Abstract
Background
Complications associated with sutured mesh fixation following open groin hernia repair have prompted surgeons to evaluate methods of atraumatic fixation such as the use of human fibrin glue. Small trials with Tissucol/Tisseel fibrin glue (Baxter Healthcare, Deerfield, IL, USA) have shown promising results that warrant further investigation.
Methods
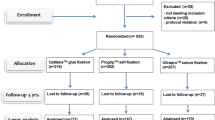
TIMELI (Tissucol/Tisseel for MEsh fixation in LIchtenstein hernia repair) is an international, controlled, randomized, patient- and evaluator-blinded study that is comparing mesh fixation with Tissucol or sutures in patients with inguinal hernia. The primary endpoint evaluates the incidence of disabling complications (chronic pain and/or numbness and/or groin discomfort) at 12 months post-surgery.
Results
Patient enrolment started in February 2006 and ended on 19 April 2007, with a total of 325 patients recruited. Initial results are expected in early 2008.
Conclusions
TIMELI is a major international trial that will provide important information on the efficacy and safety of Tissucol, compared with sutures, for mesh fixation in patients undergoing Lichtenstein technique for primary inguinal hernia repair.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amid PK (2004) Lichtenstein tension-free hernioplasty: its inception, evolution, and principles. Hernia 8:1–7
Amid PK, Lichtenstein IL (1998) Long-term results and current status of the Lichtenstein open tension-free hernioplasty. Hernia 2:89–94
Poobalan AS, Bruce J, Smith WC, King PM, Krukowski ZH, Chambers WA (2003) A review of chronic pain after inguinal herniorrhaphy. Clin J Pain 19:48–54
Fränneby U, Sandblom G, Nordin P, Nyren O, Gunnarsson U (2006) Risk factors for long-term pain after hernia surgery. Ann Surg 244:212–219
Schulman AG, Amid PK, Lichtenstein IL (1995) A survey of non-expert surgeons using the open tension-free mesh repair for primary inguinal hernias. Int Surg 80:35–36
Kingsnorth AN, Bowley DMG, Porter C (2003) A prospective study of 1000 hernias: results of the Plymouth Hernia Service. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 85:18–22
Amid PK (2004) Causes, prevention, and surgical treatment of postherniorrhaphy neuropathic inguinodynia: triple neurectomy with proximal end implantation. Hernia 8:343–349
The EU Hernia Trialists Collaboration (2002) Repair of groin hernia with synthetic mesh: meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Ann Surg 235:322–332
McCormack K, Scott NW, Go PM, Ross S, Grant AM, on behalf of the EU Hernia Trialists Collaboration (2000) Laparoscopic techniques versus open techniques for inguinal hernia repair. Cochrane Database Syst Rev DOI:10.1002/14651858.CD001785
Wellwood J, Sculpher MJ, Stoker D, Nicholls GJ, Geddes C, Whitehead A, Singh R, Spiegelhalter D (1998) Randomised controlled trial of laparoscopic versus open mesh repair for inguinal hernia: outcome and cost. BMJ 317:103–110
Douek M, Smith G, Oshowo A, Stoker DL, Wellwood JM (2003) Prospective randomized control trial of laparoscopic versus open inguinal hernia mesh repair: five year follow-up. BMJ 326:1012–1013
Muldoon RL, Marchant K, Johnson DD, Yoder GG, Read RC, Hauer-Jensen M (2004) Lichtenstein vs anterior preperitoneal prosthetic mesh placement in open inguinal hernia repair: a prospective, randomised trial. Hernia 8:98–103
Verstraete L, Swannet H (2003) Long-term follow-up after Lichtenstein hernioplasty in a general surgical unit. Hernia 7:185–190
Kumar S, Wilson RG, Nixon SJ, Macintyre IM (2002) Chronic pain after laparoscopic and open mesh repair of groin hernia. Br J Surg 89:1476–1479
Fernandez Lobato R, Garcia Septiem J, Ortega Deballon P, Martin Lucas FJ, Ruiz de Adana JC, Limones Esteban M (2001) Tissucol application in dermolipectomy and incisional hernia repair. Int Surg 86:240–245
Canonico S, Santoriello A, Campitiello F, Fattopace A, Della Corte A, Sordelli, Benevento R (2005) Mesh fixation with human fibrin glue (Tissucol) in open tension-free inguinal hernia repair: a preliminary report. Hernia 9:330–333
Hidalgo M, Castillo MJ, Eymar JL, Hidalgo A (2005) Lichtenstein inguinal hernioplasty: sutures versus glue. Hernia 9:242–244
Benizri EI, Rahili A, Avallone S, Balestro JC, Cai J, Benchimol D (2006) Open inguinal hernia repair by plug and patch: the value of fibrin sealant fixation. Hernia 10:389–394
Miserez M, Alezandre JH, Campanelli G, Corcione F, Cuccurullo D, Pascual MH, Hoeferlin A, Kingsnorth AN, Mandala V, Pulot JP, Schumpelick V, Simmermacher RK, Stoppa R, Flament JB (2007) The European Hernia Society groin hernia classification: simple and easy to remember. Hernia. DOI:10.1007/s10029-007-0198-3
Neumayer L, Giobbie-Hurder A, Jonasson O, Fitzgibbons R, Dunlop D, Gibbs J, Reda D, Henderson W (2004) Open mesh versus laparoscopic mesh repair of inguinal hernia. N Engl J Med 350:1819–1827
Redl H (2004) History of tissue adhesives. In: Saltz R, Toriumi DM (eds) Tissue glues in cosmetic surgery. Quality Medical Publishing, St Louis, pp 3–27
Dinges HP, Redl H, Thurnher M, Schiesser A, Schlag G (1986) Morphometic studies on wound healing after systemic administration of adriamycin and local application of fibrin sealant. Application of a new wound healing model using spongiosa implants. Path Res Pract 181:746–754
Guyatt G, Gutterman D, Baumann MH, Addrizzo-Harris D, Hylek EM, Phillips B, Raskob G, Lewis SZ, Schünemann H (2006) Grading strength of recommendations and quality of evidence in clinical guidelines. Report from an American College of Chest Physicians Task Force. Chest 129:174–181
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
TIMELI Investigators
-
Coordinating investigator: G. Campanelli, Milan, Italy
-
Investigators: G. Champault, Bondy, France; M. Hidalgo, Madrid, Spain; A. Hoeferlin, Mainz, Germany; A. Kingsnorth, Plymouth, UK; M. Miserez, Leuven, Belgium; J. Rosenberg, Hellerup, Denmark
-
Co-investigators: C. Barrat, Bondy, France; M. J. Castillo, Madrid, Spain; J.L. Eymar, Madrid, Spain; A. Marcos, Madrid, Spain; M. Cavalli, Milan, Italy; D. Pettinari, Milan, Italy; C. Polliand, Bondy, France
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Campanelli, G., Champault, G., Pascual, M.H. et al. Randomized, controlled, blinded trial of Tissucol/Tisseel for mesh fixation in patients undergoing Lichtenstein technique for primary inguinal hernia repair: rationale and study design of the TIMELI trial. Hernia 12, 159–165 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10029-007-0315-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10029-007-0315-3