Abstract
Introduction
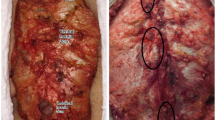
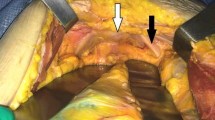
Incisional hernias to the subxiphoid region are rare and anatomically challenging, with bony and cartilaginous structures attaching, as well as conflating abdominal fascia. The repair of hernias in this region is, therefore, difficult and prone to recurrence. The surgical treatment can be done by open or laparoscopic repair but very little is known about which method is superior. We, therefore, reviewed our data of patients undergoing repair of subxiphoid hernias.
Methods
Between January 2010 and June 2015 twenty-eight patients were treated by laparoscopic (n = 8) or open (n = 20) hernia repair due to an incisional hernia in the subxiphoid region. Patients with ventral hernias with an origin more distal than the M1-area only extending into the subxiphoid region and those undergoing suture hernia repair were excluded.
Results
The hernia sizes, in terms of length, width and EHS classification, did not vary between open and laparoscopic repair. The duration of laparoscopic surgery was significantly shorter than the mean operative time for an open subxiphoid hernia repair (168.1 min vs. 96.1 min, respectively; p = 0.012). The groups did not differ significantly in terms of overall postoperative complications (p = 0.568) but the grade (Clavien–Dindo) of complications was higher following open repair leading to three reoperations. Within the follow-up time, we diagnosed significantly (p = 0.031) more subxiphoid hernia recurrences after laparoscopic repair (37.5%, n = 3) than after open repair (0%).
Conclusion
Laparoscopic and open repair of subxiphoid incisional hernias are both technically challenging compared to other midline hernias. Referring to our results laparoscopic repair has shorter operative times, lower postoperative morbidity with a higher recurrence rate compared to open repair but the sample size is too small for an overall conclusion.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Muysoms FE, Miserez M, Berrevoet F, Campanelli G, Champault GG, Chelala E, Dietz UA, Eker HH, El Nakadi I, Hauters P, Hidalgo Pascual M, Hoeferlin A, Klinge U, Montgomery A, Simmermacher RK, Simons MP, Smietanski M, Sommeling C, Tollens T, Vierendeels T, Kingsnorth A (2009) Classification of primary and incisional abdominal wall hernias. Hernia 13(4):407–414. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10029-009-0518-x
Davidson BR, Bailey JS (1986) Incisional herniae following median sternotomy incisions: their incidence and aetiology. Br J Surg 73(12):995–996
Landau O, Raziel A, Matz A, Kyzer S, Haruzi I (2001) Laparoscopic repair of poststernotomy subxiphoid epigastric hernia. Surg Endosc 15(11):1313–1314. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004640090011
Losanoff JE, Basson MD, Laker S, Weiner M, Webber JD, Gruber SA (2007) Subxiphoid incisional hernias after median sternotomy. Hernia 11(6):473–479. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10029-007-0258-8
Conze J, Prescher A, Kisielinski K, Klinge U, Schumpelick V (2005) Technical consideration for subxiphoidal incisional hernia repair. Hernia 9(1):84–87. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10029-004-0239-0
Cohen MJ, Starling JR (1985) Repair of subxiphoid incisional hernias with Marlex mesh after median sternotomy. Arch Surg 120(11):1270–1271
Mackey RA, Brody FJ, Berber E, Chand B, Henderson JM (2005) Subxiphoid incisional hernias after median sternotomy. J Am Coll Surg 201(1):71–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2005.01.025
de Mesquita GHA, Iuamoto LR, Suguita FY, Essu FF, Oliveira LT, Torsani MB, Meyer A, Andraus W (2017) Simple technique of subxiphoid hernia correction carries a low rate of early recurrence: a retrospective study. BMC Surg 17(1):51. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12893-017-0249-3
Ghanem OM, Zahiri HR, Devlin S, Sibia U, Park A, Belyansky I (2016) Laparoscopic subxiphoid hernia repair with intracorporeal suturing of mesh to the diaphragm as a means to decrease recurrence. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 26(2):129–132. https://doi.org/10.1089/lap.2015.0518
Eisenberg D, Popescu WM, Duffy AJ, Bell RL (2008) Laparoscopic treatment of subxiphoid incisional hernias in cardiac transplant patients. JSLS 12(3):262–266
Silecchia G, Campanile FC, Sanchez L, Ceccarelli G, Antinori A, Ansaloni L, Olmi S, Ferrari GC, Cuccurullo D, Baccari P, Agresta F, Vettoretto N, Piccoli M (2015) Erratum to: laparoscopic ventral/incisional hernia repair: updated consensus development conference based guidelines. Surg Endosc 29(9):2485. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-015-4470-9
Baucom RB, Ousley J, Feurer ID, Beveridge GB, Pierce RA, Holzman MD, Sharp KW, Poulose BK (2016) Patient reported outcomes after incisional hernia repair-establishing the ventral hernia recurrence inventory. Am J Surg 212(1):81–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjsurg.2015.06.007
Gurusamy KS, Allen VB (2013) Wound drains after incisional hernia repair. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 12:CD005570. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD005570.pub4
Davidson BR, Bailey JS (1987) Repair of incisional hernia after median sternotomy. Thorax 42(7):549–550
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that no conflict of interest exists.
Ethical approval
Ethical approval from the institutional review board was not required for this study.
Human and animal rights
As a retrospective review, no experimental conditions were implemented. All human participants received standard of care treatments and; thus, no rights were violated. No animals were involved in this study.
Informed consent
As a retrospective review, formal consent was not required.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raakow, J., Schulte-Mäter, J., Callister, Y. et al. A comparison of laparoscopic and open repair of subxiphoid incisional hernias. Hernia 22, 1083–1088 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10029-018-1815-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10029-018-1815-z