086/320606
Yang CC, Su YN, Chiou PC, Fietz MJ, Yu CL, Hwu WL, Lee MJ (2005) Six novel NPC1 mutations in Chinese patients with Niemann–Pick disease type C. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 76:592–595. doi:10.1136/jnnp.2004.046045
Greer ML, Dobson MJ, Girouard GS, Byers DM, Riddell DC, Neumann PE (1999) Mutations in NPC1 highlight a conserved NPC1-specifgic cysteine-rich domain. Am J Hum Genet 65:1252–1260. doi:10.1086/302620
Millat G, Marcais C, Rafi MA, Yamamoto T, Morris JA, Pentchev PG, Ohno K, Wenger DA, Vanier MT (1999) Niemann–Pick C1 disease: the I1061T substitution is a frequent mutant allele in patients of Western European descent and correlates with a classic juvenile phenotype. Am J Hum Genet 65:1321–1329. doi:10.1086/302626
Reese MG, Eeckman FH, Kulp D, Haussler D (1997) Improved splice site detection in Genie. J Comput Biol 4:311–323
Davies JP, Ioannou YA (2000) Topological analysis of Niemann–Pick C1 protein reveals that the membrane orientation of the putative sterol-sensing domain is identical to those of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase and sterol regulatory element binding protein cleavage-activating protein. J Biol Chem 275:24367–24374. doi:10.1074/jbc.M002184200
Morris JA, Zhang D, Coleman KG, Nagle J, Pentchev PG, Carstea ED (1999) The genomic organization and polymorphism analysis of the human Niemann–Pick C1 gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 261:493–498. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1999.1070
Bertolini S, Cantafora A, Averna M, Cortese C, Motti C, Martini S, Pes G, Postiglione A, Stefanutti C, Blotta I, Pisciotta L, Rolleri M, Langheim S, Ghisellini M, Rabbone I, Calandra S (2000) Clinical expression of familial hypercholesterolemia in clusters of mutations of the LDL receptor gene that cause receptor defective or receptor-negative mutations. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 20:E41–E52
Millat G, Chikh K, Naureckiene S, Sleat DE, Fensom AH, Higaki K, Elleder M, Lobel P, Vanier MT (2001) Niemann–Pick disease type C: spectrum of HE1 mutations and genotype/phenotype correlations in the NPC2 group. Am J Hum Genet 69:1013–1021. doi:10.1086/324068
Chikh K, Rodriguez C, Vey S, Vanier MT, Millat G (2005) Niemann–Pick type C disease: subcellular location and functional characterization of NPC2 protein with naturally occurring missense mutations. Hum Mutat 26:20–28. doi:10.1002/humu.20173
Naureckiene S, Sleat DE, Lackland H, Fensom A, Vanier MT, Wattiaux R, Jadot M, Lobel P (2000) Identification of HE1 as the second gene of Niemann–Pick C disease. Science 290:2298–2301. doi:10.1126/science.290.5500.2298
Klünemann HH, Elleder M, Kaminski WE, Snow K, Peyser JM, O’Brien JF, Munoz D, Schmitz G, Klein HE, Pendlebury WW (2002) Frontal lobe atrophy due to a mutation in the cholesterol binding protein HE1/NPC2. Ann Neurol 52:743–749. doi:10.1002/ana.10366
Dvorakova L, Sikora J, Hrebicek M, Hulkova H, Bouckova M, Stolnaja L, Elleder M (2006) Subclinical course of adult visceral Niemann–Pick type C1 disease. A rare or underdiagnosed disorder? J Inherit Metab Dis 29:591. doi:10.1007/s10545-006-0330-z
Wallace AC, Laskowski RA, Thornton JM (1995) LIGPLOT: a program to generate schematic diagrams of protein-ligand interactions. Protein Eng 8:127–134. doi:10.1093/protein/8.2.127
Acknowledgments
The samples were obtained from the “Cell Line and DNA Biobank from Patients Affected by Genetic Diseases” (G. Gaslini Institute)—Telethon Genetic Biobank Network (project no. GTB07001A). The study was supported by a grant from Fondazione Cassa di Risparmio di Modena to P.T. and by the Italian Association of Niemann–Pick. We also thank Dr. A. Donati (Meyer Hospital, Florence, Italy), Dr. O. Gabrielli and Dr. A. Ficcadenti (Department of Pediatrics, University of Ancona, Italy), Dr. M. Spada for their contribution of clinical information and patient samples, and Sarah Tripepi (Winteringham, BA MCIL), for assistance in manuscript revision.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fancello, T., Dardis, A., Rosano, C. et al. Molecular analysis of NPC1 and NPC2 gene in 34 Niemann–Pick C Italian Patients: identification and structural modeling of novel mutations. Neurogenetics 10, 229–239 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10048-009-0175-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10048-009-0175-3