Abstract
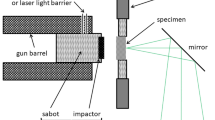
Impact tests against a hardened steel plate have been carried out to obtain the coefficient of restitution of three types of spherical granules. The dominant elastic γ-Al2O3, the elastic-plastic zeolite 4A and the dominant plastic sodium benzoate have been chosen as granule samples. An electromagnetic canon has been constructed to accelerate the granules and to measure the normal coefficient of restitution. The moisture content of the granules has been varied so that the pore saturation ranges between of S = 0–1. Thereby, the influence of the moisture content on the normal coefficient of restitution could be determined. A free fall apparatus, on which the impact angle is changeable in the range of ΘA = 0–80°, has been used to investigate the tangential coefficient of restitution. A high speed digital camera has been used to record the events of impact and rebound. The record frequency of the camera has been varied between 4,000 and 8,000 frames per second.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Eabs :
-
Energy absorption during impact [J]
- dm :
-
Mean diameter [m]
- e:
-
Coefficient of restitution [–]
- en, et :
-
Normal and tangential coefficient of restitution [–]
- Fn :
-
Normal force [N]
- Fr :
-
Friction force [N]
- G:
-
Elastic shear modulus [Pa]
- J:
-
Mass moment of inertia [kg · m2]
- K:
-
Non-dimensional radius of gyration [–]
- m:
-
Mass [kg]
- mF :
-
Mass of the wet granule [kg]
- mTS :
-
Mass of the dry granule [kg]
- R:
-
Radius [m]
- S:
-
Pore saturation [–]
- vA, vR :
-
Impact and rebound velocity [m/s]
- vn,A, vn,R, vt,A, vt,R :
-
Normal and tangential component of the impact and rebound velocity [m/s]
- vn,KA, vn,KR, vt,KA, vt,KR :
-
Normal and tangential component of the impact and rebound velocity of the contact patch [m/s]
- Wkin,A, Wkin,R :
-
Kinetic energy of the impact and rebound [J]
- XW :
-
Moisture content [kgWater/kgTS]
- \({\varepsilon}\) :
-
Porosity [–]
- θ A, θ R :
-
Impact and rebound angle [°]
- θ KR :
-
Rebound angle of the contact patch [°]
- κ :
-
Ratio of tangential to normal stiffness [–]
- μ :
-
Coefficient of Coulomb friction [–]
- ν :
-
Poisson’s ratio [–]
- ρ g :
-
Granule density [kg/m3]
- ρ s :
-
Solid density [kg/m3]
- \({\varphi_{\rm w}}\) :
-
Wall friction angle [°]
- χ :
-
Non-dimensional parameter [–]
- ΨA :
-
Non-dimensional impact angle [–]
- ΨKR :
-
Non-dimensional rebound angle of the contact patch [–]
- ω R :
-
Angular velocity after impact [ rad/s]
References
Müller, P., Antonyuk, S., Tomas, J., Heinrich, S.: Ermittlung der normalen und tangentialen Stoßzahl von Granulaten. Chem. Ing. Tech. Submitted cite.201000131.R1 (2010)
Mangwandi C., Cheong Y.S., Adams M.J., Hounslow M.J., Salman A.D.: The coefficient of restitution of different representative types of granules. Chem. Eng. Sci 62, 437–450 (2007)
Fu J., Adams M.J., Reynolds G.K., Salman A.D., Hounslow M.J.: Impact deformation and rebound of wet granules. Powder Technol. 140, 248–257 (2004)
Gorham D.A., Kharaz A.H.: The measurement of particle rebound characteristics. Powder Technol. 112, 193–202 (2000)
Ozturk I., Kara M., Uygan F., Kalkan F.: Restitution coefficient of chick pea and lentil seeds. Int. Agrophys. 24(2), 209–211 (2010)
Müller P., Antonyuk S., Tomas J., Heinrich S.: Investigations of the restitution coefficient of granules. In: Bertram, A., Tomas, J. (eds) Micro-Macro-Interactions in Structured Media and Particle Systems, pp. 235–241. Springer, Berlin (2008)
Hunter S.C.: Energy absorbed by elastic waves during impact. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 5, 162–171 (1957)
Wu C., Li L., Thornton C.: Energy dissipation during normal impact of elastic and elastic-plastic spheres. Int. J. Imp. Eng. 32, 593–604 (2005)
Maw, N., Barber, J.R., Fawcett, J.N.: The oblique impact of elastic spheres, Elsevier Sequoia S. A. Lausanne 38(1), 101–114
Koller, M.G.: Elastischer Stoß von Kugeln auf dicke Platten. Dissertation ETH Nr. 7299, Zürich (1983)
Brilliantov N., Albers N., Spahn F., Pöschel T.: Collision dynamics of granular particles with adhesion. Phys. Rev. E 76, 051302 (2007)
Dong H., Moys M.H.: Experimental study of oblique impacts with initial spin. Powder Technol. 161, 22–31 (2006)
Kharaz A.H., Gorham D.A., Salman A.D.: An experimental study of the elastic rebound of spheres. Powder Technol. 120, 281–291 (2001)
Antonyuk S., Heinrich S., Tomas J., Deen N.G., van Buijtenen M.S., Kuipers J.A.M.: Energy absorption during compression and impact of dry elastic-plastic spherical granules. Granul. Matter 12, 15–47 (2010)
Cheong Y.S., Adams M.J., Routh A.F., Hounslow M.J., Salman A.D.: The production of binderless granules and their mechanical characteristics. Chem. Eng. Sci. 60, 4045–4053 (2005)
Foerster S.F., Louge M.Y., Chang H., Allia K.: Measurements of the collision properties of small spheres. Phys. Fluids 6(3), 1108–1115 (1994)
Sondergaard R., Chaney K., Brennen C.E.: Measurement of solid spheres bouncing off flat plates. J. Appl. Mech. 112, 694–699 (1990)
Johnson K.L.: Contact Mechanics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1992)
Stronge W.J.: Impact Mechanics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2000)
Thornton C.: Coefficient of restitution for collinear collisions of elastic-perfectly plastic spheres. J. Appl. Mech. 64, 383–386 (1997)
Wu C., Thornton C., Li L.: A semi-analytical model for oblique impacts of elastoplastic spheres. Proc. R. Soc. 465, 937–960 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mueller, P., Antonyuk, S., Stasiak, M. et al. The normal and oblique impact of three types of wet granules. Granular Matter 13, 455–463 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10035-011-0256-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10035-011-0256-5