Abstract
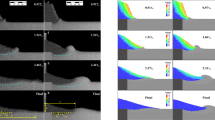
We present 2D numerical simulations of the collapse and spreading of granular columns for which the final geometry of the deposit and the runout distance are studied. Both the effects of the initial geometry and the effects of the details of the interactions between the grains are investigated. The scaling of the runout distance shows both a linear and a power-law dependence on the aspect ratio of the initial column, in agreement with previous findings (Balmforth and Kerswell in J. Fluid Mech. 538, 399–428, 2004; Lajeunesse et al. in Phys. Fluids 17, 103302, 2005; Lube et al. in Phys. Rev. E 72, 041301, 2005; Staron and Hinch in J. Fluid Mech. 545, 1–27, 2005), and independently of the value of the inter-grain friction. The latter controls the prefactor of the scaling, the effective frictional properties of the flow, and its internal structure. The non-trivial mass distribution induced by the initial geom- etry of the column strongly influences the dissipation process, and is believed to control the power-law dependence of the runout distance on the column aspect ratio.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aranson I.S. and Tsimring L.S. (2001). Continuum descrition of avalanches in granular media. Phys. Rev. E 64: R020301
Balmforth N.J. and Kerswell R.R. (2004). Granular collapse in two dimensions. J. Fluid Mech. 538: 399–428
Cleary P.W. and Campbell C.S. (1993). Self-lubrication for long run-out landslides: examination by computer simulation. J. Geophys. Res. 98(21): 911–924
Cundall P. and Stack O. (1979). Geotechnique 29(1): 47
Dade W.B. and Huppert H.E. (1998). Long-runout rockfalls. Geology 26: 803–806
Douady S., Andreotti B. and Daerr A. (1999). On granular surface flow equations. Eur. Phys. J. B 11: 131
Gray J.M.N.T., Wieland M. and Hutter K. (1999). Gravity-driven free surface flow of granular avalanches over complex basal topography. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 445: 1841–1874
Iverson R.M. (1997). The physics of debris flows. Rev. Geophys. 35: 245–296
Jean, M.: Frictional Contact in Rigid or Deformable Bodies: Numerical Simulation of geomaterials. pp. 463–486. In: Salvadurai, A.P.S., Boulon, J.M. (eds.) Elsevier, Amsterdam (1995)
Lajeunesse E., Mangeney-Castelneau A. and Vilotte J.-P. (2004). Spreading of a granular mass on an horizontal plane. Phys. Fluids 16: 2731–2381
Lajeunesse E., Monnier J.B. and Homsy G.M. (2005). Granular slumping on a horizontal surface. Phys. Fluids 17: 103302
Larrieu, E., Staron, L., Hinch, E.J.: Raining into shallow water as a description of the collapse of a column of grains. J. Fluid Mech. (in press) (2005)
Lube G., Huppert H.E., Sparks R.S.J. and Hallworth M.A. (2004). Axisymmetric collapses of granular columns. J. Fluid Mech. 508: 175–199
Lube G., Huppert H.E., Sparks R.S.J. and Freundt A. (2005). Collapse of granular columns. Phys. Rev. E 72: 041301
Lube, G., The flow and depositional mechanisms of granular matter, PhD Thesis, University of Kiel, Germany (2006)
Midi G.D.R. (2004). On dense granular flows. Eur. Phys. J. E 14: 341–365
Moreau J.-J. (1994). Some numerical methods in multibody dynamics: application to granular materials. Eur. J. Mech. A/Solids 4: 93–114
Pouliquen O. and Forterre Y. (2002). Friction law for dense granular flows: application to the motion of a mass down a rough inclined plane. J. Fluid Mech. 453: 133–151
Rajchenbach J. (2000). Granular flows. Adv. Phys. 49(2): 229–256
Savage S. and Hutter K. (1989). The motion of a finite mass of granular material down a rough incline. J. Fluid Mech. 199: 177–215
Staron L. and Hinch E.J. (2005). Study of the collapse of granular columns using two-dimensional discrete-grains simulation. J. Fluid Mech. 545: 1–27
Zenit R. (2005). Computer simulations of the collapse of a granular column. Phys. Fluid 17: 031703
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Staron, L., Hinch, E.J. The spreading of a granular mass: role of grain properties and initial conditions. Granular Matter 9, 205–217 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10035-006-0033-z
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10035-006-0033-z